In this tutorial, we are going to discuss the Timer module of 8051.
First, we will see what are timers, their working and later we will configure the 8051 timers to generate the delay of 100ms and 500ms respectively. At the end, we will see how to use the ExploreEmdedded Timer library.
Contents
Timer Basics
As the name suggests these are used to measure the time or generate the accurate time delay. The microcontroller can also generate/measure the required time delays by running loops, but the timer/counter relieves the CPU from that redundant and repetitive task, allowing it to allocate maximum processing time for other tasks.
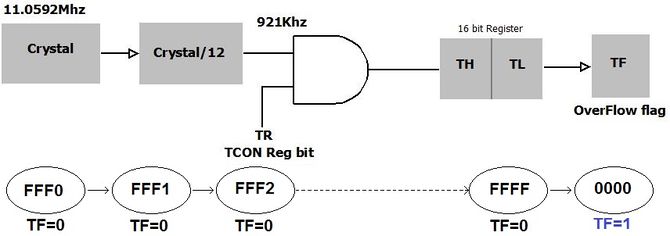
The timer is nothing but a simple binary counter that can be configured to count clock pulses(Internal/External). Once it reaches the Max value, it will roll back to zero setting up an OverFlow flag and generates the interrupt if enabled.
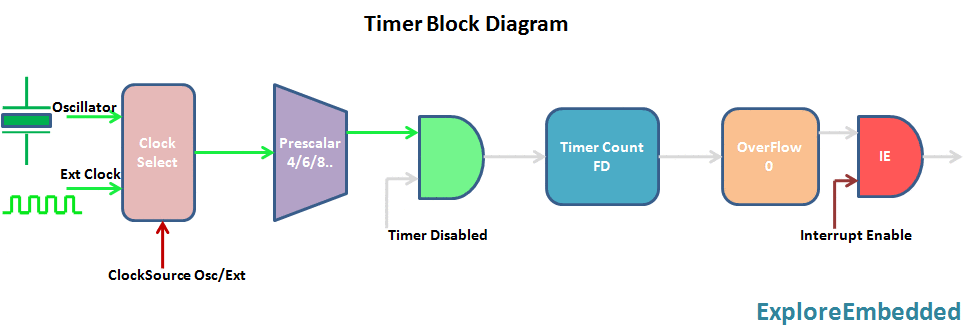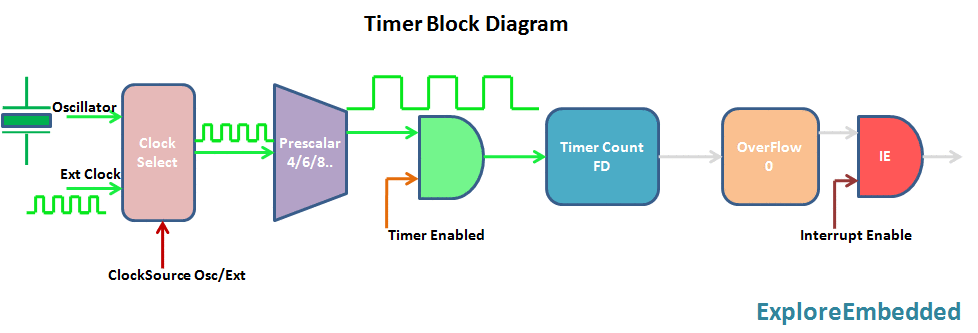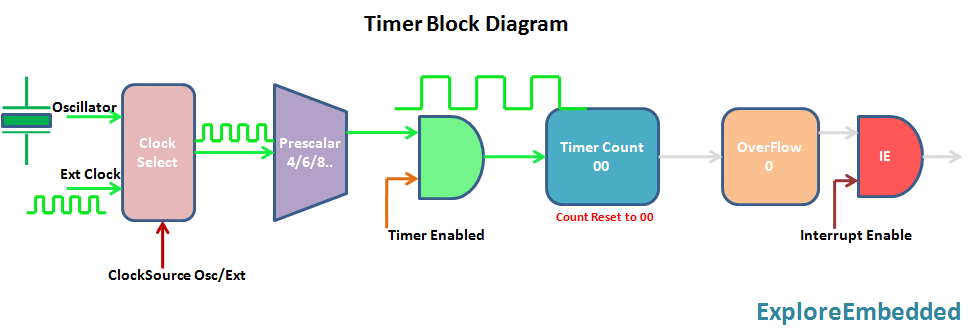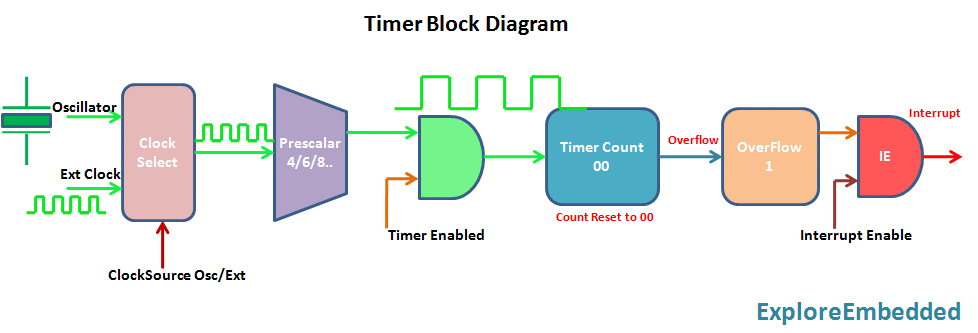
8051 Timer Module
8051 has two indepenndent timer which can be used as timer(to generate delays)/Counters(count external events).
