Difference between revisions of "1. AVR Architecture"
Karthik Bhat (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:AVR Tutorials]] | [[Category:AVR Tutorials]] | ||
| + | = Video Tutorials = | ||
| + | == AVR Architecture Part 1 == | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|GC6RSAqZ6eE}} | ||
| + | == AVR Architecture Part 2 == | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|BKg2hoD89jY}} | ||
| + | == AVR Architecture Part 3 == | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|c4ZNE2HZzmA}} | ||
=Why learn AVR Architecture?= | =Why learn AVR Architecture?= | ||
Learning architecture of the micro-controller gives deep understanding of how it works. It also enables in writing better software for the same. Also programmers who understand the underlying hardware tend to write better programs.<br> | Learning architecture of the micro-controller gives deep understanding of how it works. It also enables in writing better software for the same. Also programmers who understand the underlying hardware tend to write better programs.<br> | ||
Revision as of 10:44, 16 October 2014
Video Tutorials
AVR Architecture Part 1
AVR Architecture Part 2
AVR Architecture Part 3
Why learn AVR Architecture?
Learning architecture of the micro-controller gives deep understanding of how it works. It also enables in writing better software for the same. Also programmers who understand the underlying hardware tend to write better programs.
The entire tutorial series will be based around Atmega32 MCU from Atmel. Hence in this tutorial we will look at AVR architecture in general however all the specifics would point to Atmega32.
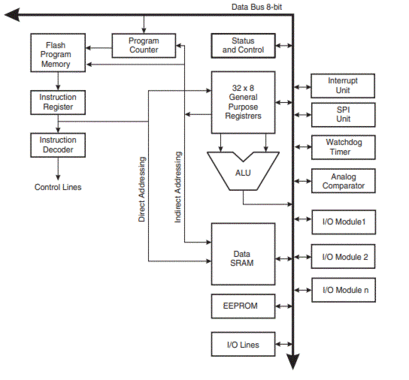
Block Diagram
Fig below shows the architecture of the MegaAVR series of controllers. As with any MCU ALU forms the core of the controller. A typical AVR Mega Series MCU has following hardware units inbuilt:
- The ALU
- 32 General Purpose Registers
- Special Function Registers
- Static RAM
- EEPROM
- Flash
- Timer/Counter
- Compartor
- Watch Dog timer
- Protocols: UART, SPI, I2C
- Interrupt Handler
- IO Ports
- Analog
- Digital
The ALU
The ALU of an AVR MCU process data 8 bits at a time. It performs the arithmetic and logical operations. The data for the ALU comes from the registers. If you wish to understand how an ALU works go through this ALU_in_Detail tutorial