Difference between revisions of "LPC1768: PWM"
| (38 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[category: LPC1768 Tutorials]] | [[category: LPC1768 Tutorials]] | ||
| − | |||
In this tutorial we are going to discuss the PWM module of LPC1768.<br> | In this tutorial we are going to discuss the PWM module of LPC1768.<br> | ||
First we will see how to configure the PWM registers to generate signals of required PWM, At the end we will see how to use the ExploreEmdedded PWM library. | First we will see how to configure the PWM registers to generate signals of required PWM, At the end we will see how to use the ExploreEmdedded PWM library. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 9: | ||
{| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
|-class="info" | |-class="info" | ||
| − | ! | + | !PWM Channel || Port Pin || Pin Functions || Associated PINSEL Register || Corresponding Match Register |
|- | |- | ||
|PWM_1|| P2.0 || 0-GPIO, 1-<b>PWM1[1]</b>, 2-TXD1, 3- ||0,1 bits of PINSEL4 ||MR1 | |PWM_1|| P2.0 || 0-GPIO, 1-<b>PWM1[1]</b>, 2-TXD1, 3- ||0,1 bits of PINSEL4 ||MR1 | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
|-class="active" | |-class="active" | ||
|PWM_6|| P2.5 || 0-GPIO, 1-<b>PWM1[6]</b>, 2-DTR1, 3-TRACEDATA[0] ||10,11 bits of PINSEL4 ||MR6 | |PWM_6|| P2.5 || 0-GPIO, 1-<b>PWM1[6]</b>, 2-DTR1, 3-TRACEDATA[0] ||10,11 bits of PINSEL4 ||MR6 | ||
| − | |}<br><br> | + | |}<br><br><br><br> |
=LPC7168 PWM Registers= | =LPC7168 PWM Registers= | ||
| Line 66: | Line 65: | ||
'''Bit 0 – Counter Enable'''<br> | '''Bit 0 – Counter Enable'''<br> | ||
| − | This bit is used to Enable or Disable the PWM Timer and PWM Prescalar Counters | + | This bit is used to Enable or Disable the PWM Timer and PWM Prescalar Counters<br> |
| − | 0- Disable the Counters | + | 0- Disable the Counters<br> |
1- Enable the Counter incrementing. | 1- Enable the Counter incrementing. | ||
'''Bit 1 – Counter reset'''<br> | '''Bit 1 – Counter reset'''<br> | ||
| − | This bit is used to clear the PWM Timer and PWM Prescalar Counter values. | + | This bit is used to clear the PWM Timer and PWM Prescalar Counter values.<br> |
| − | 0- Do not Clear. | + | 0- Do not Clear.<br> |
1- The PWM Timer Counter and the PWM Prescale Counter are synchronously reset on the next positive edge of PCLK. | 1- The PWM Timer Counter and the PWM Prescale Counter are synchronously reset on the next positive edge of PCLK. | ||
'''Bit 3 – PWM Enable'''<br> | '''Bit 3 – PWM Enable'''<br> | ||
| − | Used to | + | Used to Enable or Disable the PWM Block.<br> |
| − | 0- PWM Disabled | + | 0- PWM Disabled<br> |
1- PWM Enabled | 1- PWM Enabled | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
|-class="info" | |-class="info" | ||
| − | + | !MCR | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |31:21||20||19||18||-||5||4||3||2||1||0 |
| − | |- | + | |-class="active" |
| − | | | + | |Reserved||PWMMR6S||PWMMR6R||PWMMR6I||-||PWMMR1S||PWMMR1R||PWMMR1I||PWMMR0S||PWMMR0R||PWMMR0I |
| − | |- | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | |- | + | |
| − | | | + | |
|} | |} | ||
| + | '''PWMMRxI'''<br> | ||
| + | This bit is used to Enable or Disable the PWM interrupts when the PWMTC matches PWMMRx (x:0-6)<br> | ||
| + | 0- Disable the PWM Match interrupt<br> | ||
| + | 1- Enable the PWM Match interrupt. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''PWMMRxR'''<br> | ||
| + | This bit is used to Reset PWMTC whenever it Matches PWMRx(x:0-6)<br> | ||
| + | 0- Do not Clear.<br> | ||
| + | 1- Reset the PWMTC counter value whenever it matches PWMRx. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''PWMMRxS'''<br> | ||
| + | This bit is used to Stop the PWMTC,PWMPC whenever the PWMTC matches PWMMRx(x:0-6).<br> | ||
| + | 0- Disable the PWM stop o match feature<br> | ||
| + | 1- Enable the PWM Stop feature. This will stop the PWM whenever the PWMTC reaches the Match register value. | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| − | |||
{| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
