Difference between revisions of "LPC2148 ADC Programming"
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[category: LPC2148 Tutorials]] | [[category: LPC2148 Tutorials]] | ||
In this tutorial, we are going to discuss how to use the inbuilt LPC2148 ADC and the register associated with it<br> | In this tutorial, we are going to discuss how to use the inbuilt LPC2148 ADC and the register associated with it<br> | ||
| − | |||
Later we will see how to interface a POT,LDR,Temp Sensor(LM35).<br><br><br> | Later we will see how to interface a POT,LDR,Temp Sensor(LM35).<br><br><br> | ||
| Line 75: | Line 74: | ||
|ADCR | |ADCR | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |31:28|| 27 || 26:24|| 23:22 || 21 || 20:17 || 16|| 15:8 || 7:0 | + | |31:28|| 27 || 26:24|| 23:22 || 21 || 20 || 19:17 || 16|| 15:8 || 7:0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Reserved||EDGE||START||Reserved|| PDN || Reserved || BURST || CLCKDIV || SEL | + | |Reserved||EDGE||START||Reserved|| PDN || Reserved || CLKS || BURST || CLCKDIV || SEL |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 92: | Line 91: | ||
CLearing this bit will disable the BURST conversion. | CLearing this bit will disable the BURST conversion. | ||
| + | '''Bit 20 – CLKS'''<br> | ||
| + | This field selects the number of clocks used for each conversion in Burst mode, and the number of bits of accuracy of the result in the RESULT bits of ADDR, between 11 clocks (10 bits) and 4 clocks (3 bits).<br> | ||
| + | 000-11 clocks / 10 bits accuracy<br> | ||
| + | 001-10 clocks / 9 bits accuracy<br> | ||
| + | 010- 9 clocks / 8 bits accuracy<br> | ||
| + | 011- 8 clocks / 7 bits accuracy<br> | ||
| + | 100- 7 clocks / 6 bits accuracy<br> | ||
| + | 101- 6 clocks / 5 bits accuracy<br> | ||
| + | 110- 5 clocks / 4 bits accuracy<br> | ||
| + | 111- 4 clocks / 3 bits accuracy<br> | ||
'''Bit 21 – PDN : Power Down Mode'''<br> | '''Bit 21 – PDN : Power Down Mode'''<br> | ||
| Line 118: | Line 127: | ||
|ADGDR | |ADGDR | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |31|| | + | |31|| 30 || 26:24 || 23:16|| 15:6 || 5:0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |DONE||OVERRUN||CHN || Reserved || RESULT|| Reserved | + | |DONE||OVERRUN|| CHN || Reserved || RESULT|| Reserved |
|} | |} | ||
| − | '''Bit 15: | + | '''Bit 15:6 - RESULT'''<br> |
| − | This field contains the | + | This field contains the 10bit A/D conversion value for the selected channel in <b>ADCR.SEL</b><br> |
| − | The | + | The value from this register should be read only after the conversion is complete ie DONE bit is set. |
| − | + | ||
'''Bit 26:24 - CHN : Channel'''<br> | '''Bit 26:24 - CHN : Channel'''<br> | ||
These bits contain the channel number for which the A/D conversion is done and the converted value is available in RESULT bits(e.g. 000 identifies channel 0, 011 channel 3...). | These bits contain the channel number for which the A/D conversion is done and the converted value is available in RESULT bits(e.g. 000 identifies channel 0, 011 channel 3...). | ||
| − | + | '''Bit 30 - OVERRUN'''<br> | |
| − | '''Bit | + | |
This bit is set during the BURST mode where the previous conversion data is overwritten by the new A/D conversion value. | This bit is set during the BURST mode where the previous conversion data is overwritten by the new A/D conversion value. | ||
| − | |||
'''Bit 31 - DONE'''<br> | '''Bit 31 - DONE'''<br> | ||
| Line 146: | Line 152: | ||
One can use the A/D Global Data Register to read all data from the ADC else use the A/D Channel Data | One can use the A/D Global Data Register to read all data from the ADC else use the A/D Channel Data | ||
