Difference between revisions of "Explore Robo"
| (8 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Hack it like a arduino or build on it like an AVR. Integrated DTMF and Motor driver, will help you build you're next superbot with ease! | Hack it like a arduino or build on it like an AVR. Integrated DTMF and Motor driver, will help you build you're next superbot with ease! | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | [[File:Cart add.png|right|link=https://www.exploreembedded.com/product/Explore%20Robo]] | |
{{#ev:youtube|aFyaYK5OJYU|680}} | {{#ev:youtube|aFyaYK5OJYU|680}} | ||
[[File:DSC08839.JPG|680px]] | [[File:DSC08839.JPG|680px]] | ||
| + | [[File:DSC01972 copy.jpg|680px]] | ||
| + | [[File:DSC01973 copy.jpg|680px]] | ||
[[File:Explore_Robo Parts.JPG|680px]] | [[File:Explore_Robo Parts.JPG|680px]] | ||
<gallery mode="packed-hover"> | <gallery mode="packed-hover"> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 49: | ||
=Mechanical= | =Mechanical= | ||
==Assembling the Robot== | ==Assembling the Robot== | ||
| + | ===Quick Video=== | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|AYSAGtPI3KU|600}} | ||
===Mounting the BO Motor with Clamps=== | ===Mounting the BO Motor with Clamps=== | ||
[[File:Robo Wheel mouting 7.JPG|framed|Attaching BO Clamps to BO Motor]] | [[File:Robo Wheel mouting 7.JPG|framed|Attaching BO Clamps to BO Motor]] | ||
| Line 98: | Line 102: | ||
=Downloads= | =Downloads= | ||
| − | ==[ | + | ==[https://github.com/ExploreEmbedded/ExploreRobo_Sample-Code/archive/master.zip Code]== |
==[http://exploreembedded.com/wiki/images/b/b4/SCHEMATIC_AVR_ROBO.pdf Robo_Board Schematic]== | ==[http://exploreembedded.com/wiki/images/b/b4/SCHEMATIC_AVR_ROBO.pdf Robo_Board Schematic]== | ||
| Line 104: | Line 108: | ||
==[http://exploreembedded.com/wiki/images/b/b2/Schematic_sensor_board.pdf Sensor Sheild Schematic ]== | ==[http://exploreembedded.com/wiki/images/b/b2/Schematic_sensor_board.pdf Sensor Sheild Schematic ]== | ||
==Bootloader: optiboot== | ==Bootloader: optiboot== | ||
| − | The Explore Robo uses optiboot. Find the modified source code here. | + | The Explore Robo uses optiboot. Find the modified source code [http://exploreembedded.com/wiki/images/1/15/Optiboot_ExploreRobo.zip here.] |
Fuse settings on Explore Robo: | Fuse settings on Explore Robo: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 115: | Line 119: | ||
[http://eleccelerator.com/fusecalc/fusecalc.php?chip=atmega8&LOW=FF&HIGH=DC&LOCKBIT=CF Fuse bit details] | [http://eleccelerator.com/fusecalc/fusecalc.php?chip=atmega8&LOW=FF&HIGH=DC&LOCKBIT=CF Fuse bit details] | ||
