Difference between revisions of "ADC Using PIC16F877A"
| (19 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
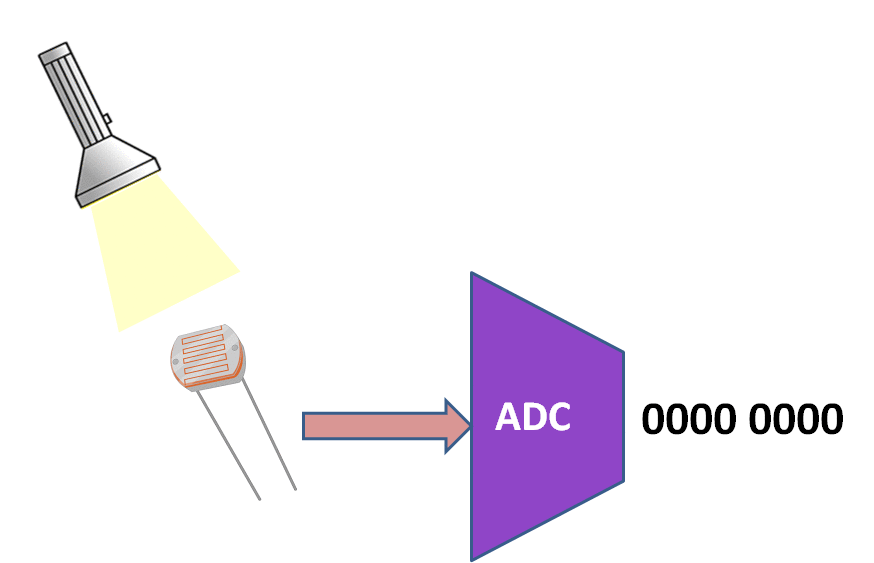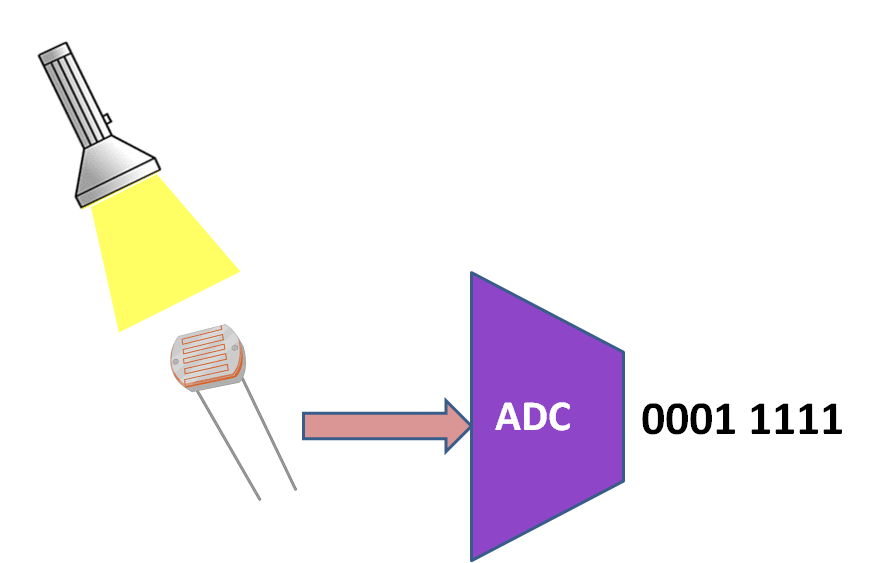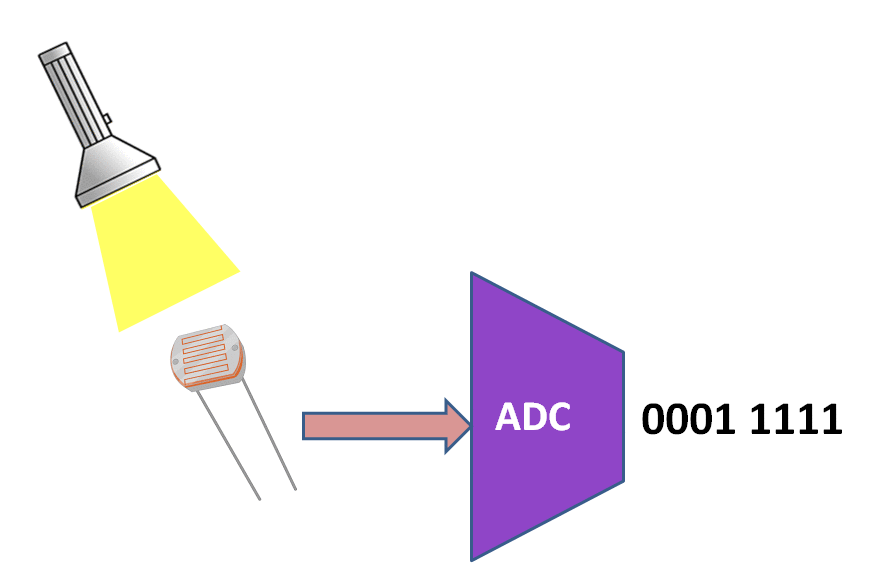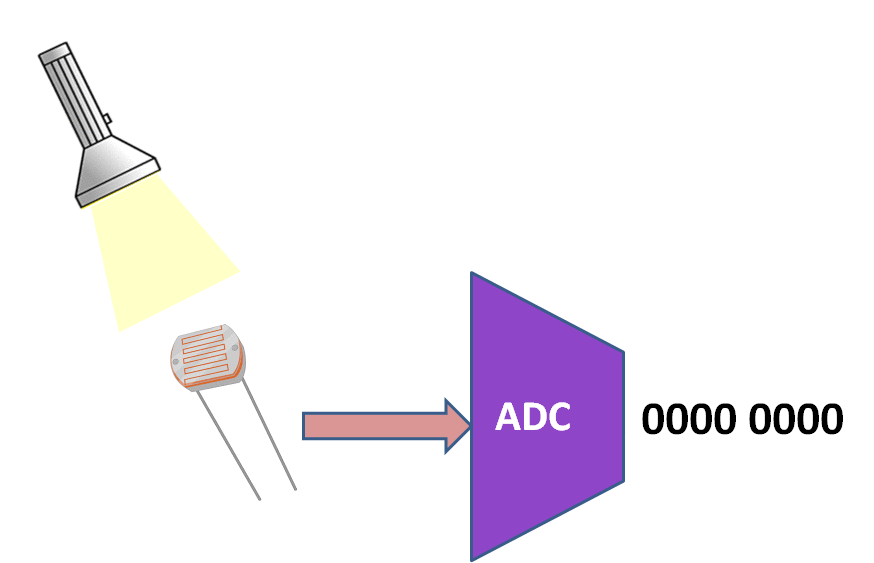
In this tutorial we are going to discuss how to use the inbuilt PIC16f877A ADC.<br> | In this tutorial we are going to discuss how to use the inbuilt PIC16f877A ADC.<br> | ||
We will be reading the ADC values from chanel Zero and transmitted on UART at 9600 baudrate. | We will be reading the ADC values from chanel Zero and transmitted on UART at 9600 baudrate. | ||
| − | [[FILE: | + | [[FILE:ADC.gif]] |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
=PIC16F877A ADC pins= | =PIC16F877A ADC pins= | ||
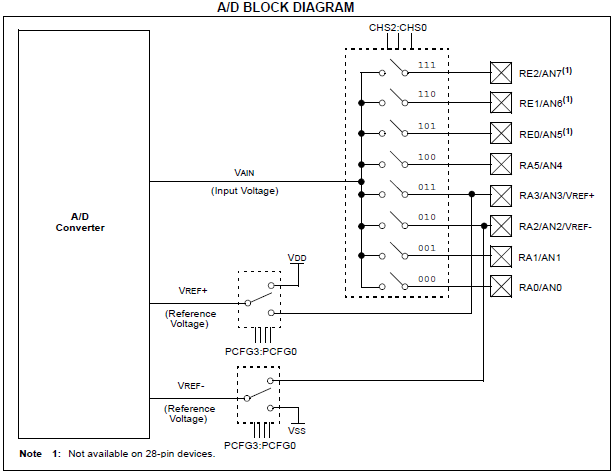
| − | PIC16F877A has inbuilt | + | PIC16F877A has an inbuilt 10 bit Successive Approximation ADC which is multiplexed among 8 input pins.<br> |
| + | The A/D module has high and low-voltage reference input that is software selectable to some combination of VDD, VSS, RA2 or RA3. | ||
| + | With 5v as the Vref the resolution of Pic16f877a ADC can be determined as below: | ||
| + | $$resolution of ADC = Vref/(2^{10}-1) = 5/1023 =0.004887 = 4.887mv$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | The below table shows the ADC input pins multiplexed with other GPIO pins.<br> | ||
| + | The ADC pin can be enabled by configuring the corresponding ACON1 register.<br> | ||
| + | When the ADC function is selected for a pin ,then other Digital signals are disconnected from the ADC input pins. | ||
{| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
|-class="info" | |-class="info" | ||
