Difference between revisions of "Interfacing LCD with PIC16F877A 4-bit mode"
(Created page with "Category:PIC Tutorials") |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:PIC Tutorials]] | [[Category:PIC Tutorials]] | ||
| + | In this tutorial, we are going to see how to interface a 2x16 LCD with PIC16f877a in 4-bit mode. | ||
| + | As per the name the 2x16 has 2 lines with 16 chars on each line. It supports all the ASCII chars and is basically used for displaying the alphanumeric characters. Here each character is displayed in a matrix of 5x7 pixels. | ||
| + | Apart from alphanumeric chars it also provides the provision to display the custom characters by creating the pattern. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =LCD UNIT= | ||
| + | Let us look at a pin diagram of a commercially available LCD like '''JHD162''' which uses a '''HD44780''' controller and then describe its operation. | ||
| + | [[FILE:Pic16f877aLcdInterface.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | | Pin Number || Symbol || Pin Function | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |1 || VSS ||Ground | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2|| VCC || +5v | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 3 || VEE || Contrast adjustment (VO) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 4 || RS || Register Select. 0:Command, 1: Data | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 5 || R/W || Read/Write, R/W=0: Write & R/W=1: Read | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 6|| EN || Enable. Falling edge triggered | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 7 || D0 || Data Bit 0 (Not used in 4-bit operation) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 8 || D1 || Data Bit 1 (Not used in 4-bit operation) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 9 || D2 || Data Bit 2 (Not used in 4-bit operation) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 10 || D3 || Data Bit 3 (Not used in 4-bit operation) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 11 || D4 || Data Bit 4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 12 || D5 || Data Bit 5 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 13 || D6 || Data Bit 6 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 14 || D7 || Data Bit 7/Busy Flag | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 15 || A/LED+ || Back-light Anode(+) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 16 || K/LED- || Back-Light Cathode(-) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Apart from the voltage supply connections the important pins from the programming perspective are the data lines(8-bit Data bus), Register select, Read/Write and Enable pin.<br><br> | ||
| + | <b>Data Bus:</b> As shown in the above figure and table, an alphanumeric LCD has a 8-bit data bus referenced as D0-D7. | ||
| + | As it is a 8-bit data bus, we can send the data/cmd to LCD in bytes. It also provides the provision to send the the data/cmd in chunks of 4-bit, which is used when there are limited number of GPIO lines on the microcontroller.<br><br> | ||
| + | <b>Register Select(RS):</b> The LCD has two register namely a Data register and Command register. Any data that needs to be displayed on the LCD has to be written to the data register of LCD. Command can be issued to LCD by writing it to Command register of LCD. | ||
| + | This signal is used to differentiate the data/cmd received by the LCD.<br> | ||