'''*Do not modify fuse bits unless you're sure of what you're doing!''' | '''*Do not modify fuse bits unless you're sure of what you're doing!''' | ||
| + | |||
=Programming= | =Programming= | ||
=====Using the Board with AVR Studio and Flashing with XploreFlash===== | =====Using the Board with AVR Studio and Flashing with XploreFlash===== | ||
| Line 127: | Line 132: | ||
Step 4: Follow the steps on images below to flash the board. | Step 4: Follow the steps on images below to flash the board. | ||
| − | <gallery "packed-hover"> | + | <gallery mode="packed-hover"> |
| − | File:CP2102_Device_Manager.JPG | + | File:CP2102_Device_Manager.JPG|Check for COM port |
| − | File:XploreFlash_Detect_MCU.JPG | + | File:XploreFlash_Detect_MCU.JPG|Hit Detect MCU |
| − | File:XploreFlash_Flash_Verify.jpg | + | File:XploreFlash_Flash_Verify.jpg|Browse file and Flash |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Note: The GUI software will require [http://www.microsoft.com/en-gb/download/details.aspx?id=16614 .NET framework] 2.0 or later please download and install it. | Note: The GUI software will require [http://www.microsoft.com/en-gb/download/details.aspx?id=16614 .NET framework] 2.0 or later please download and install it. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
===Using the Board with Arduino Software=== | ===Using the Board with Arduino Software=== | ||
{{Box|type=l_green_light|text=-> | {{Box|type=l_green_light|text=-> | ||
| Line 158: | Line 164: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | <gallery> | + | ====Steps==== |
| + | <gallery mode="packed-hover"> | ||
File:Detect Board.png|1.The board shows up in arduino software | File:Detect Board.png|1.The board shows up in arduino software | ||
File:CP2102 Device Manager.JPG|2.Check exact COM port | File:CP2102 Device Manager.JPG|2.Check exact COM port | ||
| Line 166: | Line 173: | ||
====Arduino Examples==== | ====Arduino Examples==== | ||
*[[Computer controlled Robot with Arduino]] | *[[Computer controlled Robot with Arduino]] | ||
| + | *[[Mobile controlled Robot with Arduino]] | ||
{{DISQUS}} | {{DISQUS}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:19, 10 September 2015
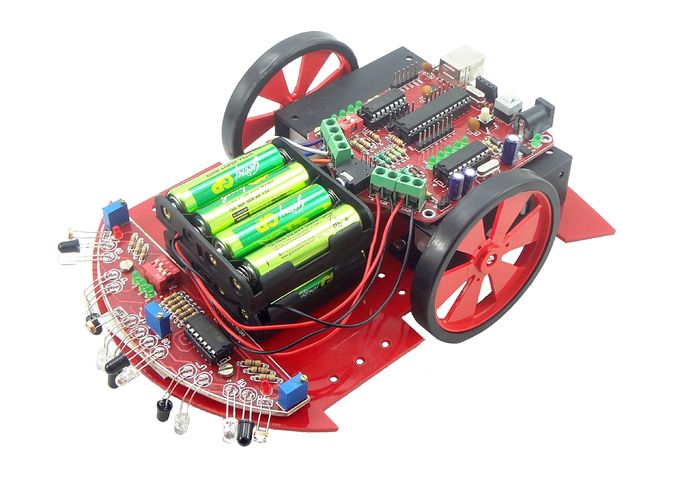
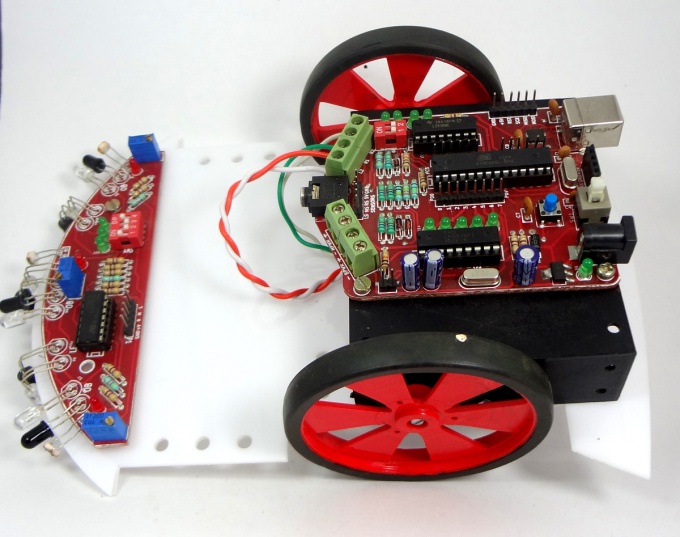
- Robotics board based on Atmega8 MCU.
- Sensor shield to make line follower, light follower and obstacle avoidance robot.
- Inbuilt DTMF decoder (MT8870) to make a Mobile controlled Robot
- USB to UART convertor (CP2102) for communicating with computer, make a computer controlled Robot.
- MCU with bootloader, no external programmer required.
- Compatible with Arduino Software.