!Adc Channel || Pic16f877a Pin || Pin Function | !Adc Channel || Pic16f877a Pin || Pin Function | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |0|| | + | |0|| RA0 || AN0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |1|| | + | |1|| RA1 || AN1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |2|| | + | |2|| RA2 || AN2/VREF- |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |3|| | + | |3|| RA3 || AN3/VREF+ |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |4|| | + | |4|| RA5 || AN4 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |2|| | + | |2|| RE0 || AN5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |3|| | + | |3|| RE1 || AN6 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |4|| | + | |4|| RE2 || AN7 |
|}<br><br> | |}<br><br> | ||
| + | =ADC Registers= | ||
| + | The below table shows the registers associated with PIC16F877A ADC.<br> | ||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | !Register || Description | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ADCON0|| Used to Turn ON the ADC, Select the Sampling Freq and also Start the conversion. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ADCON1|| Used to configure the gpio pins for ADC | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ADRESH|| Holds the higher byte of ADC result | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ADRESL|| Holds the lower byte of ADC result | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | Now lets see how to configure the individual registers for UART communication. | ||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | |ADCON0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |7 || 6 || 5 || 4 || 3 || 2 || 1 || 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ADCS1 || ADCS0 || CHS2 || CHS1 || CHS0 || GO/DONE || — || ADON | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <b>ADCS2-ADCS0:</b>A/D Conversion Clock Select bits | ||
| + | [[FILE:adc_Freq_Select.png]] | ||
| + | <b>CHS2-CHS0:</b>Analog Channel Select bits<br> | ||
| + | 000 = Channel 0 (AN0)<br> | ||