- Timer 1 is also used for generating baud rate in serial communication, which we will discuss in the next tutorial
Below table provides the details of the 8051 Timers.
| Timer | Size | Control Register | Count Register | Min Delay | Max Delay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIMER0 | 16-bit | TMOD,TCON | TH0,TL0 | 0.2usec | 13.107ms |
| TIMER1 | 16-bit | TMOD,TCON | TH1,TL1 | 0.2usec | 104.857ms |
| TIMER2(8052 only) | 16-bit | TMOD,TCON | TH1,TL1 | 0.2usec | 104.857ms |
Timer Calculation
8051 Oscillator frequency is divided by 12 and then fed to the controller,
Time to increment the Timer count by one(timer tick) can be determined as below.
tick = (1/(Fosc/12)
$$tick = 12/Fosc$$
For Fosc == 11.0592Mhz, the tick time will be
tick = 12/11.0592M = 1.085069444us = 1.085us
Now the Timer value for the required delay can be calculated as below.
Delay = TimerCount * tick
Count = (Delay/tick)
RegValue = TimerMax- Count
RegValue = TimerMax-(Delay/tick) = TimerMax - (Delay/1.085us)
$$RegValue = TimerMax-((Delay/1.085) * 10^6)$$
Timer Operation
{{Box|type=l_green_light|text=
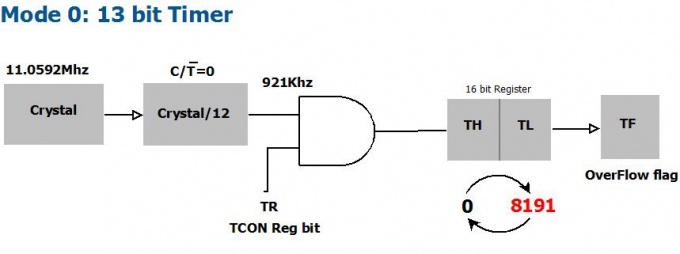
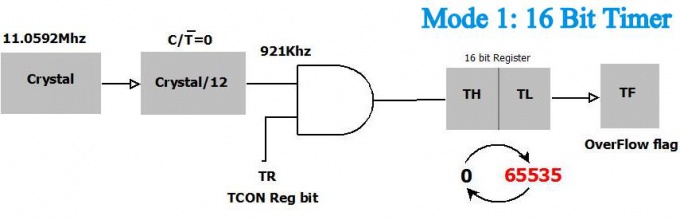
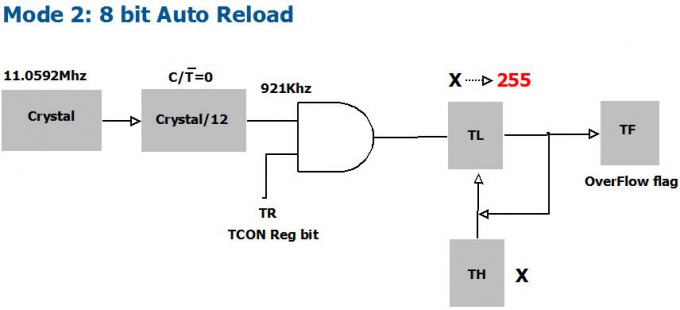
The Timer 0 is a 16 bit registers as shown. This can be accessed as 2 eight bit registers TL0 and TL1. Same applies to Timer 1.
The 8051 timer and counter is the same unit, but in this tutorial we will discuss only the timer unit to simplify the discussion.
Timer Tick
- The C/Ṫ = 0 bit of TMOD register selects operation of Timer/counter unit as timer.
- The TR bit of TCON register is used to start the timer.
Timer Registers
Timer Register T0/T1
| T0 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TH0 | TL0 | ||||||||||||||
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
TMOD Register
| M1 | M0 | Operation |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 13 bit Timer |
| 0 | 1 | 16 bit Timer |
| 1 | 0 | 8 bit Auto Reload |
| 1 | 1 | Split Mode |
| TMOD | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| Gate | C/T | M1 | M0 | Gate | C/T | M1 | M0 |
| Timer1 | Timer 0 | ||||||
TCON Register
| TCON | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| TF1 | TR1 | TF0 | TR0 | IE1 | IT1 | IE0 | IT0 |
| Timer1 | Timer 0 | Interrupts | |||||
Timer Example
#include<reg51.h> void delay_t0(void);// function prototype void delay_t0() { TMOD = 0x01; //Timer zero mode 1 TH0 = 0X4B; TL0 = 0XFF; TR0 = 1; //turn ON Timer zero while(TF0 == 0); TF0 = 0; //clear the timer TR0 = 0; } void main() { P3 = 0x00; //set port as output while(1) { P3 = 0XFF; delay_t0(); P3 = 0X00; delay_t0(); } }
{{#seo: |title=8051_Timers |titlemode=append |keywords=8051,AT89s51,at89c51,p89v51rd2,XploreLabz,Timer,Timers,8051 timers/counters,8051 timer operation,8051 Timer registers,TMOD Register,TCON register |description=8051 Timers }} Would like to have your feedback and suggestions here;