Difference between revisions of "Real Time Clock(DS1307) with AVR"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
It is uses '''I²C''' ('''Inter-Integrated Circuit''') protocol, referred to as ''I-squared-C'', ''I-two-C'', or ''IIC'') for communication with the micrcontroller.[[Serial_protocol_I2C|Check the basics of I2C]] here, if are not familiar with it. | It is uses '''I²C''' ('''Inter-Integrated Circuit''') protocol, referred to as ''I-squared-C'', ''I-two-C'', or ''IIC'') for communication with the micrcontroller.[[Serial_protocol_I2C|Check the basics of I2C]] here, if are not familiar with it. | ||
| − | |||
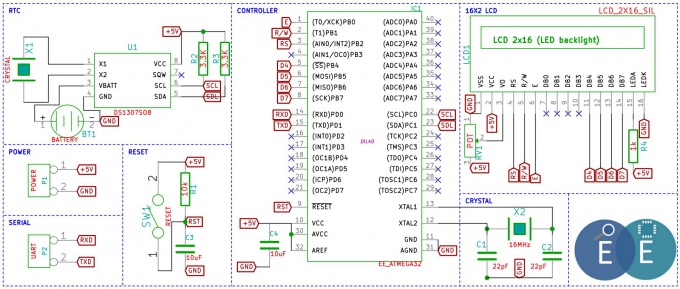
[http://exploreembedded.com/wiki/images/4/43/Schematic_AVR_Interfacing_RTC.pdf '''Schematic'''] | [http://exploreembedded.com/wiki/images/4/43/Schematic_AVR_Interfacing_RTC.pdf '''Schematic'''] | ||
| + | [[File:Schematic AVR Interfacing RTC.JPG|680px]] | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:AVR Tutorials]] | [[Category:AVR Tutorials]] | ||
Revision as of 12:27, 4 February 2015
Basics
The Real time clock DS1307 IC basically is stand alone time clock. Well, basically we can use a micrcontroller to keep time, but the value would go off as soon as it is powered off.
The RTC DS1307 is a handy solution to keep time all the way, when it is powered by a coin cell.
It is uses I²C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) protocol, referred to as I-squared-C, I-two-C, or IIC) for communication with the micrcontroller.Check the basics of I2C here, if are not familiar with it.