|-class="info" | |-class="info" | ||
| − | + | !PCR | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |31:15|| 14-9 || 8-7 || 6-2 ||1-0 |
| − | |- | + | |-class="active" |
| − | | | + | |Unused||PWMENA6-PWMENA1||Unused||PWMSEL6-PWMSEL2||Unused |
|} | |} | ||
| + | '''PWMSELx'''<br> | ||
| + | This bit is used to select the single edged and double edge mode form PWMx (x:2-6)<br> | ||
| + | 0- Single Edge mode for PWMx<br> | ||
| + | 1- Double Edge Mode for PWMx. | ||
| + | '''PWMENAx'''<br> | ||
| + | This bit is used to enable/disable the PWM output for PWMx(x:1-6)<br> | ||
| + | 0- PWMx Disable.<br> | ||
| + | 1- PWMx Enabled. | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
|-class="info" | |-class="info" | ||
| − | + | !LER | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |31-7||6||5||4||3||2||1||0 |
| − | |- | + | |-class="active" |
| − | | | + | |Unused||LEN6||LEN5||LEN4||LEN3||LEN2||LEN1||LEN0 |
|} | |} | ||
| + | '''LENx'''<br> | ||
| + | This bit is used Enable/Disable the loading of new Match value whenever the PWMTC is reset(x:0-6)<br> | ||
| + | PWMTC will be continously incrementing whenever it reaches the PWMMRO, timer will be reset depeding on PWMTCR configuraion. | ||
| + | Once the Timer is reset the New Match values will be loaded from MR0-MR6 depending on bits set in this register.<br> | ||
| + | 0- Disable the loading of new Match Values<br> | ||
| + | 1- Load the new Match values from MRx when the timer is reset. | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | =PWM Working= | ||
| + | After looking into the PWM registers, its time to see how the LPC1768 PWM module works. | ||
| + | The TC is continuously incremented and once it matches the MR1(Duty Cycle) the PWM pin is pulled Low. TC still continues to increment and once it reaches the Cycle time(Ton+Toff) the PWM module does the following things: | ||
| + | *Reset the TC value. | ||
| + | *Pull the PWM pin High. | ||
| + | *Loads the new Match register values. | ||
| + | [[File:LPC1768_PWM.gif]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| − | + | Summary of PWM operations for the above image: | |
| − | + | *Slide1: The TC is being incremented as per the Pre-scalar configuration. The PWM output is high as the TC is still less that duty cycle. | |
| − | + | *Slide2: TC is incremented to 40 and still the PWM pin as HIGH. | |
| − | + | *Slide3: TC is incremented to 60 and it matches the Duty Cycle(MR1=60). | |
| − | + | *Slide4: Now the Comparator1(Green) will trigger the R of SR latch and Pulls the PWM output to Zero(Q=0). TC still continues to increment. | |
| + | *Slide5: TC is incremented to 80 and PWM pin is low as TC>Duty Cycle. | ||
| + | *Slide6: Now TC is 100 and it matches the Cycle time(MR0==100). | ||
| + | *Slide7: Now the Comparator2(Red) will trigger the S of SR latch and pulls the PWM output to ONE(Q==1). It also resets the TC to zero. It updates Shadow buffers with new Match values from MRO,MR1. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| − | = | + | =Steps to Configure PWM= |
| − | + | #Configure the GPIO pins for PWM operation in respective PINSEL register. | |
| − | + | #Configure TCR to enable the Counter for incrementing the TC, and Enable the PWM block. | |
| − | + | #Set the required pre-scalar value in PR. In our case it will be zero. | |
| − | + | #Configure MCR to reset the TC whenever it matches MR0. | |
| − | + | #Update the Cycle time in MR0. In our case it will be 100. | |
| − | + | #Load the Duty cycles for required PWMx channels in respective match registers MRx(x: 1-6). | |
| − | + | #Enable the bits in LER register to load and latch the new match values. | |
| − | + | #Enable the required pwm channels in PCR register. | |
| − | + | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | + | =Example= | |
| − | + | Program to demonstrates the variable PWM signal generation on PWM_1-PWM_4(P2_0 - P2_3).<br> | |
| − | + | Connect the Leds to the pins P2_0 to P2_3 and observe the led brigthness change depending on the dutycycle. | |