| + | If the RS signal is <b>LOW</b> then the LCD interprets the 8-bit info as <b>Command</b> and writes it <b>Command register</b> and performs the action as per the command.<br> | ||
| + | If the RS signal is <b>HIGH</b> then the LCD interprets the 8-bit info as <b>data</b> and copies it to <b>data register</b>. After that the LCD decodes the data for generating the 5x7 pattern and finally displays on the LCD.<br><br> | ||
| + | <b>Read/Write(RW):</b> This signal is used to write the data/cmd to LCD and reads the busy flag of LCD. | ||
| + | For write operation the RW should be <b>LOW</b> and for read operation the R/W should be <b>HIGH</b>.<br><br> | ||
| + | <b>Enable(EN):</b> This pin is used to send the enable trigger to LCD. | ||
| + | After sending the data/cmd, Selecting the data/cmd register, Selecting the Write operation. An HIGH-to-LOW pulse has to be sent on this enable pin which will latch the info into the LCD register and triggers the LCD to act accordingly. | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Schematic= | ||
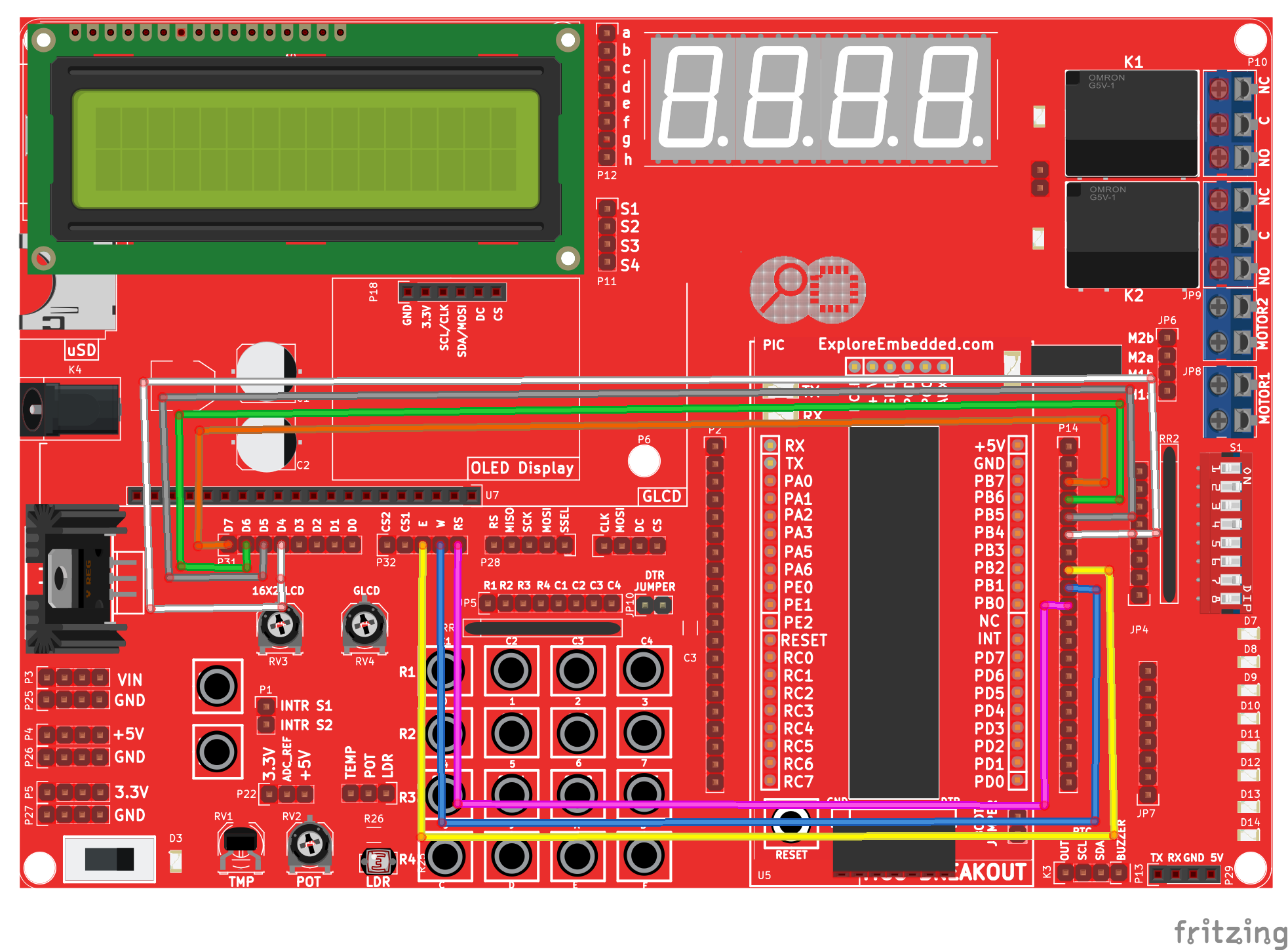
| + | Below schematic shows the minimum connection required for interfacing the LCD with the microcontroller.<br> | ||
| + | As we are interfacing the LCD in 4-bit mode, only the higher 4 data lines are used as the data bus. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Port Connection= | ||
| + | This section shows how to configure the GPIO for interfacing the LCD.<br> | ||
| + | The below configuration is as per the above schematic. You can connect the LCD to any of the PORT pins available on your boards and update this section accordingly | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/d5971646ec066d3c13a194bbf3f22576.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =LCD Operation= | ||
| + | In this section, we are going to see how to send the data/cmd to the LCD along with the timing diagrams. | ||
| + | First let's see the timing diagram for sending the data and the command signals(RS,RW,EN), accordingly, we write the algorithm and finally the code. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Timing Diagram=== | ||
| + | The below image shows the timing diagram for sending the data to the LCD.<br> | ||
| + | As shown in the timing diagram the data is written after sending the RS and RW signals. It is still ok to send the data before these signals.<br> | ||
| + | The only important thing is the data should be available on the databus before generating the High-to-Low pulse on EN pin. | ||
| + | [[File:LCD CmdWrite.jpg|figure: command write]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Steps for Sending Command:=== | ||
| + | *step1: Send the I/P command to LCD. | ||
| + | *step2: Select the Control Register by making RS low. | ||
| + | *step3: Select Write operation making RW low. | ||
| + | *step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us. | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/a1d184abe71193a035ea6778f9d9214b.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Steps for Sending Data:=== | ||
| + | *step1: Send the character to LCD. | ||
| + | *step2: Select the Data Register by making RS high. | ||
| + | *step3: Select Write operation making RW low. | ||
| + | *step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us. | ||
