Difference between revisions of "9 What is temperature there? with LM35"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<syntaxhighlight> | <syntaxhighlight> | ||
/* | /* | ||
| − | + | What is temperature there with LM35 | |
| − | Reads an Temperature | + | Reads an Temperature with LM35 Sensor . |
| − | + | ||
Also prints the results to the serial monitor. | Also prints the results to the serial monitor. | ||
The circuit: | The circuit: | ||
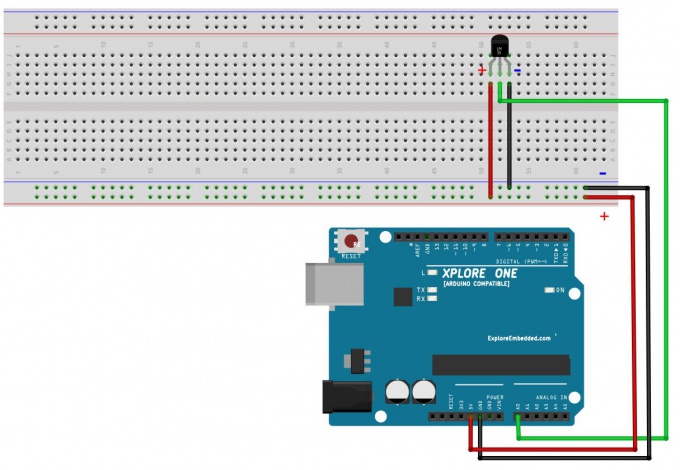
| − | * LM35 | + | * LM35 is connected to analog pin 0. |
| − | + | Center pin of the LM35 goes to the analog pin. | |
| − | * LED connected from digital pin 9 to ground | + | side pins of the LM35 go to +5V and ground |
| + | * LED connected from digital pin 9 to ground(If required) | ||
| + | */ | ||
// These constants won't change. They're used to give names | // These constants won't change. They're used to give names | ||
// to the pins used: | // to the pins used: | ||
| − | const int analogInPin = A0; // Analog input pin that | + | const int analogInPin = A0; // Analog input pin that theLM35 is attached to |
const int analogOutPin = 9; // Analog output pin that the LED is attached to | const int analogOutPin = 9; // Analog output pin that the LED is attached to | ||
| − | int sensorValue = 0; // value read from the | + | int sensorValue = 0; // value read from the LM35 |
int outputValue = 0; // value output to the PWM (analog out) | int outputValue = 0; // value output to the PWM (analog out) | ||
void setup() { | void setup() { | ||
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
analogWrite(analogOutPin, outputValue); | analogWrite(analogOutPin, outputValue); | ||
// print the results to the serial monitor: | // print the results to the serial monitor: | ||
| − | Serial.print(" | + | Serial.print("Voltage in mV = " ); |
| − | Serial.print(sensorValue); | + | Serial.print(sensorValue*5); |
| − | Serial.print("\t | + | Serial.print("\t Temperature in Degree Celsius = "); |
| − | Serial.println(outputValue); | + | Serial.println(outputValue*2); |
// wait 2 milliseconds before the next loop | // wait 2 milliseconds before the next loop | ||
// for the analog-to-digital converter to settle | // for the analog-to-digital converter to settle | ||
| Line 42: | Line 43: | ||
delay(2); | delay(2); | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 16:03, 15 September 2014
Code
/* What is temperature there with LM35 Reads an Temperature with LM35 Sensor . Also prints the results to the serial monitor. The circuit: * LM35 is connected to analog pin 0. Center pin of the LM35 goes to the analog pin. side pins of the LM35 go to +5V and ground * LED connected from digital pin 9 to ground(If required) */ // These constants won't change. They're used to give names // to the pins used: const int analogInPin = A0; // Analog input pin that theLM35 is attached to const int analogOutPin = 9; // Analog output pin that the LED is attached to int sensorValue = 0; // value read from the LM35 int outputValue = 0; // value output to the PWM (analog out) void setup() { // initialize serial communications at 9600 bps: Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { // read the analog in value: sensorValue = analogRead(analogInPin); // map it to the range of the analog out: outputValue = map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, 0, 255); // change the analog out value: analogWrite(analogOutPin, outputValue); // print the results to the serial monitor: Serial.print("Voltage in mV = " ); Serial.print(sensorValue*5); Serial.print("\t Temperature in Degree Celsius = "); Serial.println(outputValue*2); // wait 2 milliseconds before the next loop // for the analog-to-digital converter to settle // after the last reading: delay(2); }