| − | + | [[File:0_LPC1768_PWM.gif]] | |
<html> | <html> | ||
| − | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/ | + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/c721588560b77ad30396.js"></script> |
</html> | </html> | ||
| − | <br><br><br> | + | <br><br><br> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Using ExploreEmbedded Libraries :=== | ||
| + | In the above tutorial we just discussed how to configure and use the PWM module of LPC1768 <br> | ||
| + | Once you know the internals of LPC7168 PWM, you can directly use the ExploreEmbedded libraries to generate the required PWM signals for different duty cycles.<br> | ||
| + | The below sample code shows how to use the ExploreEmbedded PWM library.<br> | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| − | <script src="https://gist.github.com/ | + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/5df6b6cc86c3b9b546c2.js"></script> |
</html> | </html> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Downloads= | = Downloads= | ||
Latest revision as of 10:05, 8 May 2016
In this tutorial we are going to discuss the PWM module of LPC1768.
First we will see how to configure the PWM registers to generate signals of required PWM, At the end we will see how to use the ExploreEmdedded PWM library.
Contents
LPC1768 PWM Module
LPC1768 has 6 PWM output pins which can be used as 6-Single edged or 3-Double edged. There as seven match registers to support these 6 PWM output signals. Below block diagram shows the PWM pins and the associated Match(Duty Cycle) registers.
| PWM Channel | Port Pin | Pin Functions | Associated PINSEL Register | Corresponding Match Register |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWM_1 | P2.0 | 0-GPIO, 1-PWM1[1], 2-TXD1, 3- | 0,1 bits of PINSEL4 | MR1 |
| PWM_2 | P2.1 | 0-GPIO, 1-PWM1[2], 2-RXD1, 3- | 2,3 bits of PINSEL4 | MR2 |
| PWM_3 | P2.2 | 0-GPIO, 1-PWM1[3], 2-CTS1, 3-TRACEDATA[3] | 4,5 bits of PINSEL4 | MR3 |
| PWM_4 | P2.3 | 0-GPIO, 1-PWM1[4], 2-DCD1, 3-TRACEDATA[2] | 6,7 bits of PINSEL4 | MR4 |
| PWM_5 | P2.4 | 0-GPIO, 1-PWM1[5], 2-DSR1, 3-TRACEDATA[1] | 8,9 bits of PINSEL4 | MR5 |
| PWM_6 | P2.5 | 0-GPIO, 1-PWM1[6], 2-DTR1, 3-TRACEDATA[0] | 10,11 bits of PINSEL4 | MR6 |
LPC7168 PWM Registers
The below table shows the registers associated with LPC1768 PWM.
| Register | Description |
|---|---|
| IR | Interrupt Register: The IR can be read to identify which of eight possible interrupt sources are pending. Writing Logic-1 will clear the corresponding interrupt. |
| TCR | Timer Control Register: The TCR is used to control the Timer Counter functions(enable/disable/reset). |
| TC | Timer Counter: The 32-bit TC is incremented every PR+1 cycles of PCLK. The TC is controlled through the TCR. |
| PR | Prescalar Register: This is used to specify the Prescalar value for incrementing the TC. |
| PC | Prescale Counter: The 32-bit PC is a counter which is incremented to the value stored in PR. When the value in PR is reached, the TC is incremented. |
| MCR | Match Control Register: The MCR is used to control the reseting of TC and generating of interrupt whenever a Match occurs. |
| MR0 | Match Register: This register hold the max cycle Time(Ton+Toff). |
| MR1-MR6 | Match Registers: These registers holds the Match value(PWM Duty) for corresponding PWM channels(PWM1-PWM6). |
| PCR | PWM Control Register: PWM Control Register. Enables PWM outputs and selects PWM channel types as either single edge or double edge controlled. |
| LER | Load Enable Register: Enables use of new PWM values once the match occurs. |
Register Configuration
The below table shows the registers associated with LPC1768 PWM.
| TCR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31:4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Reserved | PWM Enable | Reserved | Counter Reset | Counter Enable |
Bit 0 – Counter Enable
This bit is used to Enable or Disable the PWM Timer and PWM Prescalar Counters
0- Disable the Counters
1- Enable the Counter incrementing.