| + | The timings are similar as above only change is that '''RS''' is made high for selecting Data register. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/c8b9677f9e1851014933d996951bbe22.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Hardware Connections= | ||
| + | [[File:LCD 16X2 4bit bb.png|none]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Code Examples = | ||
| + | Here is the complete code for displaying the data on 2x16 LCD in 4-bit mode. | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/9ebcab47701b9faa928f4e54615af779.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Using Explore Embedded Libraries := | ||
| + | In the above tutorial we just discussed how to interface 2x16Lcd in 4-bit mode.<br> | ||
| + | Once you know the working of lcd, you can directly use the ExploreEmbedded libraries to play around with your LCD.<br> | ||
| + | For that you need to include the lcd.c/lcd.h and the associated files(delay/stdutils).<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The below sample code shows how to use the already available LCD functions. | ||
| + | ==LCD 1x16== | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/sharanago/1c42e5b6253260bd8ead3d061d7a627a.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==LCD 2x16== | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/sharanago/bf69e20dc277fda3f562779fbe2acbfe.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==LCD 4x20== | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/sharanago/5a15fb1ad85c3b91271ceaa453385410.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[FILE:01LCD 4bit.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Downloads= | ||
| + | Download the complete project folder from the below link: <br> | ||
| + | [https://github.com/ExploreEmbedded/Pic16f877a_ExploreUltraPicDevKit/archive/master.zip Hardware design Files and Code Library] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Have an opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here! | ||
| + | {{DISQUS}} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:36, 27 August 2016
In this tutorial, we are going to see how to interface a 2x16 LCD with PIC16f877a in 4-bit mode. As per the name the 2x16 has 2 lines with 16 chars on each line. It supports all the ASCII chars and is basically used for displaying the alphanumeric characters. Here each character is displayed in a matrix of 5x7 pixels. Apart from alphanumeric chars it also provides the provision to display the custom characters by creating the pattern.
Contents
LCD UNIT
Let us look at a pin diagram of a commercially available LCD like JHD162 which uses a HD44780 controller and then describe its operation.
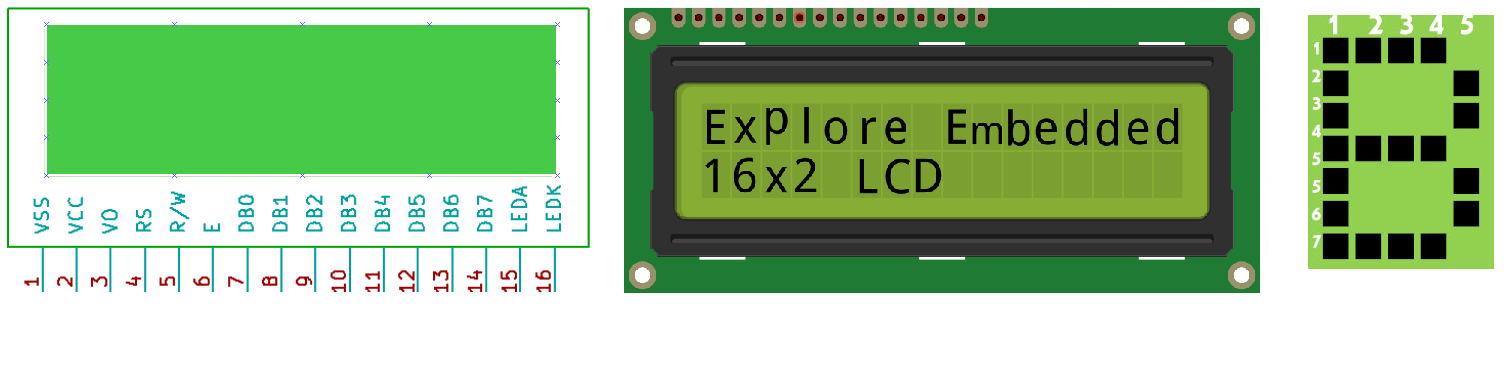
| Pin Number | Symbol | Pin Function |
| 1 | VSS | Ground |
| 2 | VCC | +5v |
| 3 | VEE | Contrast adjustment (VO) |
| 4 | RS | Register Select. 0:Command, 1: Data |
| 5 | R/W | Read/Write, R/W=0: Write & R/W=1: Read |
| 6 | EN | Enable. Falling edge triggered |
| 7 | D0 | Data Bit 0 (Not used in 4-bit operation) |
| 8 | D1 | Data Bit 1 (Not used in 4-bit operation) |
| 9 | D2 | Data Bit 2 (Not used in 4-bit operation) |
| 10 | D3 | Data Bit 3 (Not used in 4-bit operation) |
| 11 | D4 | Data Bit 4 |
| 12 | D5 | Data Bit 5 |
| 13 | D6 | Data Bit 6 |
| 14 | D7 | Data Bit 7/Busy Flag |
| 15 | A/LED+ | Back-light Anode(+) |
| 16 | K/LED- | Back-Light Cathode(-) |
Apart from the voltage supply connections the important pins from the programming perspective are the data lines(8-bit Data bus), Register select, Read/Write and Enable pin.
