AVR C Library
Contents
Introduction
Overview:
This manual is designed to help embedded programmers and students, rapidly exploit the Avr(Atmega)-Controller for embedded applications. This manual has been targeted at embedded systems programmers and Students who have basic knowledge of Avr(Atmega32/Avr) architecture and C-Language.
This manual provides the reference to all the library functions which are grouped under respective.c file. The .c files convention is as per the peripherals. The peripherals (lcd, keypad..) are connected to default PORTs which can be connect to required PORTs by changing the #defines .
Reference:
It is recommended to go through the below reference documents and datasheets before interfacing any peripherals.
- The Avr Microcontroller and Embedded Systems by Muhammad Ali Mazidi.
- Atmega32 DataSheet.
- Embedded C by Michael J Pont .
- Any of the 16x2 lcd datasheet.
- RTC-DS1307 from Dallas Semiconductors.
Feedback:
Suggestions for additions and improvements in code and documentation are always welcome. Please send your feedback via e-mail to feedback@xplorelabz.com
Disclaimer:
The libraries have been tested for Atmega16 on different development boards. We strongly believe that the library works on any Atmega boards. However, Xplore Labz disclaims any kind of hardware failure resulting out of usage of libraries, directly or indirectly. Documentation may be subject to change without prior notice.
The usage of tools and software demonstrated in the document are for educational purpose only, all rights pertaining to these belong to the respective owners. Users must ensure license terms are adhered to, for any use of the demonstrated software.
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE: The library code in this document is licensed under GNU General Public License (GPL) Copyright (C) 2012. Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies of this license document, but changing it is not allowed. Since the library is licensed free of charge, there is no warranty for the libraries and the entire risk of the quality and performance is with the user.
Errors and omissions should be reported to feedback@xplorelabz.com
ADC
Avr ADC library
- Filename: adc.c
- Controller: Atmega8/16/32/128
- Oscillator: 11.0592 MHz
- Author: XploreLabz
- website: www.xplorelabz.com
- Reference:Atmega32 dataSheet
#include<avr/io.h> #include <util/delay.h> #include "adc.h"
ADC_Init()
- Description :This function initializes the ADC control registers
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value: none
void ADC_Init() { ADCSRA=0x81; //Enable ADC , sampling freq=osc_freq/2 ADMUX=0x00; //Result right justified, select channel zero }
ADC_StartConversion()
- Description :This function does the ADC conversioin for the Selected Channel and returns the converted 10bit result
- I/P Arguments: char(channel number)
- Return value : int(10 bit ADC result)
unsigned int ADC_StartConversion(unsigned char channel) { ADMUX=channel; _delay_ms(5); ADCSRA=0xc1; while((ADCSRA & (1<<ADIF)==0); return(ADCW); }
LCD_8_bit Mode
AVR LCD library for 8-bit mode
- Filename: lcd_8_bit.c
- Controller: Atmega Family(8,16,32,64,128)
- Oscillator: 11.0592 MHz
- Author: XploreLabz
- website: www.xplorelabz.com
Note:
- Pin connection for LCD display in 8-bit mode is as shown below.By default the LCD is connected to PORTB(databus) and PORTD(controlbus).
- The code can be modified to connect the LCD to any of the PORTs by changing the "#define".
- io.h contains the defnition of all ports and SFRs delay.h contains the in built delay routines(us and ms routines).
#include <avr\io.h> #include <util\delay.h> #include "lcd.h" #define databus_direction DDRC // LCD databus Direction Configuration #define controlbus_direction DDRD // LCD Control bus Direction Configuration #define databus PORTC // LCD databus connected to PORTB #define control_bus PORTD // LCD Control bus connected to PORTD #define rs 5 // Register select pin connected 6th bit(D5) Control bus #define rw 6 // Read Write pin connected to 7th bit(D6) Control bus #define en 7 // Enable pin connected to 8th bit(D7) Control bus /* 16x2 LCD Specification */ #define LCDMaxLines 2 #define LCDMaxChars 16 #define LineOne 0x80 #define LineTwo 0xc0 #define BlankSpace ' '
LCD_Init()
- Description :This function is used to initialize the lcd in 8-bit mode
- Function name: LCD_Init()
- I/P Arguments: none.
- Return value : none
void LCD_Init() { _delay_ms(50); databus_direction = 0xff; // Configure both databus and controlbus as output controlbus_direction = 0xff; LCD_CmdWrite(0x38); // LCD 2lines, 5*7 matrix LCD_CmdWrite(0x0E); // Display ON cursor ON LCD_CmdWrite(0x01); // Clear the LCD LCD_CmdWrite(0x80); // Move the Cursor to First line First Position }
LCD_Clear()
- Description :This function clears the LCD and moves the cursor to first Position
- I/P Arguments: none.