Registers. It is important to use one method consistently because the DONE and OVERRUN flags can otherwise get out of synch between the AD0GDR and the A/D Channel Data Registers, potentially causing erroneous interrupts or DMA activity.<br><br> | Registers. It is important to use one method consistently because the DONE and OVERRUN flags can otherwise get out of synch between the AD0GDR and the A/D Channel Data Registers, potentially causing erroneous interrupts or DMA activity.<br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Hardware Connections= | =Hardware Connections= | ||
| Line 160: | Line 164: | ||
# Set the ADCR.START bit for starting the A/D conversion for selected channel. | # Set the ADCR.START bit for starting the A/D conversion for selected channel. | ||
#Wait for the conversion to complete, ADGR.DONE bit will be set once conversion is over. | #Wait for the conversion to complete, ADGR.DONE bit will be set once conversion is over. | ||
| − | # Read the | + | # Read the 10-bit A/D value from ADGR.RESULT. |
# Use it for further processing or just display on LCD.<br><br> | # Use it for further processing or just display on LCD.<br><br> | ||
=Code Examples = | =Code Examples = | ||
===Example 1 === | ===Example 1 === | ||
| − | Here we are going to do the A/D conversion for only | + | Here we are going to do the A/D conversion for only AD0.1. The result of the A/D conversion will be displayed on the LCD.<br> |
<html> | <html> | ||
| − | <script src="https://gist.github.com/ | + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/885c0091eaffb82147005d182db2dc03.js"></script> |
</html> | </html> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
===Using Explore Embedded Libraries=== | ===Using Explore Embedded Libraries=== | ||
| − | In the above example we discussed how to configure and use the inbuilt LPC1768 ADC.<br> | + | In the above example, we discussed how to configure and use the inbuilt LPC1768 ADC.<br> |
| − | Now we will see how to use the exploreEmbededd ADC | + | Now we will see how to use the exploreEmbededd ADC library to interface POT,LDR and Temperature Sensor(LM35).<br> |
| − | + | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| − | <script src="https://gist.github.com/ | + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/d31a9570985ddc12b37da6eca177249e.js"></script> |
</html> | </html> | ||
= Downloads= | = Downloads= | ||
| − | Download the complete project folder from | + | Download the complete project folder from [https://github.com/ExploreEmbedded/LPC2148_Stick this link] |
| − | https:// | + | <br><br> |
Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here! | Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here! | ||
{{DISQUS}} | {{DISQUS}} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:10, 21 July 2016
In this tutorial, we are going to discuss how to use the inbuilt LPC2148 ADC and the register associated with it
Later we will see how to interface a POT,LDR,Temp Sensor(LM35).
Contents
LPC2148 ADC Block
LPC2148 has an inbuilt 10-bit Successive Approximation ADC which is multiplexed among 6/8 input pins of ADC0/ADC1.
The ADC reference voltage is measured across GND to VREF, meaning it can do the conversion within this range. Usually, the VREFPis connected to VDD.
As LPC2148 works on 3.3 volts, this will be the ADC reference voltage.
Now the
$$resolution of ADC = 3.3/(2^{10}) = 3.3/1024 =0.003222 = 3.2mV$$
The below block diagram shows the ADC input pins multiplexed with other GPIO pins.
The ADC pin can be enabled by configuring the corresponding PINSEL register to select ADC function.