Data Bus: As shown in the above figure and table, an alphanumeric LCD has a 8-bit data bus referenced as D0-D7.
As it is a 8-bit data bus, we can send the data/cmd to LCD in bytes. It also provides the provision to send the the data/cmd in chunks of 4-bit, which is used when there are limited number of GPIO lines on the microcontroller.
Register Select(RS): The LCD has two register namely a Data register and Command register. Any data that needs to be displayed on the LCD has to be written to the data register of LCD. Command can be issued to LCD by writing it to Command register of LCD.
This signal is used to differentiate the data/cmd received by the LCD.
If the RS signal is LOW then the LCD interprets the 8-bit info as Command and writes it Command register and performs the action as per the command.
If the RS signal is HIGH then the LCD interprets the 8-bit info as data and copies it to data register. After that the LCD decodes the data for generating the 5x7 pattern and finally displays on the LCD.
Read/Write(RW): This signal is used to write the data/cmd to LCD and reads the busy flag of LCD.
For write operation the RW should be LOW and for read operation the R/W should be HIGH.
Enable(EN): This pin is used to send the enable trigger to LCD.
After sending the data/cmd, Selecting the data/cmd register, Selecting the Write operation. An HIGH-to-LOW pulse has to be sent on this enable pin which will latch the info into the LCD register and triggers the LCD to act accordingly.
Schematic
Below schematic shows the minimum connection required for interfacing the LCD with the microcontroller.
As we are interfacing the LCD in 4-bit mode, only the higher 4 data lines are used as the data bus.
Port Connection
This section shows how to configure the GPIO for interfacing the LCD.
The below configuration is as per the above schematic. You can connect the LCD to any of the PORT pins available on your boards and update this section accordingly
LCD Operation
In this section, we are going to see how to send the data/cmd to the LCD along with the timing diagrams. First let's see the timing diagram for sending the data and the command signals(RS,RW,EN), accordingly, we write the algorithm and finally the code.
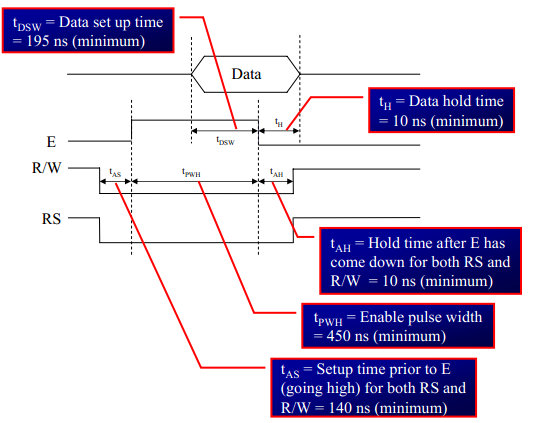
Timing Diagram
The below image shows the timing diagram for sending the data to the LCD.
As shown in the timing diagram the data is written after sending the RS and RW signals. It is still ok to send the data before these signals.
The only important thing is the data should be available on the databus before generating the High-to-Low pulse on EN pin.
Steps for Sending Command:
- step1: Send the I/P command to LCD.
- step2: Select the Control Register by making RS low.
- step3: Select Write operation making RW low.
- step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us.
Steps for Sending Data:
- step1: Send the character to LCD.
- step2: Select the Data Register by making RS high.
- step3: Select Write operation making RW low.
- step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us.
The timings are similar as above only change is that RS is made high for selecting Data register.
Hardware Connections
Code Examples
Here is the complete code for displaying the data on 2x16 LCD in 4-bit mode.
Using Explore Embedded Libraries :
In the above tutorial we just discussed how to interface 2x16Lcd in 4-bit mode.
Once you know the working of lcd, you can directly use the ExploreEmbedded libraries to play around with your LCD.
For that you need to include the lcd.c/lcd.h and the associated files(delay/stdutils).
The below sample code shows how to use the already available LCD functions.
LCD 1x16
LCD 2x16
LCD 4x20
Downloads
Download the complete project folder from the below link:
Hardware design Files and Code Library
Have an opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here!