- Return value : none
void LCD_Clear() { LCD_CmdWrite(0x01); // Clear the LCD and go to First line First Position LCD_CmdWrite(LineOne); }
LCD_GoToLineOne()
- Description :This function moves the Cursor to First line First Position
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : none
void LCD_GoToLineOne() { LCD_CmdWrite(LineOne); // Move the Cursor to First line First Position }
LCD_GoToLineTwo()
- Description :This function moves the Cursor to Second line First Position
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : none
void LCD_GoToLineTwo() { LCD_CmdWrite(LineTwo); // Move the Cursor to Second line First Position }
LCD_GoToXY()
- Description :This function moves the Cursor to specified position
- I/P Arguments: char row,char col
- row -> line number(line1=0, line2=1),For 2line LCD the I/P argument should be either 0 or 1.
- col -> char number.For 16-char LCD the I/P argument should be betwen 0-15.
- Return value : none
void LCD_GoToXY(char row, char col) { char pos; if(row<LCDMaxLines) { pos= LineOne | (row << 6); // take the line number //row0->pos=0x80 row1->pos=0xc0 if(col<LCDMaxChars) pos= pos+col; //take the char number //now pos points to the given XY pos LCD_CmdWrite(pos); // Move the Cursor to specified Position } }
LCD_CmdWrite()
- Description :This function sends a command to LCD in the following steps.
- step1: Send the I/P command to LCD.
- step2: Select the Control Register by making RS low.
- step3: Select Write operation making RW low.
- step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us.
- I/P Arguments: 8-bit command supported by LCD.
- Return value : none
void LCD_CmdWrite( char cmd) { databus=cmd; // Send the command to LCD control_bus &=~(1<<rs); // Select the Command Register by pulling RS LOW control_bus &=~(1<<rw); // Select the Write Operation by pulling RW LOW control_bus |=1<<en; // Send a High-to-Low Pusle at Enable Pin _delay_us(1); control_bus &=~(1<<en); _delay_ms(1); }
LCD_DataWrite()
- Description:This function sends a character to be displayed on LCD in the following steps.
- step1: Send the character to LCD.
- step2: Select the Data Register by making RS high.
- step3: Select Write operation making RW low.
- step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us.
- I/P Arguments: ASCII value of the char to be displayed.
- Return value : none
void LCD_DataWrite( char dat) { databus=dat; // Send the data to LCD control_bus |=1<<rs; // Select the Data Register by pulling RS HIGH control_bus &=~(1<<rw); // Select the Write Operation by pulling RW LOW control_bus |=1<<en; // Send a High-to-Low Pusle at Enable Pin _delay_us(1); control_bus &=~(1<<en); _delay_ms(1); }
LCD_DisplayString()
- Description :This function is used to display the ASCII string on the lcd.
- The string_ptr points to the first char of the string and traverses till the end(NULL CHAR).
- Each time a char is sent to LCD_DataWrite funtion to display.
- I/P Arguments: String(Address of the string) to be displayed.
- Return value : None
void LCD_DisplayString(char *string_ptr) { while(*string_ptr) LCD_DataWrite(*string_ptr++); }
LCD_DisplayNumber()
- Description :This function is used to display a 5-digit integer(0-65535).
- ex:
- if the number is 12345 then 12345 is displayed.
- if the number is 123 then 00123 is displayed.
- Function name: LCD_DisplayNumber()
- I/P Arguments: unsigned int.
- Return value : none
void LCD_DisplayNumber(unsigned int num) { LCD_DataWrite((num/10000)+0x30); num=num%10000; LCD_DataWrite((num/1000)+0x30); num=num%1000; LCD_DataWrite((num/100)+0x30); num=num%100; LCD_DataWrite((num/10)+0x30); LCD_DataWrite((num%10)+0x30); }
LCD_ScrollMessage()
- Description :This function scrolls the given message on the first line.""
- 16 chars are displayed at atime.
- Pointer is incremented to skip a char each time to give the illusion of moving chars.
- If the chars are less than 16, then the BlankSpaces are displayed.
- I/P Arguments: char *msg_ptr (msg_ptr -> pointer to the string to be scrolled)
- Return value : none
void LCD_ScrollMessage(char *msg_ptr) { unsigned char i,j; LCD_CmdWrite(0x0c); //Disable the Cursor for(i=0;msg_ptr[i];i++) //Loop to display the complete string { //each time 16 chars are displayed and //pointer is incremented to point to next char LCD_GoToLineOne(); //Move the Cursor to first line for(j=0;j<LCDMaxChars && msg_ptr[i+j];j++) //loop to Display first 16 Chars LCD_DataWrite(msg_ptr[i+j]); //or till Null char for(j=j; j<LCDMaxChars; j++) //If the chars are below 16 LCD_DataWrite(BlankSpace); //then display blank spaces _delay_ms(500); } LCD_CmdWrite(0x0E); //Enable the Cursor }
LCD_DisplayRtcTime()
- Description :This function display hour,min,sec read from DS1307.
