Difference between revisions of "Interfacing Seven Segment Displays with AVR"
Raghavendra (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:AVR Tutorials]] | [[Category:AVR Tutorials]] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
[[File:Common Anode 7Segment.jpeg|thumbnail|fig 4: Common Anode 7 segment]] | [[File:Common Anode 7Segment.jpeg|thumbnail|fig 4: Common Anode 7 segment]] | ||
Since these are basically LEDs arranged as a group they can either have anode in common or cathode thus they are named as Common-Anode/Common-Cathode displays. | Since these are basically LEDs arranged as a group they can either have anode in common or cathode thus they are named as Common-Anode/Common-Cathode displays. | ||
| − | *'''Common Cathode''': In this type of segments all the cathode terminals are made common and tied to GND. Thus the segments '''a''' to '''g''' needs a logic High signal(5v) in order to glow.This is shown in figure(3). | + | *'''Common Cathode''': In this type of segments all the cathode terminals are made common and tied to GND. Thus the segments '''a''' to '''g''' needs a logic High signal(5v) in order to glow.This is shown in figure(3). <br><br> |
*'''Common Anode''': In this type of segments all the anodes terminals are made common and tied to VCC(5v). Thus the segments '''a''' to '''g''' needs a logic LOW signal(GND) in order to glow.This is shown in figure(4).<br /> | *'''Common Anode''': In this type of segments all the anodes terminals are made common and tied to VCC(5v). Thus the segments '''a''' to '''g''' needs a logic LOW signal(GND) in order to glow.This is shown in figure(4).<br /> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Hookup= | =Hookup= | ||