When the ADC function is selected for that pin in the Pin Select register, other Digital signals are disconnected from the ADC input pins.
| Adc Channel | Port Pin | Pin Functions | Associated PINSEL Register |
|---|---|---|---|
| AD0.1 | P0_28 | 0-GPIO, 1-AD0.1, 2-CAP0.2, MAT0.2 | 24,25 bits of PINSEL1 |
| AD0.2 | P0_29 | 0-GPIO, 1-AD0.2, 2-CAP0.3, 3-MAT0.3 | 26,27 bits of PINSEL1 |
| AD0.3 | P0_30 | 0-GPIO, 1-AD0.3, 2-EINT3, 3-CAP0.0 | 28,29 bits of PINSEL1 |
| AD0.4 | P0_25 | 0-GPIO, 1-AD0.4, 2-AOUT, | 18,19 bits of PINSEL1 |
| AD0.6 | P0_4 | 0-GPIO, 1-SCK0, 2-CAP0.1 , 3-AD0.6 | 08,09 bits of PINSEL0 |
| AD0.7 | P0_5 | 0-GPIO, 1-MISO0, 2-MAT0.1 , 3-AD0.7 | 10,11 bits of PINSEL0 |
| AD1.0 | P0_6 | 0-GPIO, 1-MOSI0, 2-CAP0.2, 3-AD1.0 | 12,13 bits of PINSEL0 |
| AD1.1 | P0_8 | 0-GPIO, 1-TXD1, 2-PWM4, 3-AD1.1 | 16,17 bits of PINSEL0 |
| AD1.2 | P0_10 | 0-GPIO, 1-RTS1, 2-CAP1.0, 3-AD1.2 | 20,21 bits of PINSEL1 |
| AD1.3 | P0_12 | 0-GPIO, 1-DSR1, 2-MAT1.0, 3-AD1.3 | 24,25 bits of PINSEL1 |
| AD1.4 | P0_13 | 0-GPIO, 1-DTR1, 2-MAT1.1 , 3-AD1.4 | 26,27 bits of PINSEL3 |
| AD1.5 | P0_15 | 0-GPIO, 1-RI1, 2-EINT2 , 3-AD1.5 | 30,31 bits of PINSEL3 |
| AD1.6 | P0_21 | 0-GPIO, 1-PWM5, 2-AD1.6, 3-CAP1.3 | 10,11 bits of PINSEL1 |
| AD1.7 | P0_22 | 0-GPIO, 1-AD1.7, 2-CAP0.0, 3-MAT0.0 | 12,13 bits of PINSEL1 |
ADC Registers
The below table shows the registers associated with LPC1768 ADC.
We are going to focus only on ADCR and ADGDR as these are sufficient for simple A/D conversion.
However once you are familer with LPC1768 ADC, you can explore the other features and the associated registers.
| Register | Description |
|---|---|
| ADCR | A/D COntrol Register: Used for Configuring the ADC |
| ADGDR | A/D Global Data Register: This register contains the ADC’s DONE bit and the result of the most recent A/D conversion |
| ADINTEN | A/D Interrupt Enable Register |
| ADDR0 - ADDR7 | A/D Channel Data Register: Contains the recent ADC value for respective channel |
| ADSTAT | A/D Status Register: Contains DONE & OVERRUN flag for all the ADC channels |
ADC Register Configuration
Now lets see how to configure the individual registers for ADC conversion.
| ADCR | |||||||||
| 31:28 | 27 | 26:24 | 23:22 | 21 | 20 | 19:17 | 16 | 15:8 | 7:0 |
| Reserved | EDGE | START | Reserved | PDN | Reserved | CLKS | BURST | CLCKDIV | SEL |
Bit 7:0 – SEL : Channel Select
These bits are used to select a particular channel for ADC conversion. One bit is allotted for each channel. Setting the Bit-0 will make the ADC to sample AD0[0] for conversion. Similary setting bit-7 will do the conversion for AD0[7].
Bit 15:8 – CLCKDIV : Clock Divisor
The APB clock (PCLK_ADC0) is divided by (this value plus one) to produce the clock for the A/D converter, which should be less than or equal to 13 MHz.
Bit 16 – BURST
This bit is used for BURST conversion. If this bit is set the ADC module will do the conversion for all the channels that are selected(SET) in SEL bits.