- I/P Arguments: char hour,char min,char sec(hour,min,sec should be packed BCD format,as read from DS1307)
- Return value : none
void LCD_DisplayRtcTime(char hour,char min,char sec) { LCD_DataWrite(((hour>>4) & 0x0f) + 0x30); LCD_DataWrite((hour & 0x0f) + 0x30); LCD_DataWrite(':'); LCD_DataWrite(((min>>4) & 0x0f) + 0x30); LCD_DataWrite((min & 0x0f) + 0x30); LCD_DataWrite(':'); LCD_DataWrite(((sec>>4) & 0x0f) + 0x30); LCD_DataWrite((sec & 0x0f) + 0x30); }
LCD_DisplayRtcDate()
- Description :This function display day,month,year read from DS1307.
- I/P Arguments: char day,char month,char year(day,month,year should be packed BCD format,as read from DS1307)
- Return value : none
void LCD_DisplayRtcDate(char day,char month,char year) { LCD_DataWrite(((day>>4) & 0x0f) + 0x30); LCD_DataWrite((day & 0x0f) + 0x30); LCD_DataWrite('/'); LCD_DataWrite(((month>>4) & 0x0f) + 0x30); LCD_DataWrite((month & 0x0f) + 0x30); LCD_DataWrite('/'); LCD_DataWrite(((year>>4) & 0x0f) + 0x30); LCD_DataWrite((year & 0x0f) + 0x30); }
LCD_4_bit Mode
AVR LCD library for 4-bit mode
- Filename: lcd_4_bit.c
- Controller: Atmega Family(8,16,32,64,128)
- Oscillator: 11.0592 MHz
- Author: XploreLabz
- website: www.xplorelabz.com
Note:
- Pin connection for LCD display in 4-bit mode.
- By default the LCD is connected to PORTB.
- The code can be modified to connect the LCD to any of the PORTs by changing the "#define databus PORTB".
- io.h contains the defnition of all ports and SFRs delay.h contains the in built delay routines(us and ms routines)
#include <avr\io.h> #include <util\delay.h> #include "lcd.h" #define databus_direction DDRB // LCD data and Control bus Direction Configuration #define databus PORTB // LCD databus connected to PORTB #define control_bus PORTB // LCD Control bus connected to PORTB #define rs 0 // Register select pin connected 1st bit(D0) Control bus #define rw 1 // Read Write pin connected to 2nd bit(D1) Control bus #define en 2 // Enable pin connected to 3rd bit(D2) Control bus /* 16x2 LCD Specification */ #define LCDMaxLines 2 #define LCDMaxChars 16 #define LineOne 0x80 #define LineTwo 0xc0 #define BlankSpace ' '
LCD_Init()
- Description :This function is used to initialize the lcd in 4-bit mode
- Function name: LCD_Init()
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : none
void LCD_Init() { _delay_ms(50); databus_direction = 0xff; // Configure both databus and controlbus as output LCD_CmdWrite(0x02); //Initilize the LCD in 4bit Mode LCD_CmdWrite(0x28); LCD_CmdWrite(0x0E); // Display ON cursor ON LCD_CmdWrite(0x01); // Clear the LCD LCD_CmdWrite(0x80); // Move the Cursor to First line First Position }
LCD_CmdWrite()
- Description :This function sends a command to LCD in the following steps.
- step1: Send the Higher Nibble of the I/P command to LCD.
- step2: Select the Control Register by making RS low.
- step3: Select Write operation making RW low.
- step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us.
- step5: Send the Lower Nibble of the I/P command to LCD.
- step6: Select the Control Register by making RS low.
- step7: Select Write operation making RW low.
- step8: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us.
- I/P Arguments: 8-bit command supported by LCD.
- Return value : none
void LCD_CmdWrite( char cmd) { databus=(cmd & 0xf0); // Send the Higher Nibble of the command to LCD control_bus &=~(1<<rs); // Select the Command Register by pulling RS LOW control_bus &=~(1<<rw); // Select the Write Operation by pulling RW LOW control_bus |=1<<en; // Send a High-to-Low Pusle at Enable Pin _delay_us(1); control_bus &=~(1<<en); _delay_us(10); // wait for some time databus=((cmd<<4) & 0xf0); // Send the Lower Nibble of the command to LCD control_bus &=~(1<<rs); // Select the Command Register by pulling RS LOW control_bus &=~(1<<rw); // Select the Write Operation by pulling RW LOW control_bus |=1<<en; // Send a High-to-Low Pusle at Enable Pin _delay_us(1); control_bus &=~(1<<en); _delay_ms(1); }
LCD_DataWrite()
- Description:This function sends a character to be displayed on LCD in the following steps.
- step1: Send the higher nibble of the character to LCD.
- step2: Select the Data Register by making RS high.
- step3: Select Write operation making RW low.
- step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us.
- step5: wait for some time
- step6: Send the lower nibble of the character to LCD.
- step7: Select the Data Register by making RS high.
- step8: Select Write operation making RW low.