Bit 1 – Counter reset
This bit is used to clear the PWM Timer and PWM Prescalar Counter values.
0- Do not Clear.
1- The PWM Timer Counter and the PWM Prescale Counter are synchronously reset on the next positive edge of PCLK.
Bit 3 – PWM Enable
Used to Enable or Disable the PWM Block.
0- PWM Disabled
1- PWM Enabled
| MCR | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31:21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | - | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Reserved | PWMMR6S | PWMMR6R | PWMMR6I | - | PWMMR1S | PWMMR1R | PWMMR1I | PWMMR0S | PWMMR0R | PWMMR0I |
PWMMRxI
This bit is used to Enable or Disable the PWM interrupts when the PWMTC matches PWMMRx (x:0-6)
0- Disable the PWM Match interrupt
1- Enable the PWM Match interrupt.
PWMMRxR
This bit is used to Reset PWMTC whenever it Matches PWMRx(x:0-6)
0- Do not Clear.
1- Reset the PWMTC counter value whenever it matches PWMRx.
PWMMRxS
This bit is used to Stop the PWMTC,PWMPC whenever the PWMTC matches PWMMRx(x:0-6).
0- Disable the PWM stop o match feature
1- Enable the PWM Stop feature. This will stop the PWM whenever the PWMTC reaches the Match register value.
| PCR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31:15 | 14-9 | 8-7 | 6-2 | 1-0 |
| Unused | PWMENA6-PWMENA1 | Unused | PWMSEL6-PWMSEL2 | Unused |
PWMSELx
This bit is used to select the single edged and double edge mode form PWMx (x:2-6)
0- Single Edge mode for PWMx
1- Double Edge Mode for PWMx.
PWMENAx
This bit is used to enable/disable the PWM output for PWMx(x:1-6)
0- PWMx Disable.
1- PWMx Enabled.