| + | 001 = Channel 1 (AN1)<br> | ||
| + | 010 = Channel 2 (AN2)<br> | ||
| + | 011 = Channel 3 (AN3)<br> | ||
| + | 100 = Channel 4 (AN4)<br> | ||
| + | 101 = Channel 5 (AN5)<br> | ||
| + | 110 = Channel 6 (AN6)<br> | ||
| + | 111 = Channel 7 (AN7) | ||
| + | <b>GO/DONE:</b> A/D Conversion Status bit<br> | ||
| + | When ADON = 1:<br> | ||
| + | 1 = A/D conversion in progress (setting this bit starts the A/D conversion which is automatically cleared by hardware when the A/D conversion is complete)<br> | ||
| + | 0 = A/D conversion not in progress | ||
| + | <b>ADON:</b> A/D On bit<br> | ||
| + | 1 = A/D converter module is powered up<br> | ||
| + | 0 = A/D converter module is shut-off and consumes no operating current | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | |ADCON1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |7 || 6 || 5 || 4 || 3 || 2 || 1 || 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ADFM || ADCS2 || — || — || PCFG3 || PCFG2 || PCFG1 || PCFG0 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <b>ADFM:</b> A/D Result Format Select bit<br> | ||
| + | 1 = Right justified. Six (6) Most Significant bits of ADRESH are read as ‘0’.<br> | ||
| + | 0 = Left justified. Six (6) Least Significant bits of ADRESL are read as ‘0’. | ||
| + | [[FILE:Adc_Result_Justification.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>ADCS2:</b> A/D Conversion Clock Select bit<br> | ||
| + | Check ADCS1:ADCS0 of ADCON0 register. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>PCFG3-PCFG0:</b> A/D Port Configuration Control bits | ||
| + | [[FILE:Adc_pin_config.png]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[FILE:PicAdcBlockDiagram.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Hardware Connections= | ||
| + | [[File:ADCExample bb.png|none]] | ||
=Code= | =Code= | ||
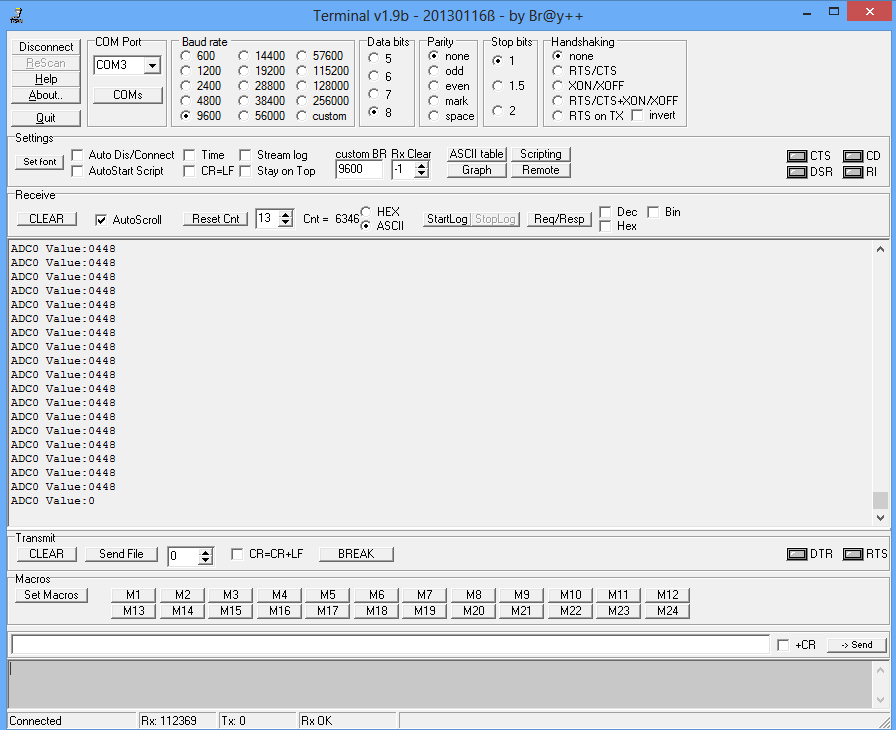