- step9: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us.
- Function name: LCD_DataWrite()
- I/P Arguments: ASCII value of the char to be displayed.
- Return value : none
void LCD_DataWrite( char dat) { databus=(dat & 0xf0); // Send the Higher Nibble of the Data to LCD control_bus |=1<<rs; // Select the Data Register by pulling RS HIGH control_bus &=~(1<<rw); // Select the Write Operation by pulling RW LOW control_bus |=1<<en; // Send a High-to-Low Pusle at Enable Pin _delay_us(1); control_bus &=~(1<<en); _delay_us(10); databus=((dat <<4) & 0xf0); // Send the Lower Nibble of the Data to LCD control_bus |=1<<rs; // Select the Data Register by pulling RS HIGH control_bus &=~(1<<rw); // Select the Write Operation by pulling RW LOW control_bus |=1<<en; // Send a High-to-Low Pusle at Enable Pin _delay_us(1); control_bus &=~(1<<en); _delay_ms(1); }
Keypad
Avr 4x4 Keypad Library
- Filename: keypad.c
- Controller:Atmega8/16/32/128
- Oscillator: 11.0592 MHz
- Author: XploreLabz
- website: www.xplorelabz.com
Note:
- Rows are connected to lower 4-bits of PORTC
- Cols are connected to higher 4-bits of PORTC
#include <avr\io.h> #include <util\delay.h> #include "keypad.h" #include "lcd.h" #define RowColDirection DDRB //Data Direction Configuration for keypad #define ROW PORTB //Lower four bits of PORTC are used as ROWs #define COL PINB //Higher four bits of PORTC are used as COLs
KEYPAD_Init()
- Description : This function the rows and colums for keypad scan
- ROW lines are configured as Output.
- Column Lines are configured as Input.
- I/P Arguments:none
- Return value : none
void KEYPAD_Init() { RowColDirection=0xf0; // Configure Row lines as O/P and Column lines as I/P }
KEYPAD_WaitForKeyRelease()
- Description : This function waits till the previous key is released.
- All the ROW lines are pulled low.
- Column Lines are read to check the key press.
- If all the Keys are released then Column lines will remain high(0x0f)
- I/P Arguments:none
- Return value : none
void KEYPAD_WaitForKeyRelease() { unsigned char key; do { ROW=0x0f; // Pull the ROW lines to low and Column high low. key=COL & 0x0f; // Read the Columns, to check the key press }while(key!=0x0f); // Wait till the Key is released, // If no Key is pressed, Column lines will remain high (0x0f) }
KEYPAD_WaitForKeyPress()
- Description : This function waits till a new key is pressed.
- All the ROW lines are pulled low.
- Column Lines are read to check the key press.
- If any Key is pressed then corresponding Column Line goes low.
- Wait for Some time and perform the above operation to ensure the True Key Press before decoding the KEY.
- I/P Arguments:none
- Return value : none
void KEYPAD_WaitForKeyPress() { unsigned char key; do { do { ROW=0x0f; // Pull the ROW lines to low and Column lines high. key=COL & 0x0F; // Read the Columns, to check the key press }while(key==0x0f); // Wait till the Key is pressed, // if a Key is pressed the corresponding Column line go low _delay_ms(1); // Wait for some time(debounce Time); ROW=0x0f; // After debounce time, perform the above operation key=COL & 0x0F; // to ensure the Key press. }while(key==0x0f); }
KEYPAD_ScanKey()
- Description :This function scans all the rows to decode the key pressed.
- Each time a ROW line is pulled low to detect the KEY.
- Column Lines are read to check the key press.
- If any Key is pressed then corresponding Column Line goes low.
- Return the ScanCode(Combination of ROW & COL) for decoding the key.
- I/P Arguments:none
- Return value : char--> Scancode of the Key Pressed
unsigned char KEYPAD_ScanKey() { unsigned char ScanKey = 0xe0,i, key; for(i=0;i<0x04;i++) // Scan All the 4-Rows for key press { ROW=ScanKey + 0x0F; // Select 1-Row at a time for Scanning the Key key=COL & 0x0F; // Read the Column, for key press if(key!= 0x0F) // If the KEY press is detected for the selected break; // ROW then stop Scanning, ScanKey=(ScanKey<<1)+ 0x10; // Rotate the ScanKey to SCAN the remaining Rows } key = key + (ScanKey & 0xf0); // Return the row and COL status to decode the key return(key); }
KEYPAD_GetKey()
- Description:This function waits till a key is pressed and returns its ASCII Value
- Wait till the previous key is released..
- Wait for the new key press.
- Scan all the rows one at a time for the pressed key.
- Decode the key pressed depending on ROW-COL combination and returns its ASCII value.