| LER | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31-7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Unused | LEN6 | LEN5 | LEN4 | LEN3 | LEN2 | LEN1 | LEN0 |
LENx
This bit is used Enable/Disable the loading of new Match value whenever the PWMTC is reset(x:0-6)
PWMTC will be continously incrementing whenever it reaches the PWMMRO, timer will be reset depeding on PWMTCR configuraion.
Once the Timer is reset the New Match values will be loaded from MR0-MR6 depending on bits set in this register.
0- Disable the loading of new Match Values
1- Load the new Match values from MRx when the timer is reset.
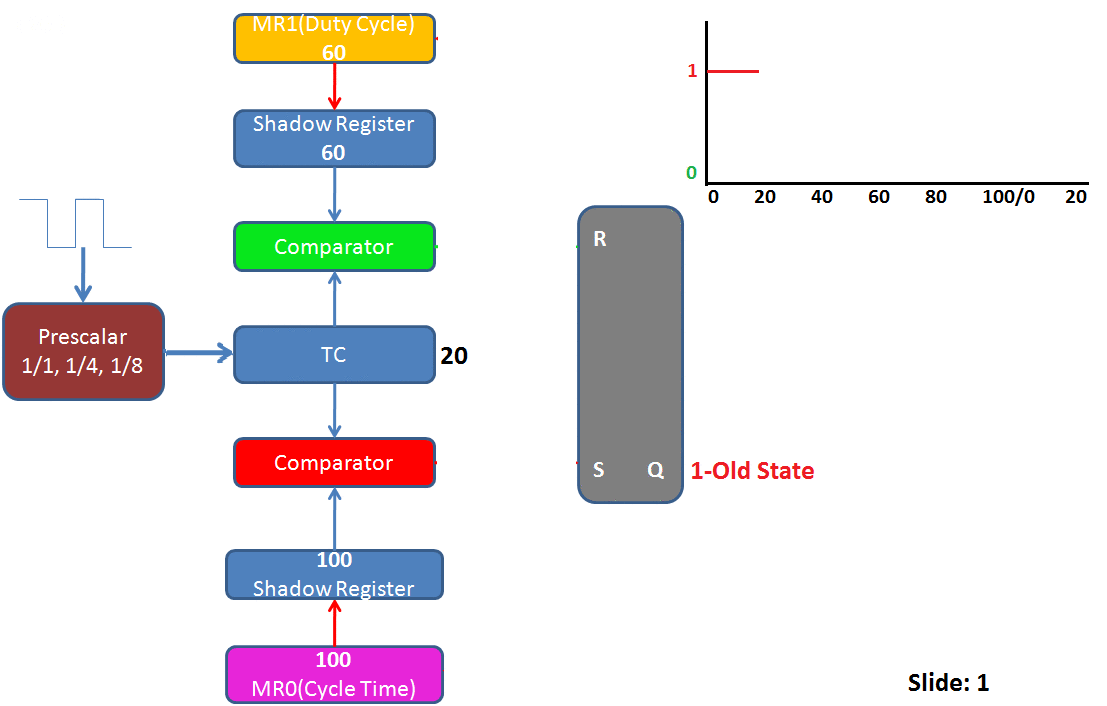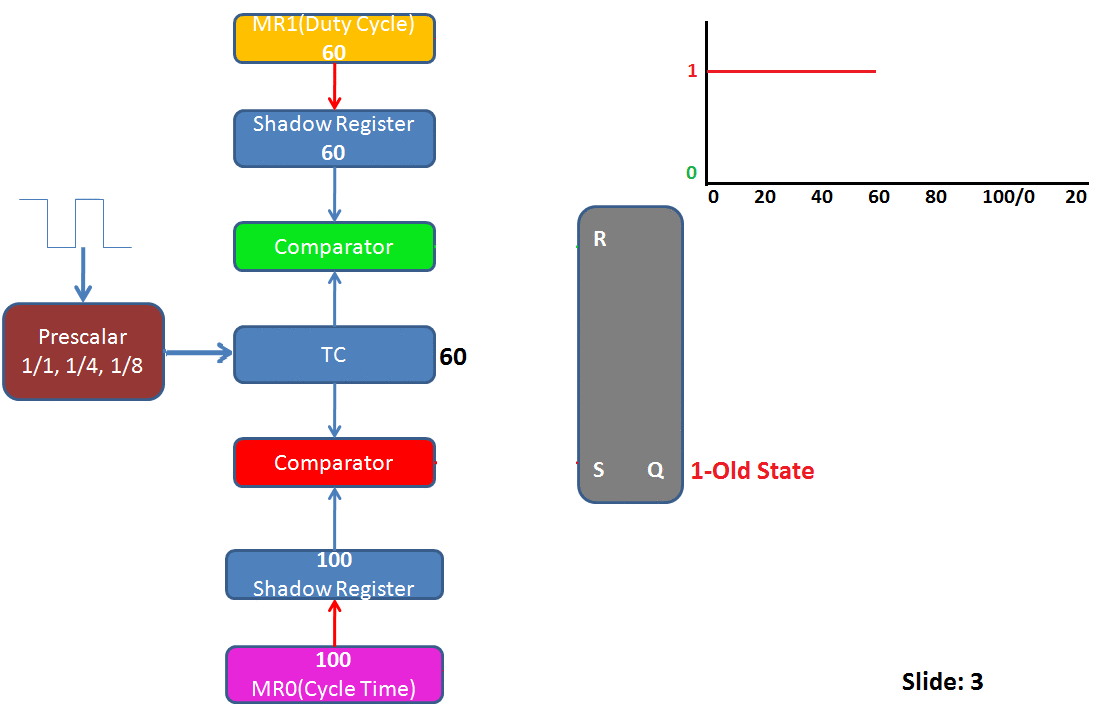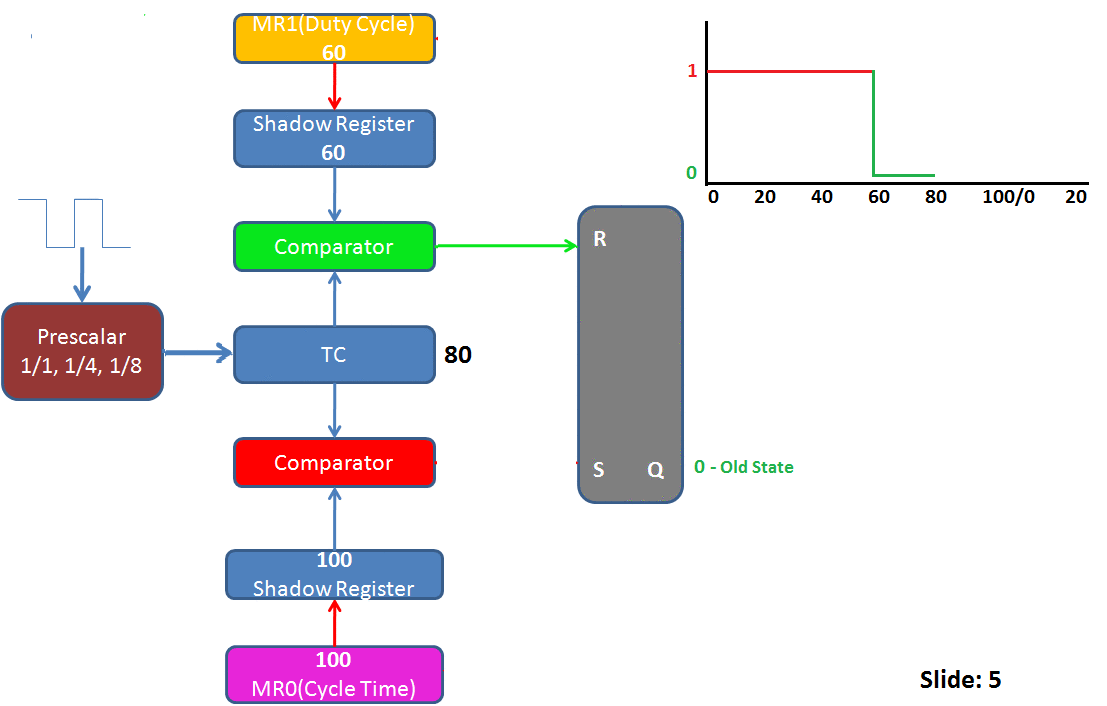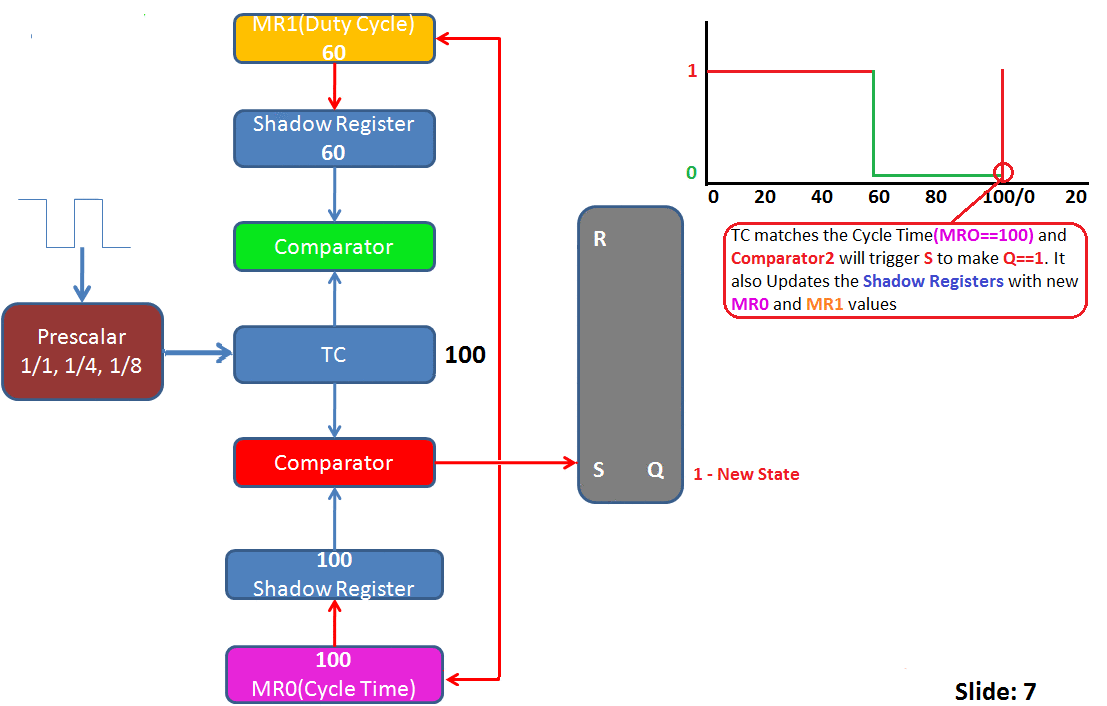
PWM Working
After looking into the PWM registers, its time to see how the LPC1768 PWM module works.
