Difference between revisions of "LPC1768: SPI Programming"
m |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[category: LPC1768 Tutorials]] | [[category: LPC1768 Tutorials]] | ||
| − | |||
=Objective= | =Objective= | ||
| + | In this tutorial we are going to discuss the SPI ( Serial Peripheral Interface). <br> | ||
| + | After understating the basics of LPC1768 SPI module, We will discuss how to use the Explore Embedded libraries to communicate with any of the SPI devices. | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
=LPC1768 SPI Block= | =LPC1768 SPI Block= | ||
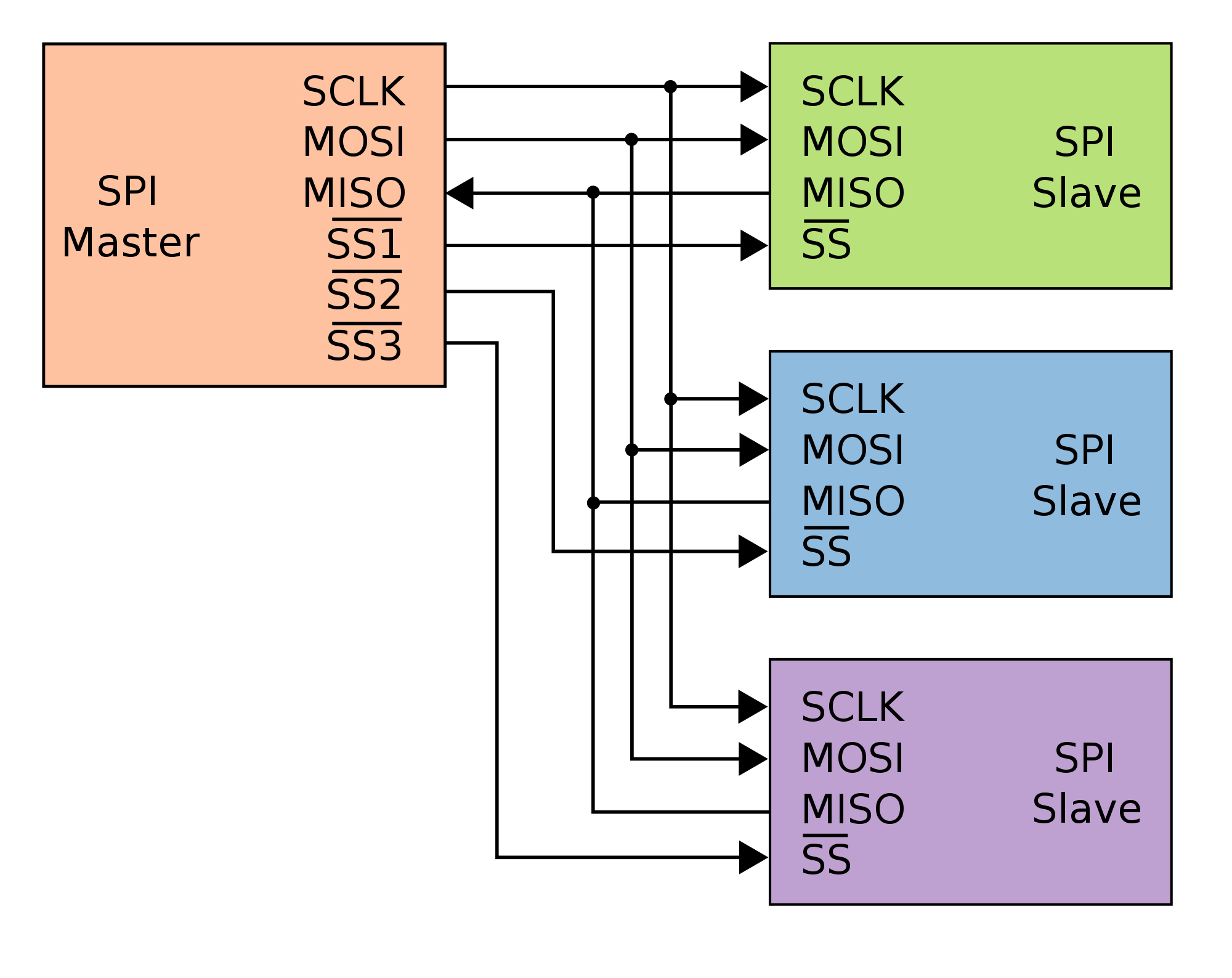
The below block diagram shows the SPI input pins multiplexed with other GPIO pins.<br> | The below block diagram shows the SPI input pins multiplexed with other GPIO pins.<br> | ||
The SPI pin can be enabled by configuring the corresponding PINSEL register to select SPI function.<br> | The SPI pin can be enabled by configuring the corresponding PINSEL register to select SPI function.<br> | ||
When the SPI function is selected for that pin in the Pin Select register, other Digital signals are disconnected from the SPI input pins.<br> | When the SPI function is selected for that pin in the Pin Select register, other Digital signals are disconnected from the SPI input pins.<br> | ||
| − | {| class=" | + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" |
| − | + | |-class="info" | |
| + | |Port Pin || PINSEL_FUNC_0 || PINSEL_FUNC_1 ||PINSEL_FUNC_2 ||PINSEL_FUNC_3 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |P0.15 | + | |P0.15 || GPIO || TXD1 || SCK0 || <b>SCK</b> |
| + | |-class="active" | ||
| + | |P0.16 || GPIO || RXD1 || SSEL0 || <b>SSEL</b> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |P0. | + | |P0.17 || GPIO || CTS1 || MISO0|| <b>MISO</b> |
| + | |-class="active" | ||
| + | |P0.18 || GPIO || DCD1 || MOSI0 || <b>MOSI</b> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | [[File:spi_diagram.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =SPI Registers= | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | |Register || Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |SPCR|| SPI Control Register : used to configure SPI |
| + | |-class="active" | ||
| + | |SPSR|| SPI status Register : | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |SPDR|| SPI Data Register : contains received data or data to be transmitted |
| + | |-class="active" | ||
| + | |SPCCR|| SPI Clock Counter Register : used to control master SCK frequency | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | |SPCR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |31:12 || 11:8|| 7 || 6 || 5 || 4 || 3 || 2 ||1: 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RESERVED || BITS|| SPIE|| LSBF || MSTR || CPOL || CPHA || BIT ENABLE || RESERVED | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 1:0 – RESERVED'''<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 2 – BIT ENABLE:'''<br> | ||
| + | This is used to clear the 16-byte Rx FIFO.<br> | ||