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : char--> ASCII value of the Key Pressed
unsigned char KEYPAD_GetKey() { unsigned char key; KEYPAD_WaitForKeyRelease(); // Wait for the previous key release _delay_ms(1); KEYPAD_WaitForKeyPress(); // Wait for the new key press key = KEYPAD_ScanKey(); // Scan for the key pressed. switch(key) // Decode the key { case 0xe7: key='0'; break; case 0xeb: key='1'; break; case 0xed: key='2'; break; case 0xee: key='3'; break; case 0xd7: key='4'; break; case 0xdb: key='5'; break; case 0xdd: key='6'; break; case 0xde: key='7'; break; case 0xb7: key='8'; break; case 0xbb: key='9'; break; case 0xbd: key='A'; break; case 0xbe: key='B'; break; case 0x77: key='C'; break; case 0x7b: key='D'; break; case 0x7d: key='E'; break; case 0x7e: key='F'; break; default: key='z'; } return(key); // Return the key }
UART
AVR UART library for Serial Communication for 9600 baud rate at 11.0592Mhz
- Filename: uart.c
- Controller: Atmega8/16/32/128
- Oscillator: 11.0592 MHz
- Author: XploreLabz
- website: www.xplorelabz.com
#include<avr/io.h>UART_Init()
- Description :This function is used to initialize the UART at 9600 baud rate by below configuration.
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : none
void UART_Init() { UCSRB= 0x18; // Enable Receiver and Transmitter UCSRC= 0x86; // Asynchronous mode 8-bit data and 1-stop bit UCSRA= 0x00; // Normal Baud rate(no doubling), Single processor commn UBRRH= 0; UBRRL= 71; // 9600 Baud rate at 11.0592MHz }
UART_RxChar()
- Description :This function is used to receive a char from UART module.
- It waits till a char is received ie.till RXC is set,
- RXC will be set once a CHAR is received.
- Finally returns the received char.
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : char
char UART_RxChar() { while((UCSRA & (1<<RXC))==0); // Wait till the data is received return(UDR); // return the received char }
UART_TxChar()
- Description : This function is used to transmit a char through UART module.
- It waits till previous char is transmitted ie.till UDRE is set.
- UDRE will be set once a CHAR is transmitted ie UDR becomes empty.
- Finally the new Char to be transmitted is loaded into UDR.
- I/P Arguments: char--> data to be transmitted
- Return value : none
void UART_TxChar(char ch) { while((UCSRA & (1<<UDRE))==0); // Wait till Transmitter(UDR) register becomes Empty UDR =ch; // Load the data to be transmitted }
UART_TxString()
- Description :This function is used to transmit the ASCII string through UART.
- The string_ptr points to the first char of the string.
- And it is incremented each time to traverse till the end(NULL CHAR).
- Each time a char is sent to UART_TxChar() fun to transmit it through UART
- I/P Arguments: String(Address of the string) to be transmitted.
- Return value : none
void UART_TxString(char *string_ptr) { while(*string_ptr) UART_TxChar(*string_ptr++); }
UART_RxString()
- Description :This function is used to receive a ASCII string through UART till the carriage_return/New_line.
- The string_ptr points to the begining of the string and each time UART_RxChar() function is called to receive a char and copy it into the buffer(STRING) and incrment string_ptr.
- Once the carriage_return/New_line is encountered the loop is breaked and the String is NULL terminated.
- I/P Arguments: *string_ptr(Address of the string where the received data needs to be stored)
- Return value : none
NOTE:
- The received char is ECHOED back,if not required then comment UART_TxChar(ch) in the code.
- BackSlash is not taken care.
void UART_RxString(char *string_ptr) { char ch; while(1) { ch=UART_RxChar(); //Reaceive a char UART_TxChar(ch); //Echo back the received char if((ch=='\r') || (ch=='\n')) //read till enter key is pressed { //once enter key is pressed *string_ptr=0; //null terminate the string break; //and break the loop } *string_ptr=ch; //copy the char into string. string_ptr++; //and increment the pointer } }
UART_TxNumber()
- Description :This function is used to transmit a 5-digit integer(0-65535).
- ex:
- if the number is 12345 then 12345 is transmitted.
- if the number is 123 then 00123 is transmitted.
- I/P Arguments: unsigned int
- Return value : none
void UART_TxNumber(unsigned int num) { UART_TxChar((num/10000)+0x30); num=num%10000; UART_TxChar((num/1000)+0x30); num=num%1000; UART_TxChar((num/100)+0x30); num=num%100; UART_TxChar((num/10)+0x30); UART_TxChar((num%10)+0x30); }
I2C
Avr I2C library
- Filename: I2C.c
- Controller: Atmega8/16/32/128
- Oscillator: 11.0592 MHz
- Author: XploreLabz
- website: www.xplorelabz.com
Refer Atmega32 for register description.
#include<avr\io.h> #include<util\delay.h> #include "i2c.h"
I2C_Init()
- Description :This function is used to initialize the I2c Module.