| − | Below is the sample code to read the ADC value of channel0 and | + | Below is the sample code to read the ADC value of channel0 and send it on UART at 9600 baud rate.<br> |
| − | + | <html> | |
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/051cc0daca8d1cafcf662449a5fe271a.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Using ExploreEmbedded Libraries= | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<script src="https://gist.github.com/sharanago/83a7537783383c8130576a79a493c87a.js"></script> | <script src="https://gist.github.com/sharanago/83a7537783383c8130576a79a493c87a.js"></script> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 122: | ||
[[File:Pic16f877aADC01.PNG]]<br><br> | [[File:Pic16f877aADC01.PNG]]<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Downloads= | ||
| + | Download the complete project folder from the below link:<br> | ||
| + | [https://github.com/ExploreEmbedded/Pic16f877a_ExploreUltraPicDevKit/archive/master.zip Hardware design Files and Code Library] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here! | ||
| + | {{DISQUS}} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:17, 24 May 2016
In this tutorial we are going to discuss how to use the inbuilt PIC16f877A ADC.
We will be reading the ADC values from chanel Zero and transmitted on UART at 9600 baudrate.
Contents
PIC16F877A ADC pins
PIC16F877A has an inbuilt 10 bit Successive Approximation ADC which is multiplexed among 8 input pins.
The A/D module has high and low-voltage reference input that is software selectable to some combination of VDD, VSS, RA2 or RA3.
With 5v as the Vref the resolution of Pic16f877a ADC can be determined as below:
$$resolution of ADC = Vref/(2^{10}-1) = 5/1023 =0.004887 = 4.887mv$$
The below table shows the ADC input pins multiplexed with other GPIO pins.
The ADC pin can be enabled by configuring the corresponding ACON1 register.