- Electronics
- Robotics Board Based on Atmega8, with L293D driver and MT8870 DTMF Decoder
- Sensor Sheild for line, light and obstacle detecting robots
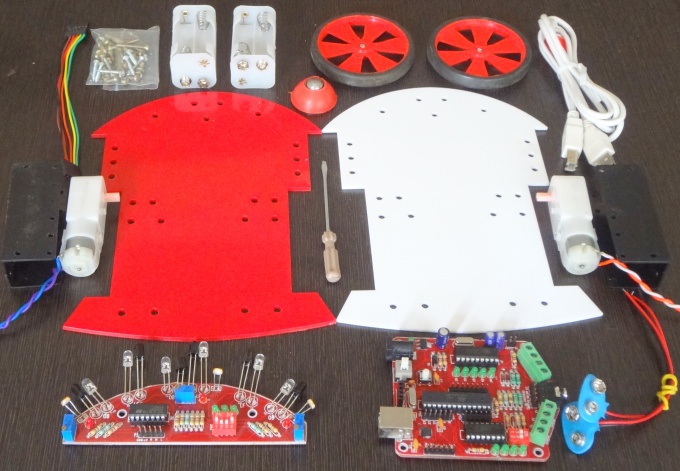
- Mechanical
- Chasis(Red and White Basis)
- BO Motor Clamps
- DC BO Motors 150 RPM
- Wheels x2
- Castor Wheel
- Screws
- Battery Holder x2
- Other
- USB Cable
- 5 Pin Sensor cable
Mechanical
Assembling the Robot
Quick Video
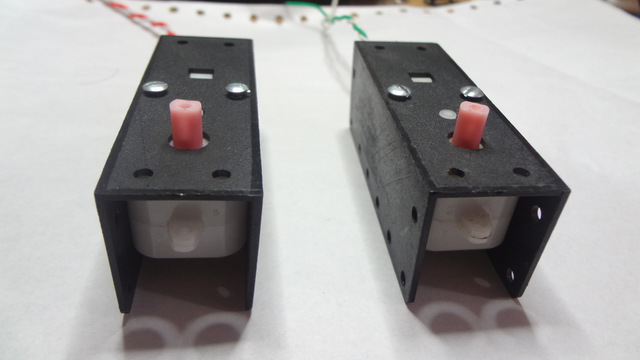
Mounting the BO Motor with Clamps
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
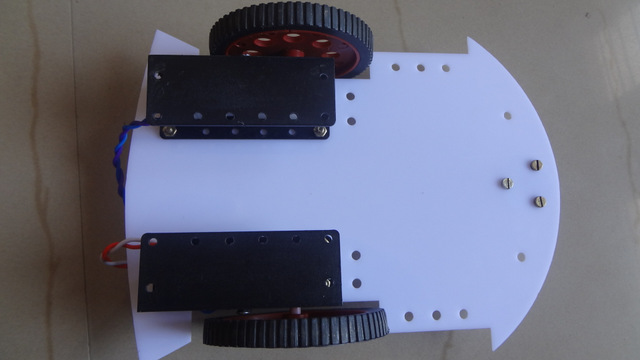
Attaching Wheels to chasis
Assembling the Base
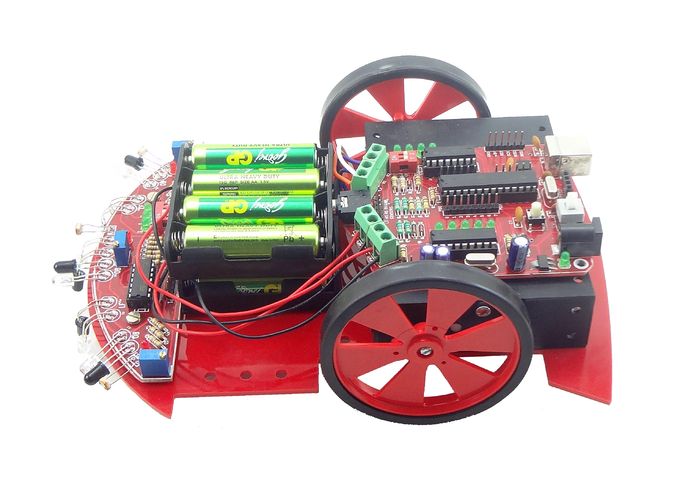
Electronics
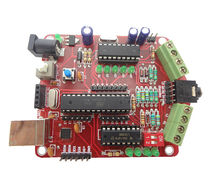
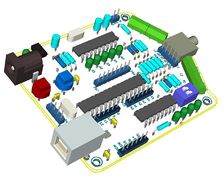
Robo Controller Board
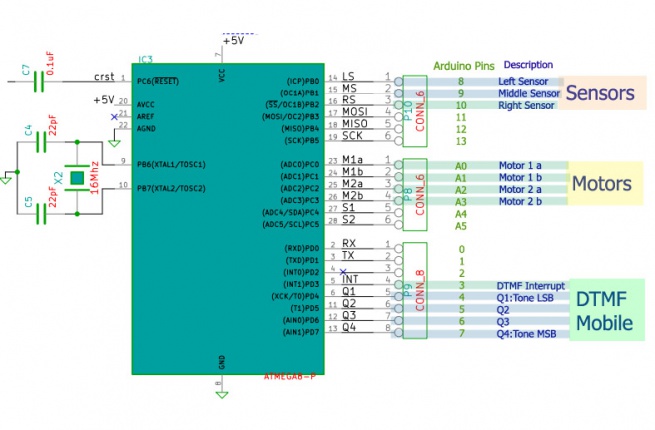
- The Robo Board: This is the heart of the robot. The board has following ICs
- Motor Driver: A L293D Motor driver on board is used to control the two driving motors of the Robot
- DTMF Decoder: A MT8870 or compatible IC is used to convert DTMF mobile tones to digits, which helps in making Mobile controlled Robot
- Microcontroller: The board feature a Atmega8 (Atmega328 can also be used) controller. Figure below shows the way in which various units are connected to the microcontroller.