| + | 0-- .<br> | ||
| + | 1-- .<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 3 – CPHA:'''<br> | ||
| + | 0-- .<br> | ||
| + | 1-- .<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 4 – CPOL:'''<br> | ||
| + | This is used for controlling clock polarity.<br> | ||
| + | 0 -- SCK is active high.<br> | ||
| + | 1 -- SCK is active low.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 5 – MSTR:'''<br> | ||
| + | This bit is used for Master mode select.<br> | ||
| + | 0 -- Slave Mode.<br> | ||
| + | 1 -- Master Mode.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 6 – LSBF:'''<br> | ||
| + | 0 -- .<br> | ||
| + | 1 -- .<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 4 – SPIE:'''<br> | ||
| + | This bit is used to enable SPI interrupt.<br> | ||
| + | 0 -- .<br> | ||
| + | 1 -- .<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 11:8 – BITS:'''<br> | ||
| + | When bit 2 ( BIT ENABLE ) of this register is 1, this field controls the number of bits per transfer:<br> | ||
| + | 1000 -- 8 Bits per transfer<br> | ||
| + | 1001 -- 9 Bits per transfer<br> | ||
| + | 1010 -- 10 Bits per transfer<br> | ||
| + | 1011 -- 11 Bits per transfer<br> | ||
| + | 1100 -- 12 Bits per transfer<br> | ||
| + | 1101 -- 13 Bits per transfer<br> | ||
| + | 1110 -- 14 Bits per transfer<br> | ||
| + | 1111 -- 15 Bits per transfer<br> | ||
| + | 0000 -- 16 Bits per transfer<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 31:12 – RESERVED'''<br> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | |SPSR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |31:8|| 7 || 6 || 5 || 4 || 3 || 2 : 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RESERVED || SPIF || WCOL || ROVR || MODF || ABRT || RESERVED | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 2:0 – RESERVED'''<br> | ||
| + | '''Bit 3 – ABRT:'''<br> | ||
| + | '''Bit 4 – MODF:'''<br> | ||
| + | '''Bit 5 – ROVR:'''<br> | ||
| + | '''Bit 6 – WCOL:'''<br> | ||
| + | '''Bit 7 – SPIF:'''<br> | ||
| + | '''Bit 31:8 – RESERVED:'''<br> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | |SPDR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |31:16 || 15:8 || 7: 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RESERVED || Data High || Data Low | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 7:0 – Data Low : '''<br> | ||
| + | '''Bit 15:8 – Data High :'''<br> | ||
| + | '''Bit 31:16 – RESERVED'''<br> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | |SPCCR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |31:8|| 7 : 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RESERVED || COUNTER | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bit 7:0 – COUNTER :'''<br> | ||
| + | '''Bit 31:8 – RESERVED'''<br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Steps for using SPI= | =Steps for using SPI= | ||
===Initialize SPI=== | ===Initialize SPI=== | ||
Latest revision as of 20:20, 14 April 2016
Contents
Objective
In this tutorial we are going to discuss the SPI ( Serial Peripheral Interface).
