Difference between revisions of "Interfacing glcd with 8051"
m (Explorer moved page Setting up 8051 Development Board Ultra x51 to Interfacing glcd with 8051) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[category:8051 tutorials]] | [[category:8051 tutorials]] | ||
| − | In this tutorial we will | + | In this tutorial, we will see how to interface and graphical LCD(GLCD) with 8051. We will be interfacing KS0108 controller based JHD12864E display. There are many displays out there based on KS0108 or compatible display controller. They all work the same way but make sure to check the datasheet for the pin diagram before doing the connection. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | We will look at the working of the display, the hardware setup and programming with 8051. We have it tested and working on 8051, AVR, PIC and ARM. We have similar tutorials on these MCUs in respective controller tutorial section. | |
| − | + | Unlike a 16 x 2 display, this does not have a character map for ASCII values stored in its ROM. However, it allows us the flexibility of creating fonts like Arial, times new roman etc. We could also display bitmap images on it and stretch it little further we can make GUI's and little animation, but that's for another day. So let's get started. | |
| + | |||
| + | =GLCD Internals And Pinout= | ||
| + | Below image shows the internal block diagram of 128x64 GLCD along with its pin out. | ||
| + | [[FILE:GLCD 128x64 BlockDiagram.png]] | ||
| + | As per the name it has 128pixels on X-axis and 64-pixels on Y-axis. Further, the X-axis is divided into two parts of 64 pixels each and controlled by unique controller/driver IC as shown in the above image. | ||
| + | Below table provides the detailed info of all the GLCD pins. | ||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | | Pin Number || Symbol || Pin Function | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |1 || VSS ||Ground | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2|| VCC || +5v | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 3 || VO || Contrast adjustment (VO) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 4 || RS/DI || Register Select/Data Instruction. 0:Instruction, 1: Data | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 5 || R/W || Read/Write, R/W=0: Write & R/W=1: Read | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 6|| EN || Enable. Falling edge triggered | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 7 || D0 || Data Bit 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 8 || D1 || Data Bit 1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 9 || D2 || Data Bit 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 10 || D3 || Data Bit 3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 11 || D4 || Data Bit 4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 12 || D5 || Data Bit 5 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 13 || D6 || Data Bit 6 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 14 || D7 || Data Bit 7/Busy Flag | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 15 || CS1 || Chip Select for IC1/PAGE0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 16 || CS2 || Chip Select for IC2/PAGE1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 17 || RST || Reset the LCD module | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 18 || VEE || Negative voltage used along with Vcc for brightness control | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 15 || A/LED+ || Back-light Anode(+) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 16 || K/LED- || Back-Light Cathode(-) | ||
| + | |} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | To | + | =Page, Line and Cursor Selection= |
| − | <br /> | + | [[FILE:GLCD Pages.png]] |
| + | Lets view the GLCD as a open book with 2pages constisting of 8lines on each page.<br> | ||
| + | Each line has 64 cursors positions to display data/images.<br> | ||
| + | The required page can be selected using CS1,CS2 pins as shown below.<br> | ||
| + | <b>CS2-CS1:</b>Chip Select Lines<br> | ||
| + | 00 = None<br> | ||
| + | 01 = Page 0<br> | ||
| + | 10 = Page 1<br> | ||
| + | 11 = Both Pages | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Line Selection== | ||
| + | To select the lines we need to send the command/line address to GLCD.<br> | ||
| + | The line address starts from 0xb8 and goes till 0xbf as shown below. | ||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | |7 || 6 || 5 || 4 || 3 || 2 || 1 || 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |1|| 0 || 1 || 1 || 1 || Y2 || Y1 || Y0 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <b>Y2-Y0:</b>Line Selection<br> | ||
| + | 000 = Line0 (Address = 0xB8)<br> | ||
| + | 001 = Line1 (Address = 0xB9)<br> | ||
| + | 010 = Line2 (Address = 0xBA)<br> | ||
| + | 011 = Line3 (Address = 0xBB)<br> | ||