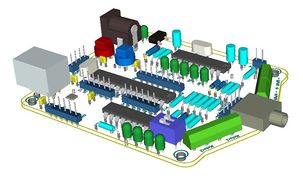
Sensor Sheild
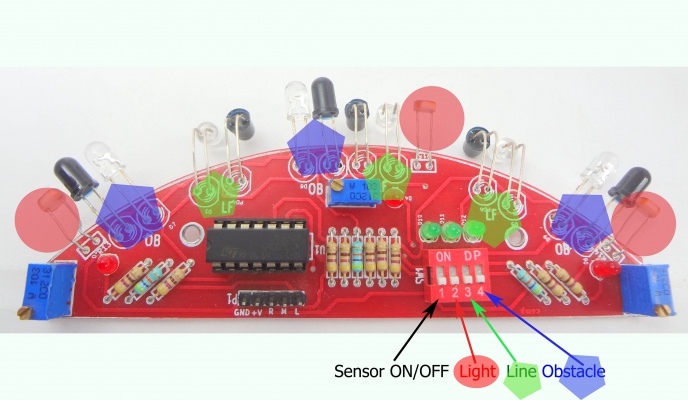
The sensor sheild has a comparator IC that gives logical high when any of the right, Middle or left sensors are detected.The sensor sheild has following sensors:
- 3 IR pairs for line following
- 3 IR Pairs for obstacle avoidance
- 3 Light Dependent Resistors
Notice the DIP switch shown in the image below, it used to select the above three sensor options.
Downloads
Code
Robo_Board Schematic
Sensor Sheild Schematic
Bootloader: optiboot
The Explore Robo uses optiboot. Find the modified source code here. Fuse settings on Explore Robo:
L FUSE H FUSE LOCK 0xFF 0xDC 0xCF Fuse bit details *Do not modify fuse bits unless you're sure of what you're doing!
Programming
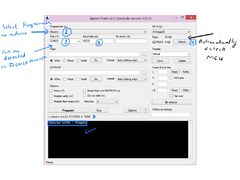
Using the Board with AVR Studio and Flashing with XploreFlash
Step 1: Xplore flash is based on various opensource software, it requires avrdude. Avrdude is part of WinAVR GCC complier. Download and install it.Step 2:To connect Development board with computer USB driver is required. Windows USB to UART Drivers for CP2102
- For Other Operating system please download from Silicon Labs website.
Step 3: Download and install XploreFlash GUI. (XploreFlash GUI is based on AVRDUDESS)
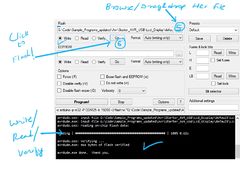
Step 4: Follow the steps on images below to flash the board.
Check for COM port
Hit Detect MCU
Browse file and Flash
Note: The GUI software will require .NET framework 2.0 or later please download and install it.
Using the Board with Arduino Software
->For the board to appear in the arduino software add the following lines in the boards.txt file.
File location:e.g: C:\Program Files\Arduino\hardware\arduino#################################################
atmega8.name=Explore Robo w/ ATmega8
atmega8.upload.protocol=arduino
atmega8.upload.maximum_size=7168
atmega8.upload.speed=19200
atmega8.bootloader.low_fuses=0xdf
atmega8.bootloader.high_fuses=0xca
atmega8.bootloader.path=atmega8
atmega8.bootloader.file=ATmegaBOOT-prod-firmware-2009-11-07.hex
atmega8.bootloader.unlock_bits=0x3F
atmega8.bootloader.lock_bits=0x0F
atmega8.build.mcu=atmega8
atmega8.build.f_cpu=16000000L
atmega8.build.core=arduino
atmega8.build.variant=standard
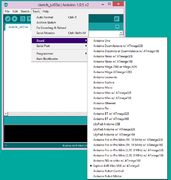
Steps
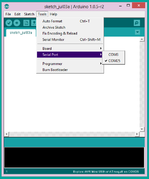
1.The board shows up in arduino software
2.Check exact COM port
3.Select the COM port.
Arduino Examples