| − | + | [[File:Interfacing Seven Segment Displays with AVR bb.png|none]] | |
| + | =Code= | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/raghavendrahassy/05af8109f493afdddf47dc62fd115fde.js"> | ||
| + | </script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 44: | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| − | + | [[File:0Interfacing Seven Segment Displays with AVR.gif|none]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | =Video Tutorial= | |
| − | + | For those of you, who would like to watch instead of read we have made a video with all the gyan. | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | + | {{#ev:youtubehd|-lNAmSNV2-Q|640}} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | { | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | = Downloads= | |
| + | Download the complete project folder from the below link: | ||
| + | https://github.com/ExploreEmbedded/ATmega32_ExploreUltraAvrDevKit/archive/master.zip<br> | ||
Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here! | Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here! | ||
{{DISQUS}} | {{DISQUS}} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 4 May 2016
In the earlier tutorials we saw how to interface the Leds to Atmega32 and wrote the code to blink, generate up counter, ringcounter etc. How ever the leds cannot be used to display any user information like numbers, char's etc. To display numeric values we can use seven segment displays.
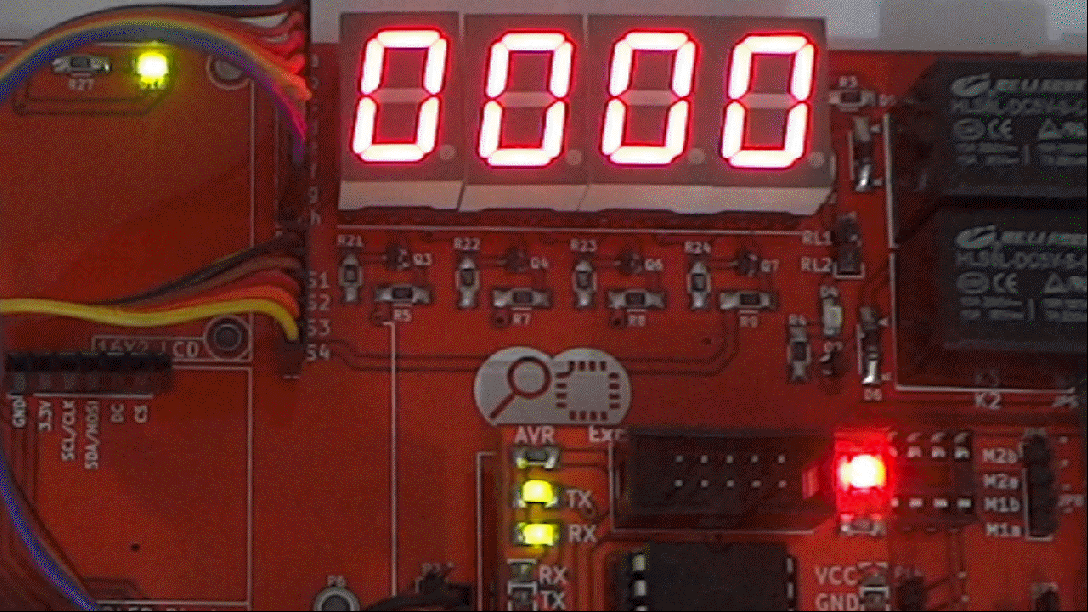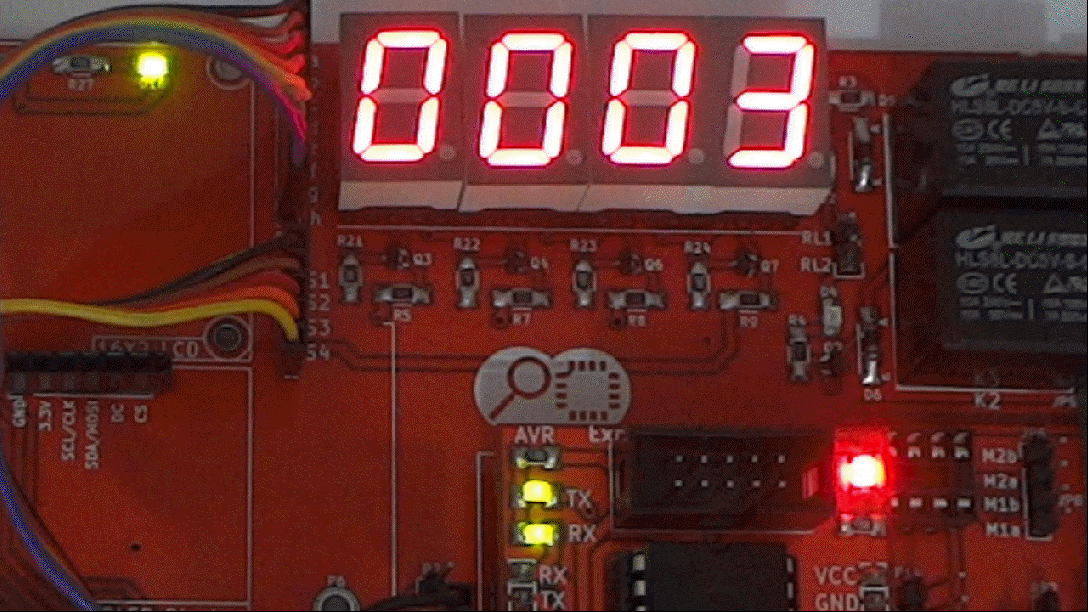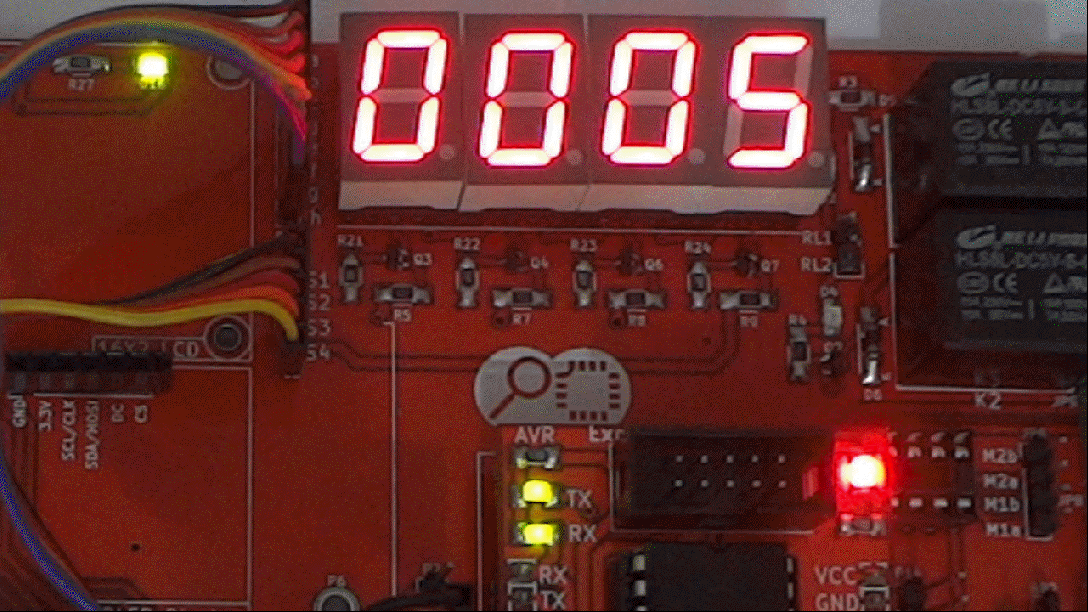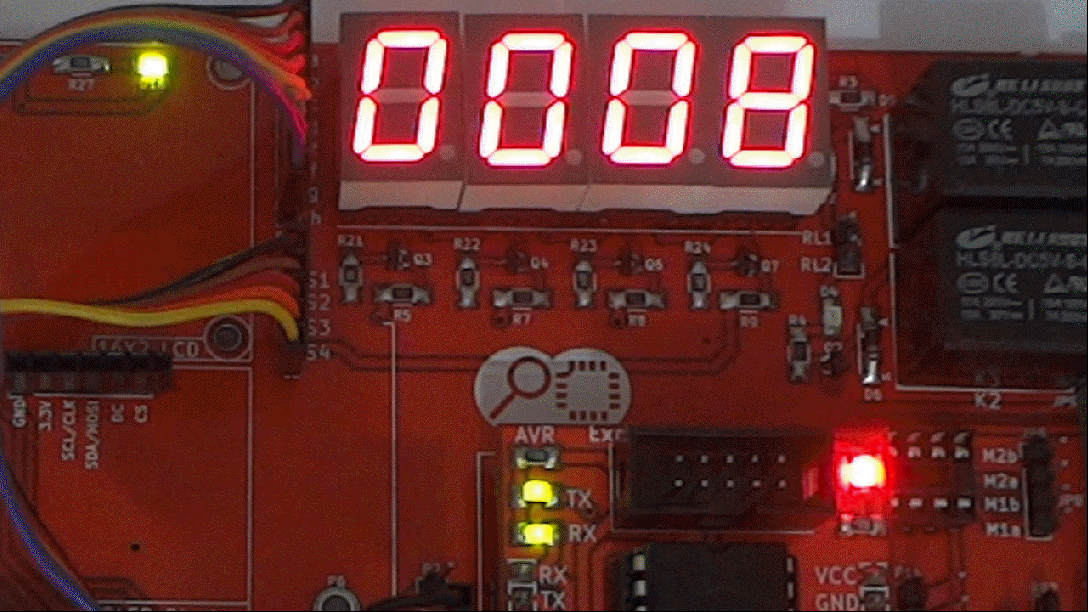