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : none
void I2C_Init() { TWSR=0x00; //set presca1er bits to zero TWBR=0x46; //SCL frequency is 100K for XTAL = 7.3728M TWCR=0x04; //enab1e TWI module }
I2C_Start()
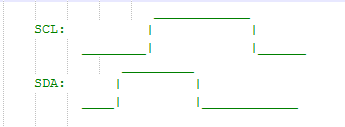
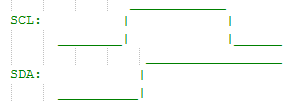
- Description :This function is used to generate I2C Start Condition.
- Start Condition: SDA goes low when SCL is High.
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : none
void I2C_Start() { TWCR = ((1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWSTA) | (1<<TWEN)); while (!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); }
I2C_Stop()
- Description :This function is used to generate I2C Stop Condition.
- Stop Condition: SDA goes High when SCL is High.
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : none
void I2C_Stop(void) { TWCR = ((1<< TWINT) | (1<<TWEN) | (1<<TWSTO)); _delay_us(10) ; //wait for a short time }
I2C_Write()
- Description :This function is used to send a byte on SDA line using I2C protocol
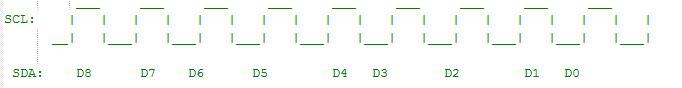
- 8bit data is sent bit-by-bit on each clock cycle.
- MSB(bit) is sent first and LSB(bit) is sent at last.
- Data is sent when SCL is low.
- I/P Arguments: unsigned char-->8bit data to be sent.
- Return value: none
void I2C_Write(unsigned char dat) { TWDR = dat ; TWCR = ((1<< TWINT) | (1<<TWEN)); while (!(TWCR & (1 <<TWINT))); }
I2C_Read()
- Description :This fun is used to receive a byte on SDA line using I2C protocol.
- 8bit data is received bit-by-bit each clock and finally packed into Byte.
- MSB(bit) is received first and LSB(bit) is received at last.
- I/P Arguments: char: Acknowledgement for the Ninth clock cycle.
- Return value : Unsigned char(received byte)
unsigned char I2C_Read(unsigned char ack) { TWCR = ((1<< TWINT) | (1<<TWEN) | (ack<<TWEA)); while ( !(TWCR & (1 <<TWINT))); return TWDR; }
RTC_DS1307
DS1307 library
- Filename: DS1307.c
- Controller: Atmega8/16/32/128
- Oscillator: 11.0592 MHz
- Author: XploreLabz
- website: www.xplorelabz.com
#include <avr\io.h> #include <util\delay.h> #include "ds1307.h" #include "i2c.h"
- Below values are fixed and should not be changed.
- Refer Ds1307 DataSheet for more info
#define DS1307_ID 0xD0 // DS1307 ID #define SEC_ADDRESS 0x00 // Address to access Ds1307 SEC register #define DATE_ADDRESS 0x04 // Address to access Ds1307 DATE register #define CONTROL 0x07 // Address to access Ds1307 CONTROL register
DS1307_Init()
- Description :This function is used to initialize the Ds1307 RTC.
- Ds1307 ic is enabled by sending the DS1307 id on the I2C bus.
- After selecting DS1307, write 0x00 into Control register of Ds1307
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : none
void DS1307_Init() { I2C_Init(); // Initilize the I2c module. I2C_Start(); // Start I2C communication I2C_Write(DS1307_ID); // Connect to DS1307 by sending its ID on I2c Bus I2C_Write(CONTROL); // Select the Ds1307 ControlRegister to configure Ds1307 I2C_Write(0x00); // Write 0x00 to Control register to disable SQW-Out I2C_Stop(); // Stop I2C communication after initilizing DS1307 }
DS1307_SetTime()
- Description :This function is used to set Time(hh,mm,ss) into the Ds1307 RTC.
- Ds1307 ic is enabled by sending the DS1307 id on the I2C bus.
- After selecting DS1307, select the RAM address 0x00 to point to sec.
- Initilze Sec, MIN, Hour one after the other.
- Stop the I2c communication.
- I/P Arguments: char,char,char-->hh,mm,ss to initilize the time into DS1307.
- Return value : none
void DS1307_SetTime(unsigned char hh, unsigned char mm, unsigned char ss) { I2C_Start(); // Start I2C communication I2C_Write(DS1307_ID); // connect to DS1307 by sending its ID on I2c Bus I2C_Write(SEC_ADDRESS); // Select the SEC RAM address I2C_Write(ss); // Write sec on RAM address 00H I2C_Write(mm); // Write min on RAM address 01H I2C_Write(hh); // Write hour on RAM address 02H I2C_Stop(); // Stop I2C communication after Setting the Time }
DS1307_SetDate()
- Description :This function is used to set Date(dd,mm,yy) into the Ds1307 RTC.
- Ds1307 ic is enabled by sending the DS1307 id on the I2C bus.
- After selecting DS1307, select the RAM address 0x04 to point to day.
