Difference between revisions of "Basics of AVR Interrupts"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:AVR Tutorials]] | [[Category:AVR Tutorials]] | ||
| − | Interrupts, are perhaps one of the most important pieces that you need to understand for completing most of your micro-controller projects. Interrupts allow micro-controllers to continue doing their main job and provide mechanism to handle all other tasks which need the | + | Interrupts, are perhaps one of the most important pieces that you need to understand for completing most of your micro-controller projects. Interrupts allow micro-controllers to continue doing their main job and provide mechanism to handle all other tasks which need the controller attention. |
| − | + | Before we go ahead with the examples here, are a few situations where you may want to use these: | |
| − | + | ||
* Let's say you have a device like GSM interfaced to your Micro-controller using UART or other serial interface. You simple do not know when you'll receive a new text message or a call. One way to handle this is continuously monitor for the even to occur. The other way is to configure a serial interrupt. Yes, you guessed it right, this is a Software Interrupt indeed. | * Let's say you have a device like GSM interfaced to your Micro-controller using UART or other serial interface. You simple do not know when you'll receive a new text message or a call. One way to handle this is continuously monitor for the even to occur. The other way is to configure a serial interrupt. Yes, you guessed it right, this is a Software Interrupt indeed. | ||
* Now let's say you're building a music player. The main task of the processor is to read and play back the audio file. However the player should be able to play/pause/forward/rewind. And this could happen any time. How about connecting the switches to hardware interrupt pins? The processor will be notified any time the events happen. | * Now let's say you're building a music player. The main task of the processor is to read and play back the audio file. However the player should be able to play/pause/forward/rewind. And this could happen any time. How about connecting the switches to hardware interrupt pins? The processor will be notified any time the events happen. | ||
| + | |||
| + | With AVR Micro-controllers, you can configure interrupts on various sources such as: | ||
| + | * Port Pins : INT0, INT1 and INT2 | ||
| + | * Timers | ||
| + | * UART | ||
| + | * SPI | ||
| + | * ADC | ||
| + | * EEPROM | ||
| + | * Analog Comparator | ||
| + | * TWI or I2C | ||
| + | |||
| + | The vector table below shows | ||
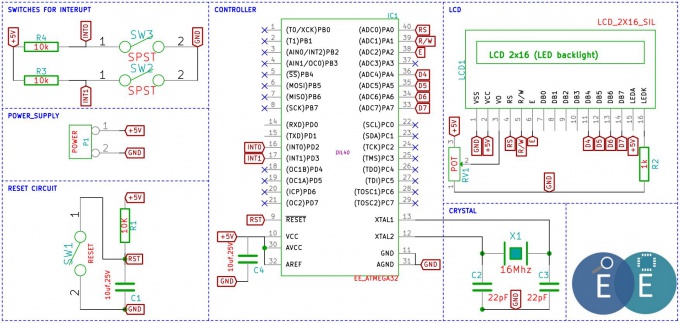
[http://exploreembedded.com/wiki/images/a/a9/Schematic_AVR_Interupt.pdf '''Schematic'''] | [http://exploreembedded.com/wiki/images/a/a9/Schematic_AVR_Interupt.pdf '''Schematic'''] | ||
[[File:Schematic AVR Interupt.JPG|680px]] | [[File:Schematic AVR Interupt.JPG|680px]] | ||
Revision as of 12:49, 19 March 2016
Interrupts, are perhaps one of the most important pieces that you need to understand for completing most of your micro-controller projects. Interrupts allow micro-controllers to continue doing their main job and provide mechanism to handle all other tasks which need the controller attention. Before we go ahead with the examples here, are a few situations where you may want to use these:
- Let's say you have a device like GSM interfaced to your Micro-controller using UART or other serial interface. You simple do not know when you'll receive a new text message or a call. One way to handle this is continuously monitor for the even to occur. The other way is to configure a serial interrupt. Yes, you guessed it right, this is a Software Interrupt indeed.
- Now let's say you're building a music player. The main task of the processor is to read and play back the audio file. However the player should be able to play/pause/forward/rewind. And this could happen any time. How about connecting the switches to hardware interrupt pins? The processor will be notified any time the events happen.
With AVR Micro-controllers, you can configure interrupts on various sources such as:
- Port Pins : INT0, INT1 and INT2
- Timers
- UART
- SPI
- ADC
- EEPROM
- Analog Comparator
- TWI or I2C
The vector table below shows Schematic