CLearing this bit will disable the BURST conversion.
Bit 20 – CLKS
This field selects the number of clocks used for each conversion in Burst mode, and the number of bits of accuracy of the result in the RESULT bits of ADDR, between 11 clocks (10 bits) and 4 clocks (3 bits).
000-11 clocks / 10 bits accuracy
001-10 clocks / 9 bits accuracy
010- 9 clocks / 8 bits accuracy
011- 8 clocks / 7 bits accuracy
100- 7 clocks / 6 bits accuracy
101- 6 clocks / 5 bits accuracy
110- 5 clocks / 4 bits accuracy
111- 4 clocks / 3 bits accuracy
Bit 21 – PDN : Power Down Mode
Setting this bit brings ADC out of power down mode and makes it operational.
Clearing this bit will power down the ADC.
Bit 24:26 – START
When the BURST bit is 0, these bits control whether and when an A/D conversion is started:
000 - Conversion Stopped
001- Start Conversion Now
The remaining cases (010 to 111) are about starting conversion on occurrence of edge on a particular CAP or MAT pin.
Bit 27 - EDGE
This bit is significant only when the START field contains 010-111.
It starts conversion on selected CAP or MAT input.
0 - On Falling Edge
1 - On Rising Edge
ADGDR ( ADC Global Data Register )
| ADGDR | |||||
| 31 | 30 | 26:24 | 23:16 | 15:6 | 5:0 |
| DONE | OVERRUN | CHN | Reserved | RESULT | Reserved |
Bit 15:6 - RESULT
This field contains the 10bit A/D conversion value for the selected channel in ADCR.SEL
The value from this register should be read only after the conversion is complete ie DONE bit is set.
Bit 26:24 - CHN : Channel
These bits contain the channel number for which the A/D conversion is done and the converted value is available in RESULT bits(e.g. 000 identifies channel 0, 011 channel 3...).
Bit 30 - OVERRUN
This bit is set during the BURST mode where the previous conversion data is overwritten by the new A/D conversion value.
Bit 31 - DONE
This bit is set to 1 when an A/D conversion completes. It is cleared when this register is read and when the ADCR is written. If the ADCR is written while a conversion is still in progress, this bit is set and a new conversion is started.
Some other registers
Though there are some more registers, we are restricting ourselves to use these registers only as this will be more convenient.
Apart from ADC Global Data register there are more 8 ADC Data registers (one Data register per ADC channel). DONE and OVERRUN bits for each channel can be monitored separately from the bits present in ADC Status register.
One can use the A/D Global Data Register to read all data from the ADC else use the A/D Channel Data
Registers. It is important to use one method consistently because the DONE and OVERRUN flags can otherwise get out of synch between the AD0GDR and the A/D Channel Data Registers, potentially causing erroneous interrupts or DMA activity.