- Initilze Day,Month and Year one after the other.
- Stop the I2c communication.
- I/P Arguments: char,char,char-->day,month,year to initilize the Date into DS1307.
- Return value : none
void DS1307_SetDate(unsigned char dd, unsigned char mm, unsigned char yy) { I2C_Start(); // Start I2C communication I2C_Write(DS1307_ID); // connect to DS1307 by sending its ID on I2c Bus I2C_Write(DATE_ADDRESS); // Request DAY RAM address at 04H I2C_Write(dd); // Write date on RAM address 04H I2C_Write(mm); // Write month on RAM address 05H I2C_Write(yy); // Write year on RAM address 06h I2C_Stop(); // Stop I2C communication after Setting the Date }
DS1307_GetTime()
- Description :This function is used to get the Time(hh,mm,ss) from Ds1307 RTC.
- Ds1307 ic is enabled by sending the DS1307 id on the I2C bus.
- After selecting DS1307, select the RAM address 0x00 to point to sec.
- Get Sec, MIN, Hour one after the other.
- Stop the I2c communication.
- I/P Arguments: char *,char *,char *-->pointers to get the hh,mm,ss.
- Return value : none
void DS1307_GetTime(unsigned char *h_ptr,unsigned char *m_ptr,unsigned char *s_ptr) { I2C_Start(); // Start I2C communication I2C_Write(DS1307_ID); // connect to DS1307 by sending its ID on I2c Bus I2C_Write(SEC_ADDRESS); // Request Sec RAM address at 00H I2C_Stop(); // Stop I2C communication after selecting Sec Register I2C_Start(); // Start I2C communication I2C_Write(0xD1); // connect to DS1307( under Read mode) //by sending its ID on I2c Bus *s_ptr = I2C_Read(1); // read second and return Positive ACK *m_ptr = I2C_Read(1); // read minute and return Positive ACK *h_ptr = I2C_Read(0); // read hour and return Negative/No ACK I2C_Stop(); // Stop I2C communication after reading the Time }
DS1307_GetDate()
- Description :This function is used to get the Date(y,m,d) from Ds1307 RTC.
- Ds1307 ic is enabled by sending the DS1307 id on the I2C bus.
- After selecting DS1307, select the RAM address 0x00 to point to DAY.
- Get Day, Month, Year one after the other.
- Stop the I2c communication.
- I/P Arguments: char *,char *,char *-->pointers to get the y,m,d.
- Return value : none
void DS1307_GetDate(unsigned char *d_ptr,unsigned char *m_ptr,unsigned char *y_ptr) { I2C_Start(); // Start I2C communication I2C_Write(DS1307_ID); // connect to DS1307 by sending its ID on I2c Bus I2C_Write(DATE_ADDRESS); // Request DAY RAM address at 04H I2C_Stop(); // Stop I2C communication after selecting DAY Register I2C_Start(); // Start I2C communication I2C_Write(0xD1); // connect to DS1307( under Read mode) // by sending its ID on I2c Bus *d_ptr = I2C_Read(1); // read Day and return Positive ACK *m_ptr = I2C_Read(1); // read Month and return Positive ACK *y_ptr = I2C_Read(0); // read Year and return Negative/No ACK I2C_Stop(); // Stop I2C communication after reading the Time }
EEPROM
Avr Eeprom library
- Filename: eeprom.c
- Controller: Atmega8/16/32/128
- Oscillator: 11.0592 MHz
- Author: XploreLabz
- website: www.xplorelabz.com
- Reference: Atmega8/16/32 dataSheet for Control register description.
#include<avr\io.h> #include<util\delay.h>
- The below value should be set depending on the controller by refering the respective data sheet.
#define MaxEepromSize 1024
EEPROM_WriteByte()
- Description:This function is used to write the data at specified EEPROM_address.
- Wait till previous write operation is completed(ie wait till EEWE becomes zero).
- Load the eeprom address into EEAR at which the data has to be stored.
- Load the data into EEDR which has to be stored in Eeprom.
- Set the EEMWE(Eeprom Master Write Enable) and within four clock cycles.
- set EEWE(Eeprom Write Enable) to trigger the Eeprom Write Opeartion.
- I/P Arguments: int,char-->eeprom_address at which eeprom_data is to be written.
- Return value : none
void EEPROM_WriteByte(unsigned int eeprom_Address, unsigned char eeprom_Data) { while(EECR & (1<<EEWE)); // Wait for completion of previous write, EEWE will be // cleared by hardware once Eeprom write is completed EEAR = eeprom_Address; //Load the eeprom adddress and data EEDR = eeprom_Data; EECR |= (1<<EEMWE); // Write logical one to EEMWE EECR |= (1<<EEWE); // Start eeprom write by setting EEWE }
EEPROM_ReadByte()
- Description: This function is used to read the data from specified EEPROM_address.
- WAit for completion of previous Write operation.
- EEWE will be cleared once EEprom write is completed.