When the ADC function is selected for a pin ,then other Digital signals are disconnected from the ADC input pins.
| Adc Channel | Pic16f877a Pin | Pin Function |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | RA0 | AN0 |
| 1 | RA1 | AN1 |
| 2 | RA2 | AN2/VREF- |
| 3 | RA3 | AN3/VREF+ |
| 4 | RA5 | AN4 |
| 2 | RE0 | AN5 |
| 3 | RE1 | AN6 |
| 4 | RE2 | AN7 |
ADC Registers
The below table shows the registers associated with PIC16F877A ADC.
| Register | Description |
|---|---|
| ADCON0 | Used to Turn ON the ADC, Select the Sampling Freq and also Start the conversion. |
| ADCON1 | Used to configure the gpio pins for ADC |
| ADRESH | Holds the higher byte of ADC result |
| ADRESL | Holds the lower byte of ADC result |
Now lets see how to configure the individual registers for UART communication.
| ADCON0 | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| ADCS1 | ADCS0 | CHS2 | CHS1 | CHS0 | GO/DONE | — | ADON |
ADCS2-ADCS0:A/D Conversion Clock Select bits
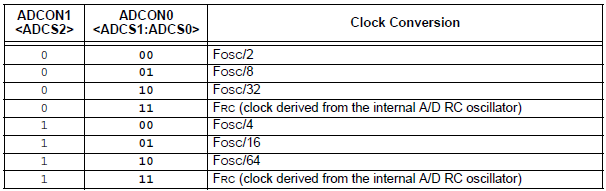
CHS2-CHS0:Analog Channel Select bits
000 = Channel 0 (AN0)
001 = Channel 1 (AN1)
010 = Channel 2 (AN2)
011 = Channel 3 (AN3)
100 = Channel 4 (AN4)
101 = Channel 5 (AN5)
110 = Channel 6 (AN6)
111 = Channel 7 (AN7)
GO/DONE: A/D Conversion Status bit
When ADON = 1:
1 = A/D conversion in progress (setting this bit starts the A/D conversion which is automatically cleared by hardware when the A/D conversion is complete)
0 = A/D conversion not in progress
ADON: A/D On bit
1 = A/D converter module is powered up
0 = A/D converter module is shut-off and consumes no operating current
| ADCON1 | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| ADFM | ADCS2 | — | — | PCFG3 | PCFG2 | PCFG1 | PCFG0 |
ADFM: A/D Result Format Select bit
1 = Right justified. Six (6) Most Significant bits of ADRESH are read as ‘0’.
0 = Left justified. Six (6) Least Significant bits of ADRESL are read as ‘0’.
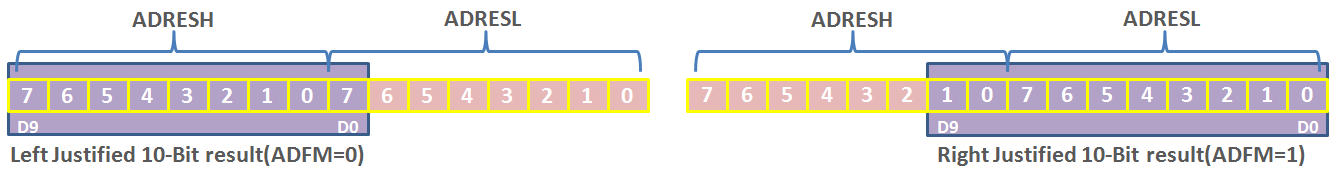
ADCS2: A/D Conversion Clock Select bit
Check ADCS1:ADCS0 of ADCON0 register.
PCFG3-PCFG0: A/D Port Configuration Control bits
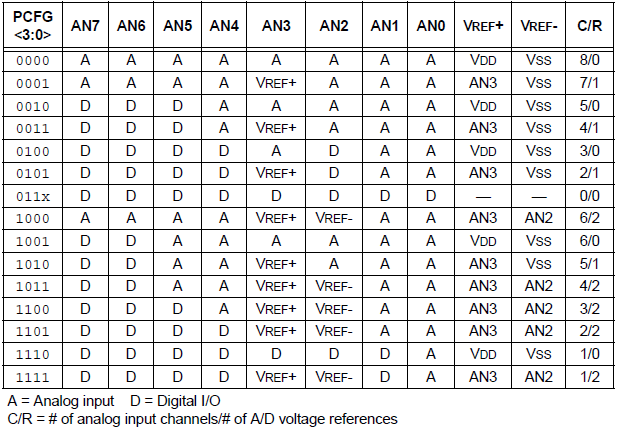
Hardware Connections
Code
Below is the sample code to read the ADC value of channel0 and send it on UART at 9600 baud rate.
Using ExploreEmbedded Libraries
Downloads
Download the complete project folder from the below link:
Hardware design Files and Code Library
Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here!