In this tutorial we will interface a seven segment to ATmega32 and display a single digit hex counter(0-F). Later same will be extended to multiplex 4 seven segment displays to generate a 4-digit counter.
Contents
Seven Segment Display
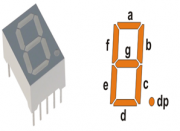
Well, the name 7 segments implies there are 7 LED segments arranged as shown in figure 1. After LEDs, these are the easiest interfaces to a microcontroller. There is also a decimal point or dp. It is used when decimal digits like 5.1 etc are displayed.
Applications
Seven segment are widely used in applications where digits[0-9] are required to be displayed.Although they also display letters A to F as shown in figure(2) simulation. This is a very simple and convenient way to display numbers in a bright fashion.
Form Factor
- Sizes:They come in various sizes; 0.28”, 0.3”, 0.32”, 0.36”, 0.39”, 0.4”, 0.5”, 0.56”, 0.6”, 0.8”, 1.0”, 1.2”, 1.5”, 1.8”, 2.0”, 2.3”, 3.0”, 4.0”, 5.0”, 7.0”)
- Colors: and varied colors too; Red, Green, Yellow, Orange, Blue, and White.
Working
Since these are basically LEDs arranged as a group they can either have anode in common or cathode thus they are named as Common-Anode/Common-Cathode displays.
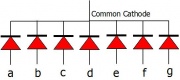
- Common Cathode: In this type of segments all the cathode terminals are made common and tied to GND. Thus the segments a to g needs a logic High signal(5v) in order to glow.This is shown in figure(3).
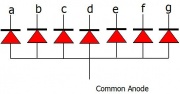
- Common Anode: In this type of segments all the anodes terminals are made common and tied to VCC(5v). Thus the segments a to g needs a logic LOW signal(GND) in order to glow.This is shown in figure(4).