The TC is continuously incremented and once it matches the MR1(Duty Cycle) the PWM pin is pulled Low. TC still continues to increment and once it reaches the Cycle time(Ton+Toff) the PWM module does the following things:
- Reset the TC value.
- Pull the PWM pin High.
- Loads the new Match register values.
Summary of PWM operations for the above image:
- Slide1: The TC is being incremented as per the Pre-scalar configuration. The PWM output is high as the TC is still less that duty cycle.
- Slide2: TC is incremented to 40 and still the PWM pin as HIGH.
- Slide3: TC is incremented to 60 and it matches the Duty Cycle(MR1=60).
- Slide4: Now the Comparator1(Green) will trigger the R of SR latch and Pulls the PWM output to Zero(Q=0). TC still continues to increment.
- Slide5: TC is incremented to 80 and PWM pin is low as TC>Duty Cycle.
- Slide6: Now TC is 100 and it matches the Cycle time(MR0==100).
- Slide7: Now the Comparator2(Red) will trigger the S of SR latch and pulls the PWM output to ONE(Q==1). It also resets the TC to zero. It updates Shadow buffers with new Match values from MRO,MR1.
Steps to Configure PWM
- Configure the GPIO pins for PWM operation in respective PINSEL register.
- Configure TCR to enable the Counter for incrementing the TC, and Enable the PWM block.