After understating the basics of LPC1768 SPI module, We will discuss how to use the Explore Embedded libraries to communicate with any of the SPI devices.
LPC1768 SPI Block
The below block diagram shows the SPI input pins multiplexed with other GPIO pins.
The SPI pin can be enabled by configuring the corresponding PINSEL register to select SPI function.
When the SPI function is selected for that pin in the Pin Select register, other Digital signals are disconnected from the SPI input pins.
| Port Pin | PINSEL_FUNC_0 | PINSEL_FUNC_1 | PINSEL_FUNC_2 | PINSEL_FUNC_3 |
| P0.15 | GPIO | TXD1 | SCK0 | SCK |
| P0.16 | GPIO | RXD1 | SSEL0 | SSEL |
| P0.17 | GPIO | CTS1 | MISO0 | MISO |
| P0.18 | GPIO | DCD1 | MOSI0 | MOSI |
SPI Registers
| Register | Description |
| SPCR | SPI Control Register : used to configure SPI |
| SPSR | SPI status Register : |
| SPDR | SPI Data Register : contains received data or data to be transmitted |
| SPCCR | SPI Clock Counter Register : used to control master SCK frequency |
| SPCR | ||||||||
| 31:12 | 11:8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1: 0 |
| RESERVED | BITS | SPIE | LSBF | MSTR | CPOL | CPHA | BIT ENABLE | RESERVED |
Bit 1:0 – RESERVED
Bit 2 – BIT ENABLE:
This is used to clear the 16-byte Rx FIFO.
0-- .
1-- .
Bit 3 – CPHA:
0-- .
1-- .
Bit 4 – CPOL:
This is used for controlling clock polarity.
0 -- SCK is active high.
1 -- SCK is active low.
Bit 5 – MSTR:
This bit is used for Master mode select.
0 -- Slave Mode.
1 -- Master Mode.
Bit 6 – LSBF:
0 -- .
1 -- .
Bit 4 – SPIE:
This bit is used to enable SPI interrupt.
0 -- .
1 -- .
Bit 11:8 – BITS:
When bit 2 ( BIT ENABLE ) of this register is 1, this field controls the number of bits per transfer:
1000 -- 8 Bits per transfer
1001 -- 9 Bits per transfer
1010 -- 10 Bits per transfer
1011 -- 11 Bits per transfer
1100 -- 12 Bits per transfer
1101 -- 13 Bits per transfer
1110 -- 14 Bits per transfer
1111 -- 15 Bits per transfer
0000 -- 16 Bits per transfer
Bit 31:12 – RESERVED
| SPSR | ||||||
| 31:8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 : 0 |
| RESERVED | SPIF | WCOL | ROVR | MODF | ABRT | RESERVED |
Bit 2:0 – RESERVED
Bit 3 – ABRT:
Bit 4 – MODF:
Bit 5 – ROVR:
Bit 6 – WCOL:
Bit 7 – SPIF:
Bit 31:8 – RESERVED:
| SPDR | ||
| 31:16 | 15:8 | 7: 0 |
| RESERVED | Data High | Data Low |
Bit 7:0 – Data Low :
Bit 15:8 – Data High :
Bit 31:16 – RESERVED
| SPCCR | |
| 31:8 | 7 : 0 |
| RESERVED | COUNTER |
Bit 7:0 – COUNTER :
Bit 31:8 – RESERVED
Steps for using SPI
Initialize SPI
Send Data
Receive Data
Code
Example 1
Using Explore Embedded Libraries