Difference between revisions of "Creating a Task from other Tasks"
(Created page with "category: Free RTOS with Arduino In earlier tutorials, we saw how to create in the init and use it.<br> In this tutorial, we will see how to create a task from other tasks...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[category: Free RTOS with Arduino]] | [[category: Free RTOS with Arduino]] | ||
| − | In earlier tutorials, we saw how to create in | + | In earlier tutorials, we saw how to create a task in init and use it.<br> |
In this tutorial, we will see how to create a task from other tasks.<br> | In this tutorial, we will see how to create a task from other tasks.<br> | ||
Revision as of 15:04, 28 June 2016
In earlier tutorials, we saw how to create a task in init and use it.
In this tutorial, we will see how to create a task from other tasks.
API Details
Here we will discuss some of the most frequently used APIs related to tasks.
1.xTaskCreate(): This interface is used to create a new Task, if the task is successfully created then it returns pdPass(1) or else errCOULD_NOT_ALLOCATE_REQUIRED_MEMORY(-1). Check this link for more details.
2.vTaskDelay(): This function is used to delay/block the task for specified delay time(ticks). INCLUDE_vTaskDelay needs to be set to 1 in FreeRtosConfig.h file for using this function. Check this link for more details.
3.vTaskDelete():This function is used to delete as task. We need to pass the taskHandle of the task to be deleted.
To delete the own task we should pass NULL as parameter.
Please check this link for detials.
Example
Output
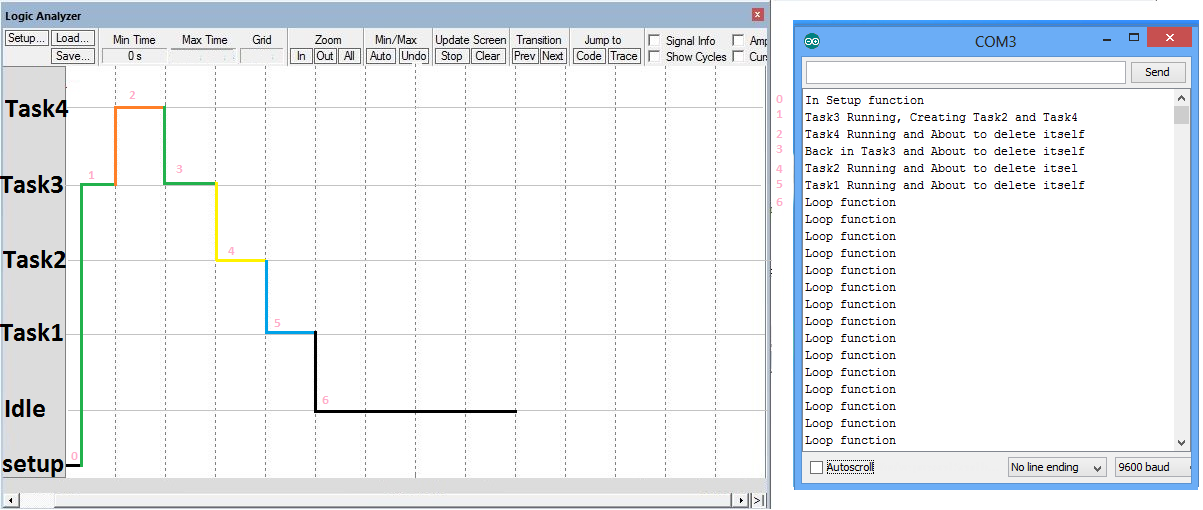
0. Serial port is initialized and 2-Tasks are created with different priorities. Setup message is printed.
- Cpu chooses Task3 out of the tasks(1,3,and idle) as it has higher priority. Now Task3 will create two more tasks with priority2,4. Now CPU has tasks(1,2,3,4,IDLE). Since Task4 has the highest priority it will preempt the Task3 and starts running.
- Task4 will run for some time and deletes itself.
- Now Tasks(1,2,3,IDLE) are available and Task3 will run again because for its higher priority. It will Run for some time and deletes itself.
- Now Tasks(1,2,Idle) are remaining and Task2 will run and deletes itself once its job is done.
- Out of Task(1,Idle), Task1 runs and it also deletes itself.
- CPU is left out with Idle task and it keeps running.