- Load the eeprom address into EEAR from where the data needs to be read.
- Trigger the eeprom read operation by setting EERE(Eeprom Read Enable).
- Wait for some time and collect the read data from EEDR.
- I/P Arguments: int-->eeprom_address from where eeprom_data is to be read.
- Return value : char-->data read from Eeprom.
unsigned char EEPROM_ReadByte(unsigned int eeprom_Address) { while(EECR & (1<<EEWE)); //Wait for completion of previous write if any. EEAR = eeprom_Address; //Load the address from where the datas needs to be read. EECR |=(1<<EERE); // start eeprom read by setting EERE _delay_ms(1); return EEDR; // Return data from data register }
EEPROM_WriteNBytes()
- Description:This function is used to write N-bytes of data at specified EEPROM_address.
- EEPROM_WriteByte() function is called to write a byte at atime.
- Source(RAM) and destination(EEPROM) address are incremented after each write.
- NoOfBytes is Decemented each time a byte is written.
- Above Operation is carried out till all the bytes are written(NoOfBytes!=0).
- I/P Arguments:
- int,-->eeprom_address from where the N-bytes are to be written.
- char*-->Pointer to the N-bytes of data to be written.
- char --> Number of bytes to be written
- Return value : none
void EEPROM_WriteNBytes(unsigned int EepromAddr, unsigned char *RamAddr, char NoOfBytes) { while(NoOfBytes != 0) { EEPROM_WriteByte(EepromAddr,*RamAddr); //Write a byte from RAM to EEPROM EepromAddr++; //Incerement the Eeprom Address RamAddr++; //Increment the RAM Address NoOfBytes--; //Decrement NoOfBytes after writing each Byte } }
EEPROM_ReadNBytes()
- Description: This function is used to Read N-bytes of data from specified EEPROM_address.
- EEPROM_ReadByte() func is called to read a byte at a time.
- Source(RAM) and destination(EEPROM) address are incremented each time.
- NoOfBytes is Decemented after a byte is read.
- Above Operation is carried out till all the bytes are read(NoOfBytes!=0).
- I/P Arguments:
- int,-->eeprom_address from where the N-bytes is to be read.
- char*-->Pointer into which the N-bytes of data is to be read.
- char --> Number of bytes to be Read
- Return value : none
void EEPROM_ReadNBytes(unsigned int EepromAddr, unsigned char *RamAddr, char NoOfBytes) { while(NoOfBytes != 0) { *RamAddr = EEPROM_ReadByte(EepromAddr);//Read a byte from EEPROM to RAM EepromAddr++; //Incerement the Eeprom Address RamAddr++; //Increment the RAM Address NoOfBytes--; //Decrement NoOfBytes after Reading each Byte } }
EEPROM_WriteString()
- Description: This function is used to Write a String at specified EEPROM_address.
- EEPROM_WriteByte() function is called to write a byte at a time.
- Source(RAM) and destination(EEPOM) address are incremented each time.
- Above Operation is carried out till Null char is identified.
- I/P Arguments:
- int,-->eeprom_address where the String is to be written.
- char*-->Pointer to String which has to be written.
- Return value : none
- NOTE: Null char is also written into the eeprom.
void EEPROM_WriteString(unsigned int eeprom_address, unsigned char * source_address) { do { EEPROM_WriteByte(eeprom_address,*source_address); //Write a byte from RAM to EEPROM source_address++; //Increment the RAM Address eeprom_address++; //Increment the Eeprom Address } while(*(source_address-1) !=0); }
EEPROM_ReadString()
- Description: This function is used to Read a String from specified EEPROM_address.
- EEPROM_ReadByte() function is called to read a byte at a time.
- Source(EEPROM) and destination(RAM) address are incremented each time.
- Above Operation is carried out till Null char is identified.
- I/P Arguments:
- int,-->eeprom_address from where the String is to be read.
- char*-->Pointer into which the String is to be read.
- Return value : none
void EEPROM_ReadString(unsigned int eeprom_address, unsigned char * destination_address) { char eeprom_data; do { eeprom_data = EEPROM_ReadByte(eeprom_address); //Read a byte from EEPROM to RAM *destination_address = eeprom_data; //Copy the data into String Buffer destination_address++; //Increment the RAM Address eeprom_address++; //Increment the Eeprom Address }while(eeprom_data!=0); }
EEPROM_Erase()
- Description: This function is used to erase the entire Eeprom memory.
- Eeprom is filled with 0xFF to accomplish the Eeprom Erase.
- EEPROM_WriteByte() function is called to write a byte at a time.
- Whole memory(0-MaxEepromSize) is traversed and filled with 0xFF.
- I/P Arguments: none
- Return value : none
void EEPROM_Erase() { unsigned int eeprom_address; for(eeprom_address=0;eeprom_address<MaxEepromSize;eeprom_address++) { EEPROM_WriteByte(eeprom_address,0xff); // Write Each memory location with OxFF } }