- Set the required pre-scalar value in PR. In our case it will be zero.
- Configure MCR to reset the TC whenever it matches MR0.
- Update the Cycle time in MR0. In our case it will be 100.
- Load the Duty cycles for required PWMx channels in respective match registers MRx(x: 1-6).
- Enable the bits in LER register to load and latch the new match values.
- Enable the required pwm channels in PCR register.
Example
Program to demonstrates the variable PWM signal generation on PWM_1-PWM_4(P2_0 - P2_3).
Connect the Leds to the pins P2_0 to P2_3 and observe the led brigthness change depending on the dutycycle.
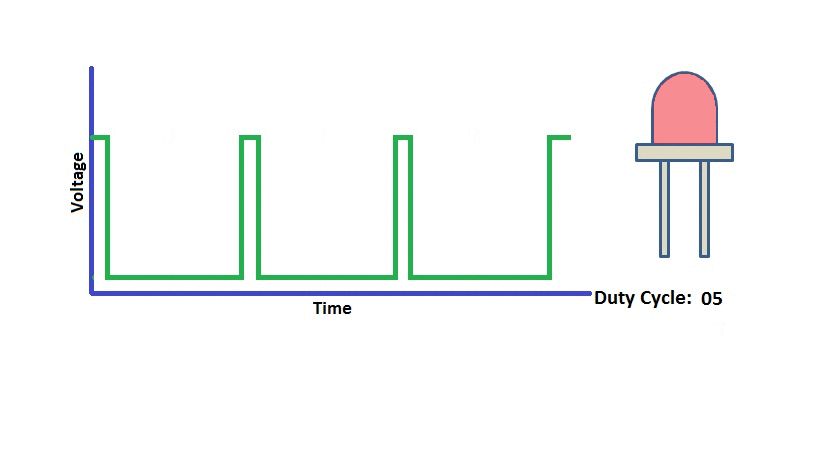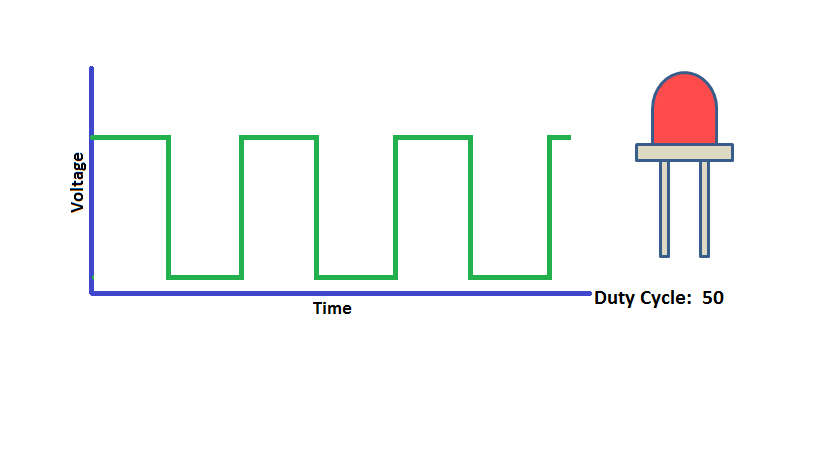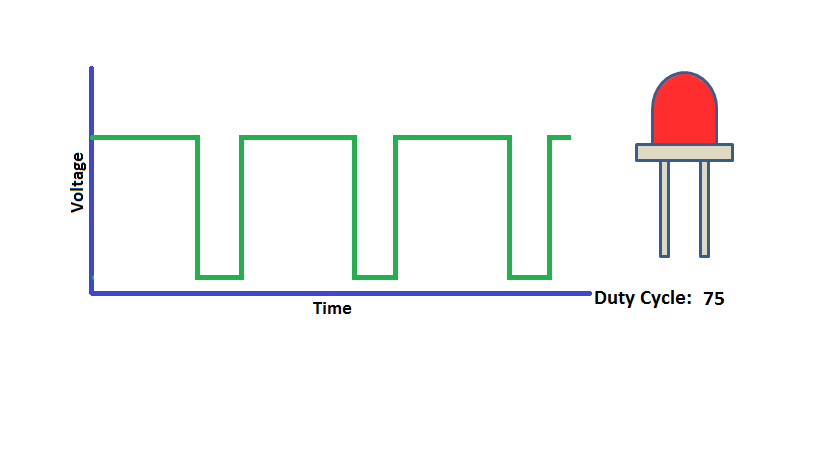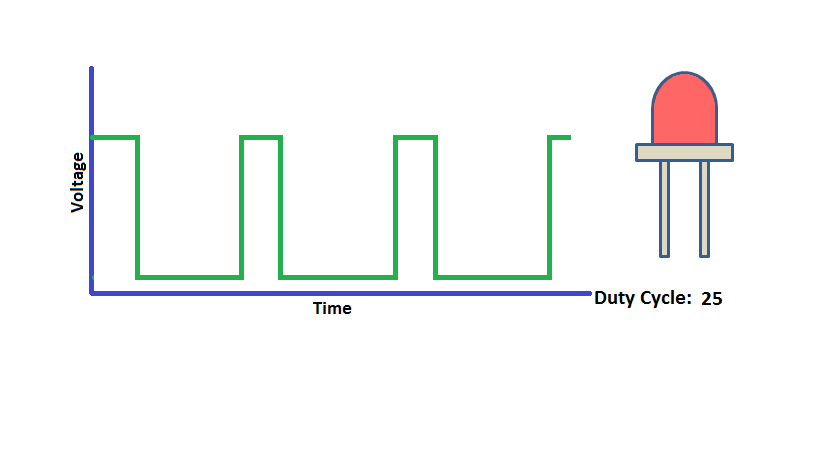
Using ExploreEmbedded Libraries :
In the above tutorial we just discussed how to configure and use the PWM module of LPC1768
Once you know the internals of LPC7168 PWM, you can directly use the ExploreEmbedded libraries to generate the required PWM signals for different duty cycles.
The below sample code shows how to use the ExploreEmbedded PWM library.
Downloads
Download the complete project folder from the below link:
https://codeload.github.com/ExploreEmbedded/Explore-Cortex-M3-LPC1768-Stick-DVB-14001/zip/master
Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here!