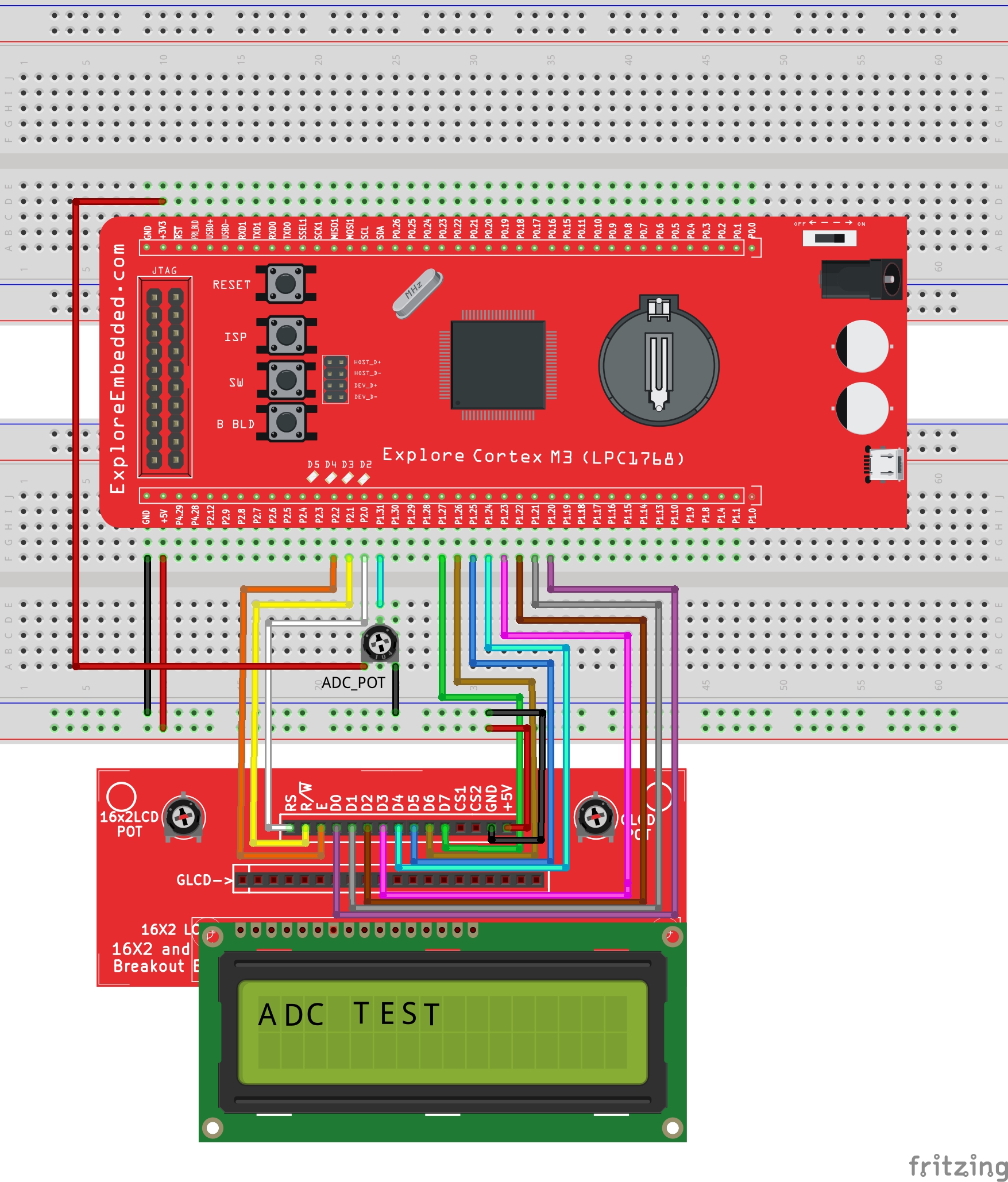
Hardware Connections
Steps for Configuring ADC
Below are the steps for configuring the LPC1768 ADC.
- Configure the GPIO pin for ADC function using PINSEL register.
- Enable the CLock to ADC module.
- Deselect all the channels and Power on the internal ADC module by setting ADCR.PDN bit.
- Select the Particular channel for A/D conversion by setting the corresponding bits in ADCR.SEL
- Set the ADCR.START bit for starting the A/D conversion for selected channel.
- Wait for the conversion to complete, ADGR.DONE bit will be set once conversion is over.
- Read the 10-bit A/D value from ADGR.RESULT.
- Use it for further processing or just display on LCD.
Code Examples
Example 1
Here we are going to do the A/D conversion for only AD0.1. The result of the A/D conversion will be displayed on the LCD.
Using Explore Embedded Libraries
In the above example, we discussed how to configure and use the inbuilt LPC1768 ADC.
Now we will see how to use the exploreEmbededd ADC library to interface POT,LDR and Temperature Sensor(LM35).
Downloads
Download the complete project folder from this link
Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here!