| + | 100 = Line4 (Address = 0xBC)<br> | ||
| + | 101 = Line5 (Address = 0xBD)<br> | ||
| + | 110 = Line6 (Address = 0xBE)<br> | ||
| + | 111 = Line7 (Address = 0xBF) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Cursor/Char Position=== | ||
| + | To set the cursor position(0-63) we need to send its address to GLCD.<br> | ||
| + | The cursor positions address starts from 0x40 and goes till 0x7f as shown below. | ||
| + | {| class="table table-striped table-hover table-condensed table-bordered" | ||
| + | |-class="info" | ||
| + | |7 || 6 || 5 || 4 || 3 || 2 || 1 || 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |0|| 1 || x5 || x4 || x3 || x2 || x1 || x0 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <b>x5-x0:</b>Line Selection<br> | ||
| + | 000000 = Cursor Position 0 (Address = 0x40)<br> | ||
| + | 000001 = Cursor Position 1 (Address = 0x41)<br> | ||
| + | 000010 = Cursor Position 2 (Address = 0x42)<br> | ||
| + | '<br> | ||
| + | 111111 = Cursor Position 63 (Address = 0x7F) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Instruction Set=== | ||
| + | Below is the complete instruction table. | ||
| + | [[FILE:GLCD InstructionSet.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Steps= | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Steps for Sending Command:=== | ||
| + | *step1: Send the I/P command to LCD. | ||
| + | *step2: Select the Control Register by making RS low. | ||
| + | *step3: Select Write operation making RW low. | ||
| + | *step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us. | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/f56a8cb536a46213f4132455f0190e2d.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Steps for Sending Data:=== | ||
| + | *step1: Send the character to LCD. | ||
| + | *step2: Select the Data Register by making RS high. | ||
| + | *step3: Select Write operation making RW low. | ||
| + | *step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay. | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/466f8bd7feae27e51f9593e34379070b.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =Code= | ||
| + | Below is the sample code for displaying HELLO WORLD on two different pages of GLCD. | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/9a50df223dc284c41074345369636d42.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
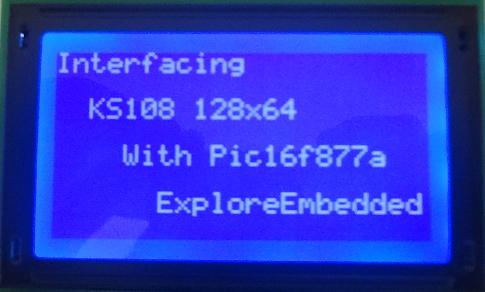
| + | =Using ExploreEmbedded GLCD Lib= | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/18af0f168e1263ce5bcf0110e296ef12.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | [[FILE:0Glcd iterfacing with PIC16f877a.png]] | ||
| + | |||
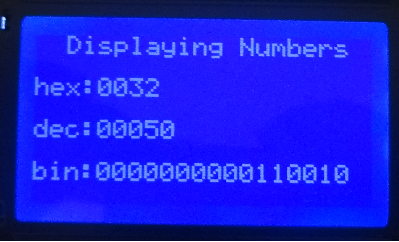
| + | =Displaying Numbers= | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/17b64c4e262e9173b3823d12d1eced4a.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | [[FILE:Glcd DisplayNumber.png]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
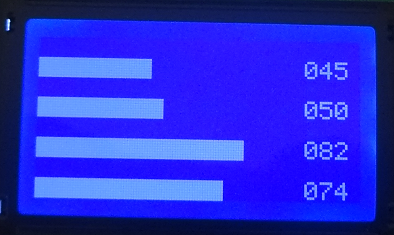
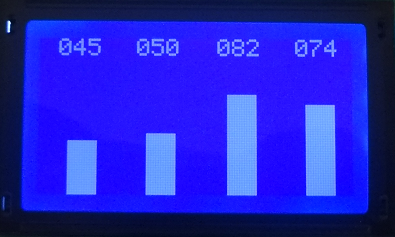
| + | =Displaying Bar Graphs= | ||
| − | = | + | <html> |
| − | + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/49e0ad0b4d5617535430989c6736d8af.js"></script> | |
| − | + | </html> | |
| − | + | [[FILE:Glcd HorizontalGraph.png]] | |
| − | + | <br><br> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <br | + | |
| − | |||
| − | < | + | <html> |
| + | <script src="https://gist.github.com/SaheblalBagwan/28b1f36fc769b7ab785c414672380eff.js"></script> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | [[FILE:Glcd VerticalGraph.png]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | =Downloads= | ||
| + | Download the complete project folder from the below link:<br> | ||
| + | [https://github.com/ExploreEmbedded/Pic16f877a_ExploreUltraPicDevKit/archive/master.zip Hardware design Files and Code Library] | ||
| + | Have an opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here! | ||
{{DISQUS}} | {{DISQUS}} | ||
Revision as of 18:52, 23 August 2016
In this tutorial, we will see how to interface and graphical LCD(GLCD) with 8051. We will be interfacing KS0108 controller based JHD12864E display. There are many displays out there based on KS0108 or compatible display controller. They all work the same way but make sure to check the datasheet for the pin diagram before doing the connection.
We will look at the working of the display, the hardware setup and programming with 8051. We have it tested and working on 8051, AVR, PIC and ARM. We have similar tutorials on these MCUs in respective controller tutorial section.
Unlike a 16 x 2 display, this does not have a character map for ASCII values stored in its ROM. However, it allows us the flexibility of creating fonts like Arial, times new roman etc. We could also display bitmap images on it and stretch it little further we can make GUI's and little animation, but that's for another day. So let's get started.
