Difference between revisions of "PIC16f877a Timer"
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
{| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
|-class="info" | |-class="info" | ||
| − | !Timer || Size || Control Register || Count Register | + | !Timer || Size || Control Register || Count Register || Min Delay || Max Delay |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |TIMER0|| 8-bit || T0CON || TMR0 | + | |TIMER0|| 8-bit || T0CON || TMR0 || 0 || 0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |TIMER1|| 16-bit || T1CON || TMR1H,TMR1L | + | |TIMER1|| 16-bit || T1CON || TMR1H,TMR1L || 0 || 0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |TIMER2|| 8-bit || T2CON || TMR2 | + | |TIMER2|| 8-bit || T2CON || TMR2 || 0 || 0 |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 12:06, 6 May 2016
In this tutorial we are going to discuss the Timer module of Pic16f877a.
First we will see what are timers, their working and later we will configure the PIC16f877a timers to generate delay of 100ms and 500ms respectively. At the end we will see how to use the ExploreEmdedded Timer library.
Timer Basics
As the name suggests these are used to measure the time or generate the accurate time delay. The microcontroller can also generate/measure the required time delays by running loops, but the timer/counter peripheral relieves the CPU from that redundant and repetitive task, allowing it to allocate maximum processing time for other tasks.
Timer is nothing but a simple binary counter that can be configured to count clock pulses(Internal/External). Once it reaches the Max value, it will roll back to zero setting up an OverFlow flag and generates the interrupt if enabled.
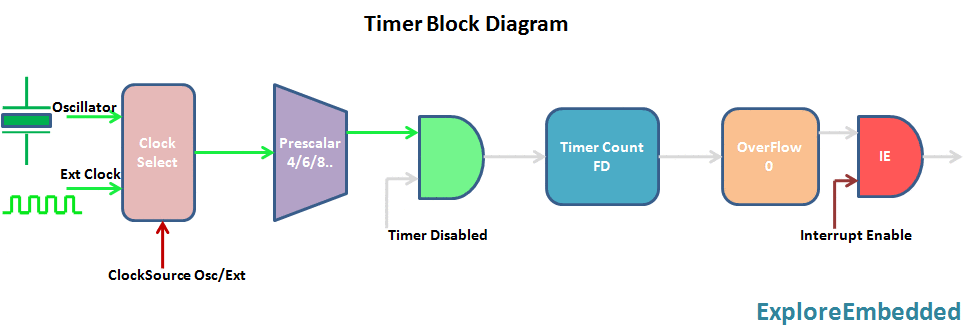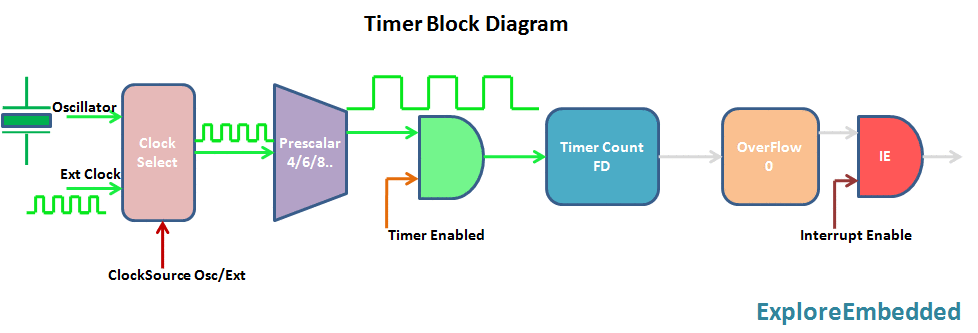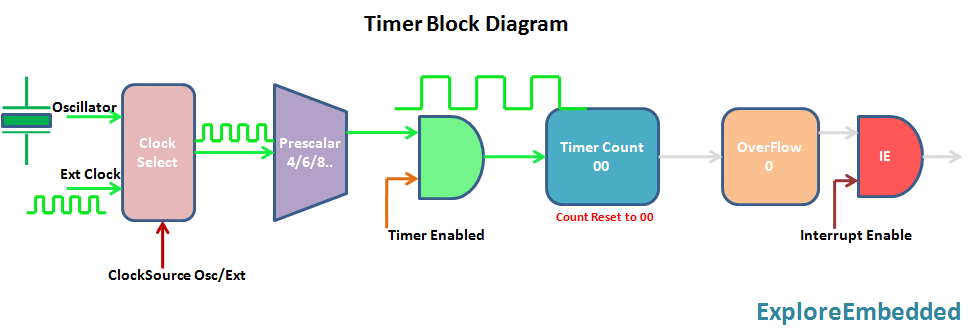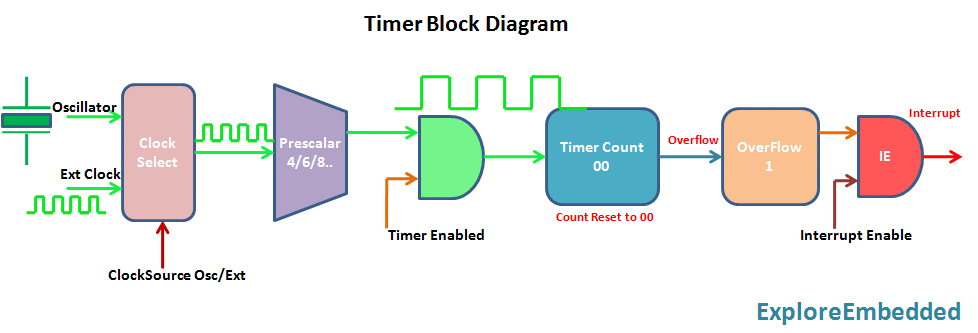
PIC Timer Module
Pic16f877a has three indepenndent timer which can be used as timer,Counters or for PWM generation.
Below table provides the details of the three Timers.
| Timer | Size | Control Register | Count Register | Min Delay | Max Delay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIMER0 | 8-bit | T0CON | TMR0 | 0 | 0 |
| TIMER1 | 16-bit | T1CON | TMR1H,TMR1L | 0 | 0 |
| TIMER2 | 8-bit | T2CON | TMR2 | 0 | 0 |