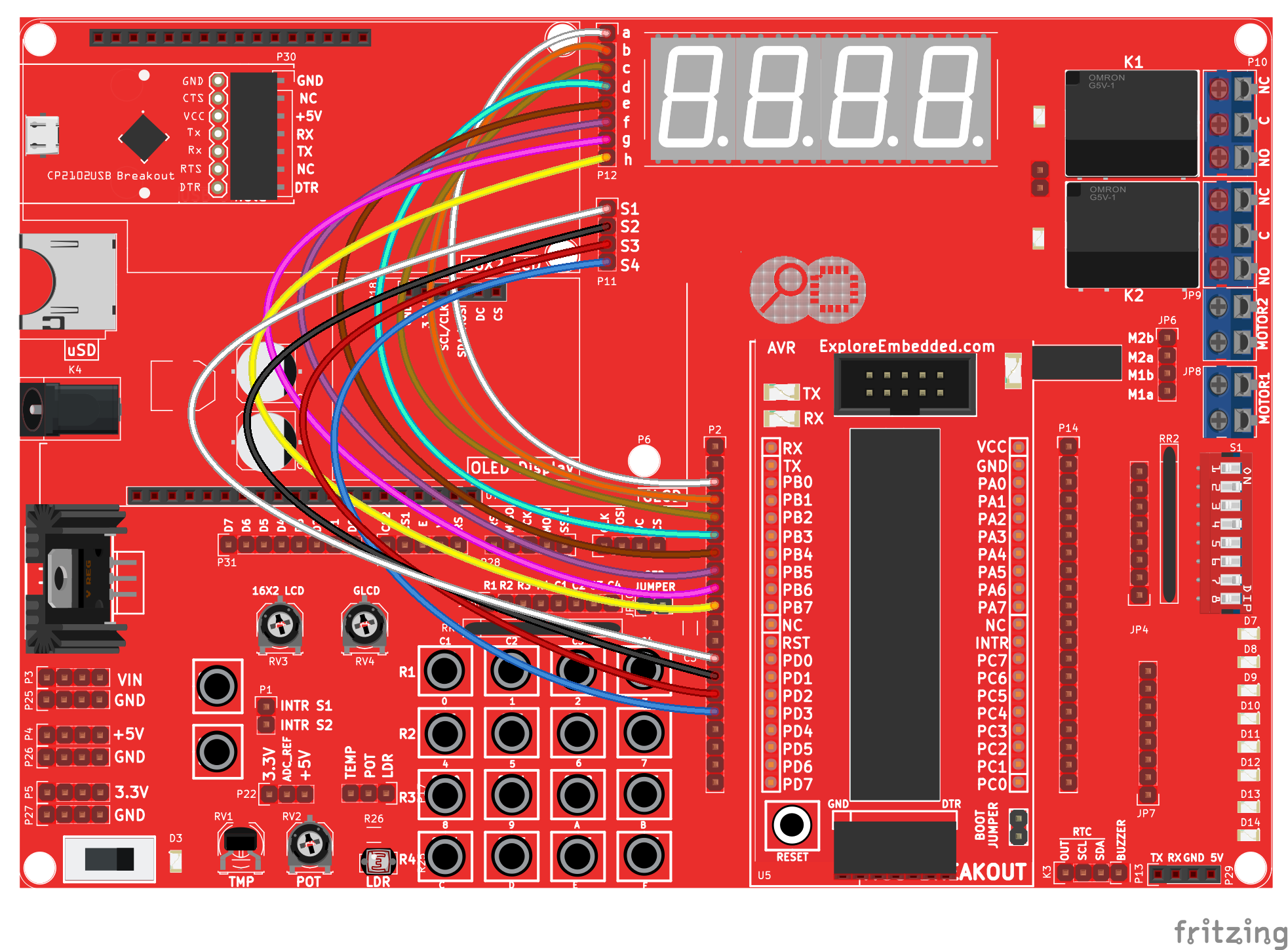
Hookup
Code
- Explore Ultra AVR Dev Kit: Buy from EE Store

Video Tutorial
For those of you, who would like to watch instead of read we have made a video with all the gyan.
Downloads
Download the complete project folder from the below link:
https://github.com/ExploreEmbedded/ATmega32_ExploreUltraAvrDevKit/archive/master.zip
Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here!