Contents
GLCD Internals And Pinout
Below image shows the internal block diagram of 128x64 GLCD along with its pin out.
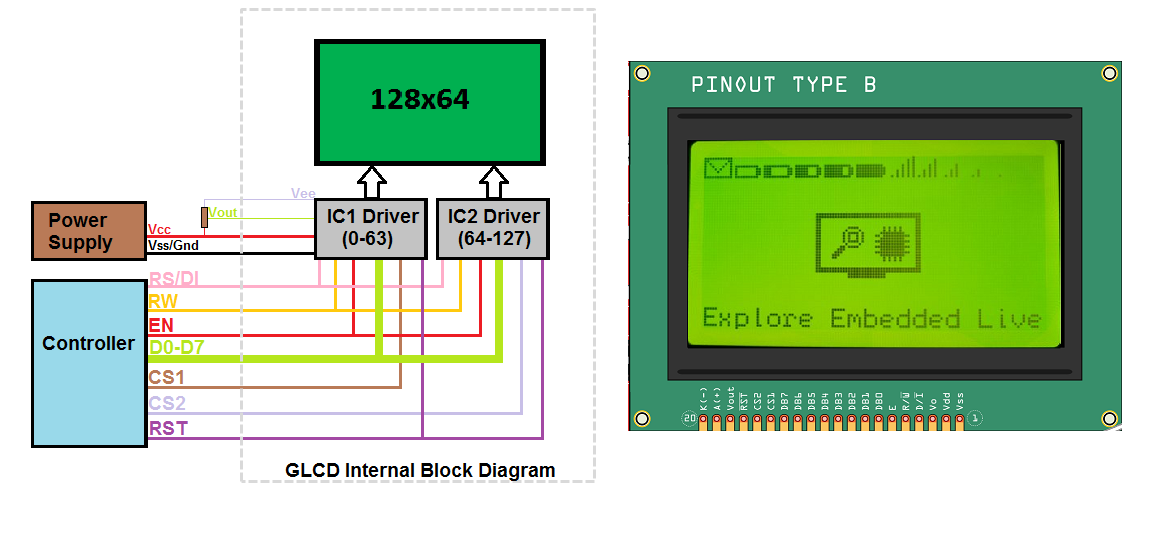 As per the name it has 128pixels on X-axis and 64-pixels on Y-axis. Further, the X-axis is divided into two parts of 64 pixels each and controlled by unique controller/driver IC as shown in the above image.
Below table provides the detailed info of all the GLCD pins.
As per the name it has 128pixels on X-axis and 64-pixels on Y-axis. Further, the X-axis is divided into two parts of 64 pixels each and controlled by unique controller/driver IC as shown in the above image.
Below table provides the detailed info of all the GLCD pins.
| Pin Number | Symbol | Pin Function |
| 1 | VSS | Ground |
| 2 | VCC | +5v |
| 3 | VO | Contrast adjustment (VO) |
| 4 | RS/DI | Register Select/Data Instruction. 0:Instruction, 1: Data |
| 5 | R/W | Read/Write, R/W=0: Write & R/W=1: Read |
| 6 | EN | Enable. Falling edge triggered |
| 7 | D0 | Data Bit 0 |
| 8 | D1 | Data Bit 1 |
| 9 | D2 | Data Bit 2 |
| 10 | D3 | Data Bit 3 |
| 11 | D4 | Data Bit 4 |
| 12 | D5 | Data Bit 5 |
| 13 | D6 | Data Bit 6 |
| 14 | D7 | Data Bit 7/Busy Flag |
| 15 | CS1 | Chip Select for IC1/PAGE0 |
| 16 | CS2 | Chip Select for IC2/PAGE1 |
| 17 | RST | Reset the LCD module |
| 18 | VEE | Negative voltage used along with Vcc for brightness control |
| 15 | A/LED+ | Back-light Anode(+) |
| 16 | K/LED- | Back-Light Cathode(-) |
Page, Line and Cursor Selection
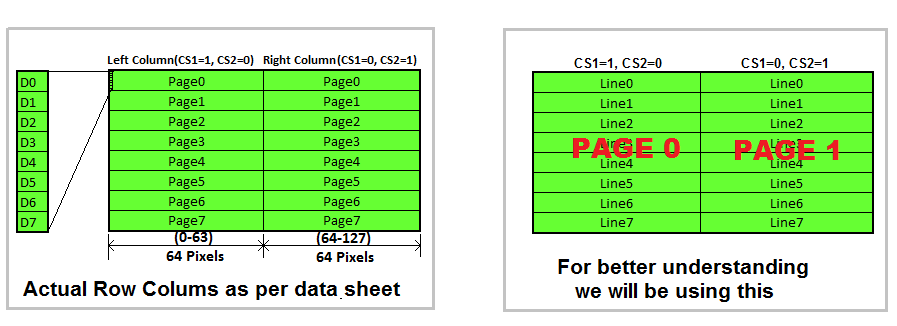 Lets view the GLCD as a open book with 2pages constisting of 8lines on each page.
