Setting up Bare Metal Development Toolchain for ESP32
(Tutorial in the making!...)
The Espressif Internet Development Framework (ESP-IDF) is core development tool-chain for the ESP32 chip. It includes the compiler, programming tools and various software components that enable software development on the chip. In this tutorial we will look at setting it up and describing in brief, the structure of the framework.
Contents
Windows ESP-IDF Setup
The setup on other operating systems should be easier than Windows. I did set it up on Ubuntu and it was easier, so lets get started.
Step 1: Download the pre-compiled MYSYS2 environment for ESP32
There are other ways to accomplish this like compiling the environment itself but I would rather recommend doing this. So download it from the link below.
https://dl.espressif.com/dl/esp32_win32_msys2_environment_and_toolchain-20160816.zip
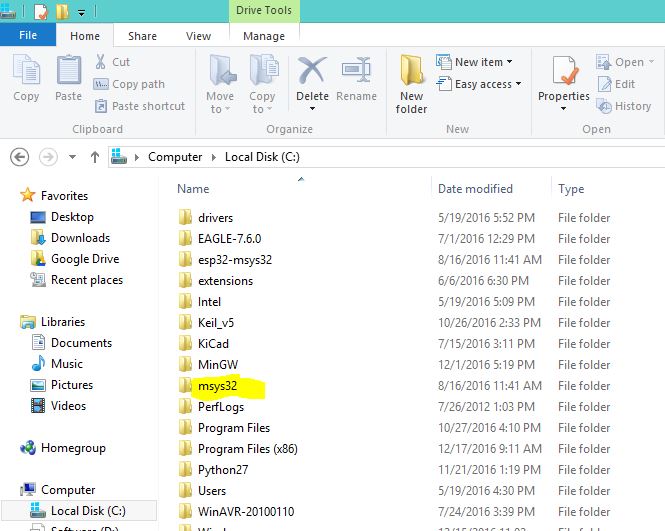
Step 2: Extract the tool-chain to the C: drive
This will create a folder called msys32 as shown.
Step 3: Download the ESP-IDF
You may either download it by cloning it with git like so
git clone --recursive https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf.git
or you download the repository directory.
Note: When downloading the git ensure that recursive is there, so that it can download all the required dependencies.
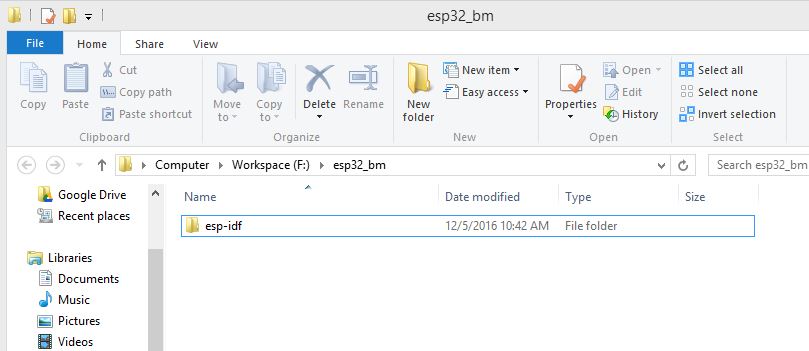
I did it under a directory called esp_bm (bm-baremetal) so that I can keep everything organized like so
Step 4: Download a project template
The project template has all the essentials setup. Download and extract it from the like so:
git clone https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf-template.git blink
This will download the example template in the blink directory. You may also manually download it from the repo.
