Difference between revisions of "1.8051 Architecture"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Box|type=green_light|text=8051 Architecture}} | {{Box|type=green_light|text=8051 Architecture}} | ||
| + | =====Introduction===== | ||
{{Box|type=l_green_light|text= | {{Box|type=l_green_light|text= | ||
In this tutorial we will discuss, the internal architecture of 8051. Well, not to worry; we will break it down in smaller pieces to understand it. I think a basic understand of Digital electronics would help. Nonetheless, for using 8051 in interfaces and applications, you might just go through it once. Being said that, a through understand will not only help in understand microcontrollers in depth, but will also help in programming efficiently. | In this tutorial we will discuss, the internal architecture of 8051. Well, not to worry; we will break it down in smaller pieces to understand it. I think a basic understand of Digital electronics would help. Nonetheless, for using 8051 in interfaces and applications, you might just go through it once. Being said that, a through understand will not only help in understand microcontrollers in depth, but will also help in programming efficiently. | ||
| + | [[File:8051 Architecture.jpg|600x500px|8051 Architecture]]<br /> | ||
As we have seen in the [[Introduction_to_8051|Previous tutorial]], it basically consists of a ALU, RAM, ROM, IO Ports, Timers/Counters, Serial Port and Interrupt Structure. Well, it also has some internal resisters.<br /> | As we have seen in the [[Introduction_to_8051|Previous tutorial]], it basically consists of a ALU, RAM, ROM, IO Ports, Timers/Counters, Serial Port and Interrupt Structure. Well, it also has some internal resisters.<br /> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 10: | ||
}} | }} | ||
===== Arithmetic and Logical Unit (ALU) ===== | ===== Arithmetic and Logical Unit (ALU) ===== | ||
| − | {{Box|type=l_green_light|text= | + | {{Box|type=l_green_light|text=<br /> |
ALU performs arithmetic like addition, subtraction, multiplication and Logical Operations like NAND, NOR etc. Since 8051 is an 8 bit microcontroller, it takes input from two 8 bit registers namely A and B and processes them. If would like a deeper insight as to how an ALU is built from basic building blocks(logic gates) you may go refer to this [[ALU_in_Detail|tutorial:(4 bit ALU in detail)]]. It would give you a deeper understanding of the microcontrollers, and it it would link your basic concepts like logical gates to the microcontrollers. | ALU performs arithmetic like addition, subtraction, multiplication and Logical Operations like NAND, NOR etc. Since 8051 is an 8 bit microcontroller, it takes input from two 8 bit registers namely A and B and processes them. If would like a deeper insight as to how an ALU is built from basic building blocks(logic gates) you may go refer to this [[ALU_in_Detail|tutorial:(4 bit ALU in detail)]]. It would give you a deeper understanding of the microcontrollers, and it it would link your basic concepts like logical gates to the microcontrollers. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ===== Registers of 8051 ===== | ||
| + | {{Box|type=l_green_light|text=<br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ===== Internal RAM in Detail ===== | ||
| + | {{Box|type=l_green_light|text=<br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== System Timing, Interrupts, Timers, Data Buffers and Memory Cotrol ===== | ||
| + | {{Box|type=l_green_light|text=<br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== IO port structure===== | ||
| + | {{Box|type=l_green_light|text=<br /> | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 11:01, 10 December 2013
8051 Architecture
Contents
Introduction
In this tutorial we will discuss, the internal architecture of 8051. Well, not to worry; we will break it down in smaller pieces to understand it. I think a basic understand of Digital electronics would help. Nonetheless, for using 8051 in interfaces and applications, you might just go through it once. Being said that, a through understand will not only help in understand microcontrollers in depth, but will also help in programming efficiently.
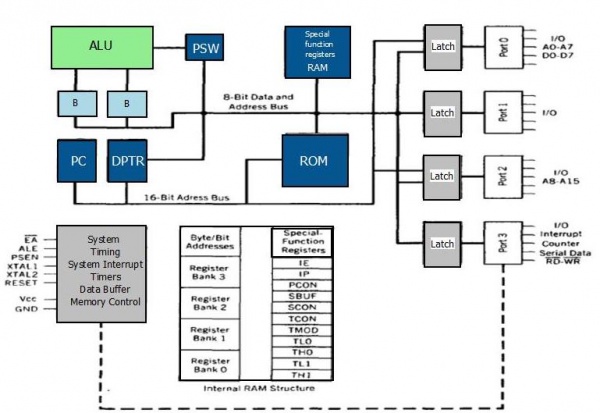

As we have seen in the Previous tutorial, it basically consists of a ALU, RAM, ROM, IO Ports, Timers/Counters, Serial Port and Interrupt Structure. Well, it also has some internal resisters.
Let us start discussing the ALU, as it is the main unit. Understanding of ALU, will allow us to put other units in their place.
Arithmetic and Logical Unit (ALU)
ALU performs arithmetic like addition, subtraction, multiplication and Logical Operations like NAND, NOR etc. Since 8051 is an 8 bit microcontroller, it takes input from two 8 bit registers namely A and B and processes them. If would like a deeper insight as to how an ALU is built from basic building blocks(logic gates) you may go refer to this tutorial:(4 bit ALU in detail). It would give you a deeper understanding of the microcontrollers, and it it would link your basic concepts like logical gates to the microcontrollers.
Registers of 8051
Internal RAM in Detail
System Timing, Interrupts, Timers, Data Buffers and Memory Cotrol
IO port structure