Lets view the GLCD as a open book with 2pages constisting of 8lines on each page.
Each line has 64 cursors positions to display data/images.
The required page can be selected using CS1,CS2 pins as shown below.
CS2-CS1:Chip Select Lines
00 = None
01 = Page 0
10 = Page 1
11 = Both Pages
Line Selection
To select the lines we need to send the command/line address to GLCD.
The line address starts from 0xb8 and goes till 0xbf as shown below.
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y0 |
Y2-Y0:Line Selection
000 = Line0 (Address = 0xB8)
001 = Line1 (Address = 0xB9)
010 = Line2 (Address = 0xBA)
011 = Line3 (Address = 0xBB)
100 = Line4 (Address = 0xBC)
101 = Line5 (Address = 0xBD)
110 = Line6 (Address = 0xBE)
111 = Line7 (Address = 0xBF)
Cursor/Char Position
To set the cursor position(0-63) we need to send its address to GLCD.
The cursor positions address starts from 0x40 and goes till 0x7f as shown below.
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | x5 | x4 | x3 | x2 | x1 | x0 |
x5-x0:Line Selection
000000 = Cursor Position 0 (Address = 0x40)
000001 = Cursor Position 1 (Address = 0x41)
000010 = Cursor Position 2 (Address = 0x42)
'
111111 = Cursor Position 63 (Address = 0x7F)
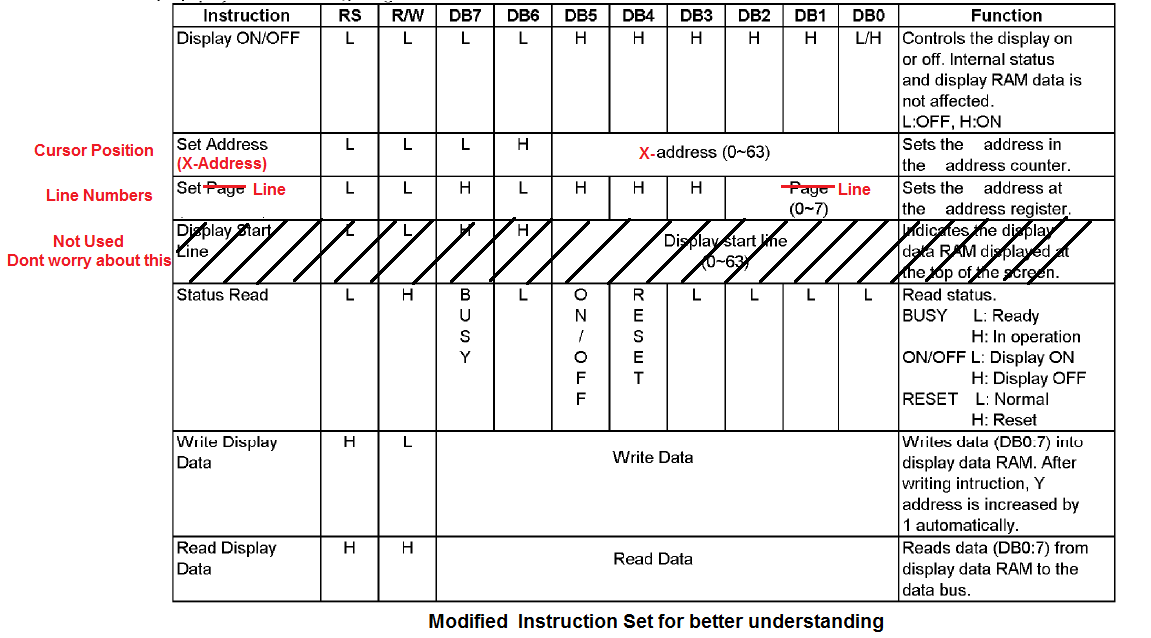
Instruction Set
Below is the complete instruction table.
Steps
Steps for Sending Command:
- step1: Send the I/P command to LCD.
- step2: Select the Control Register by making RS low.
- step3: Select Write operation making RW low.
- step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay_us.
Steps for Sending Data:
- step1: Send the character to LCD.
- step2: Select the Data Register by making RS high.
- step3: Select Write operation making RW low.
- step4: Send a High-to-Low pulse on Enable PIN with some delay.
Code
Below is the sample code for displaying HELLO WORLD on two different pages of GLCD.
Using ExploreEmbedded GLCD Lib
Displaying Numbers
Displaying Bar Graphs
Downloads
Download the complete project folder from the below link:
Hardware design Files and Code Library
Have an opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here!